Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Most people experience a short flu-like illness 2 to 6 weeks after HIV infection, which lasts for a week or 2.
After these symptoms disappear, HIV may not cause any symptoms for many years, although the virus continues to damage your immune system.
This means many people with HIV do not know they’re infected.
Anyone who thinks they could have HIV should get tested.
Some people are advised to have regular tests as they’re at particularly high risk.
Diagnosing Hiv Infection & Aids
Doctors at NYU Langone diagnose human immunodeficiency virus, known as HIV, a chronic viral infection that destroys certain infection-fighting white blood cells. If left untreated, HIV weakens the immune system, so the body is unable to fight infections and disease. When this occurs, HIV infection leads to a chronic, possibly life-threatening illness called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS.
HIV is transmitted through sex by sharing needles, syringes, or other equipment through contact with infected blood or through pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
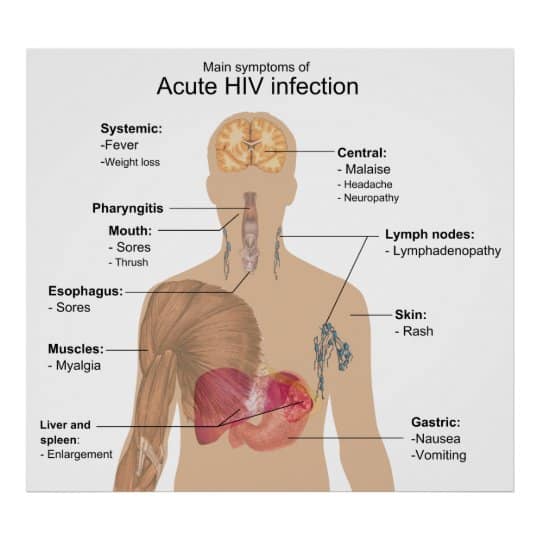
A few weeks to three months after becoming infected with HIV, many people develop intense flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. They may also experience weight loss and night sweats during this initial phase. However, many people who are infected with the virus have no symptoms for 10 years or longer.
After the initial phase of an HIV infection, the disease moves into a period called clinical latency. This means the virus is developing but is producing few if any mild symptoms. Even when it causes no symptoms, the virus can be transmitted to others.
If a person with HIV infection is not treated, they are likely to develop AIDS, though its impossible to predict how long that may take. With treatment, people develop AIDS very slowlyor not at all.
Who Does Hiv Affect
Its a myth that HIV only infects certain people. Anyone can get HIV if theyre exposed to the virus. Having sex without a condom or sharing needles to inject drugs are the most common ways that HIV spreads.
Some populations are statistically more affected by HIV than others. Groups disproportionately affected by HIV include:
- People who identify as gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men .
- Certain races such as people who are Black or Hispanic.
- Those who exchange sex for money or other items are also at high risk for HIV infection.
While these arent the only populations impacted by HIV, its important to consider that they face unique barriers to accessing preventative care, getting tested, and receiving comprehensive treatment. Homophobia, racism, poverty, and social stigmas around HIV continue to drive inequities and keep people from accessing high-quality healthcare.
Read Also: Otc Skin Yeast Infection Treatment
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
01 November 2022
Eduardo A. Albornoz, Alberto A. Amarilla, Trent M. Woodruff
02 November 2022
Nima Sayyadi, Irene Justiniano, James A. Piper
volume 9, Article number: 5418
How Hiv Is Not Spread
The virus doesn’t survive well outside the body. So HIV cannot be spread through casual contact with an infected person, such as by sharing drinking glasses, by casual kissing, or by coming into contact with the person’s sweat or urine.
It is now extremely rare in the United States for HIV to be transmitted by blood transfusions or organ transplants.
Also Check: Zinc Oxide For Yeast Infection
Get Tested Regularly If You Are At Greater Risk Of Hiv
If you are at greater risk of HIV get tested regularly.
Gay, bisexual, trans and other men who have sex with men should get tested every 3 months . This may vary depending on how many sexual partners you have during the year.
Talk with your doctor or sexual health specialist for advice. They can also provide information about how to reduce your risk for HIV and other STIs.
Transmission Of Hiv Infection
HIV is not transmitted by casual contact or by close, nonsexual contact at work, school, or home. No case of HIV transmission has been traced to the coughing or sneezing of an infected person or to a mosquito bite. Transmission from an infected doctor or dentist to a patient is extremely rare.
HIV is usually transmitted in the following ways:
-
Injection of contaminated blood, as can occur when needles are shared or a health care worker is accidentally pricked with an HIV-contaminated needle
-
Transfer from an infected mother to a child before birth, during birth, or after birth through the mothers milk
-
Medical procedures, such as transfusion of blood that contains HIV, procedures done with inadequately sterilized instruments, or transplantation Overview of Transplantation Transplantation is the removal of living, functioning cells, tissues, or organs from the body and then their transfer back into the same body or into a different body. The most common type of… read more of an infected organ or tissues
HIV is more likely to be transmitted if skin or a mucous membrane is torn or damagedeven if minimally.
|
Also Check: Old Root Canal Infection Symptoms
Diagnosis Of Hiv Infection
-
Tests to detect antibodies to the HIV virus in a sample of blood or saliva
-
Tests to detect HIV RNA in a sample of blood
Early diagnosis of HIV infection is important because it makes early treatment possible. Early treatment enables infected people to live longer, be healthier, and be less likely to transmit HIV to other people.
Doctors usually ask about risk factors for HIV infection Transmission of HIV Infection Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . HIV is transmitted… read more and about symptoms .
Doctors also do a complete physical examination to check for signs of opportunistic infections, such as swollen lymph nodes and white patches inside the mouth , and for signs of Kaposi sarcoma of the skin or mouth.
How Is Hiv Not Spread
HIV is not spread by:
- Mosquitoes, ticks, or other insects
- Saliva, tears, sweat, feces, or urine that is not mixed with the blood of a person with HIV
- Shaking hands hugging sharing toilets sharing dishes, silverware, or drinking glasses or engaging in closed-mouth or social kissing with a person with HIV
- Drinking fountains
- Other sexual activities that dont involve the exchange of body fluids .
You May Like: Can You Take Yeast Infection Medication While On Antibiotics
What Are The Different Types Of Blood Infections
We live in a world filled with germs and often fall prey to infections that invade our bodies. It could be a skin infection, ear infection, or chest infection. But, more rarely, germs can also cause a blood infection. And all the usual suspects bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites can infect your blood. Heres a closer look at these blood infections.
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes. Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. If taken as prescribed, HIV medicine can reduce a persons HIV viral load very low level, which keeps the immune system working and prevents illness. This is called viral suppression, defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
HIV medicine can also make the viral load so low that a standard lab test cant detect it. This is called having an undetectable level viral load. Almost everyone who takes HIV medicine as prescribed can achieve an undetectable viral load, usually within 6 months after starting treatment.
As noted above, people with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long and healthy lives and will not transmit HIVto their HIV-negative partnersthrough sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only if the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine as prescribed and visit their health care provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Tooth Get Infected
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Most people have no symptoms or just a mild flu-like illness when they are first infected, and it may be difficult to tell the HIV apart from other viral infections. This illness, called seroconversion illness, often occurs around 10 to 14 days after infection.
Seroconversion illness can have a range of symptoms, including:
- swollen lymph glands in the neck, underarm or groin areas
After the initial illness, people with HIV infection usually have no other symptoms. However, the virus remains in the body.
Escherichia Coli And Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
In the nosocomial setting, Gram-negative bacteria are a minor source of BSI compared to Gram-positive.55,11,33 In a 12 months multicenter prospective study of patients with advanced HIV infection, Petrosillo et al. found Gram-negative organisms accounting for approximately one-fifth of all BSI and 12.9% of catheter-related BSI. E. coli and P. aeruginosa were the most frequent Gram-negative isolates.55 Afessa et al. found that Gram-negative bacteria caused 31% of nosocomial bacteremia in hospitalized HIV-infected patients, with P. aeruginosa as the most common pathogen.11 Similarly, in a retrospective study by Ortega et al., Gram-negative bacteria caused 31% of nosocomial BSI both in the pre-cART and in the cART era. P. aeruginosa and E. coli were the most frequently isolated microorganisms in these studies.33
Also Check: Z Pack Antibiotic For Ear Infection
Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
Hiv And Your Complete Blood Count
If you are living with HIV, your doctor will order regular blood tests to check the status of your immune system .
In addition to these tests, others will be performed to ensure that your body is functioning normally and there are no signs of illness or drug toxicity. Central to this is a panel of tests called the complete blood count .
The CBC measures the composition of cells in a sample of blood to flag for changes that fall outside of the “normal” range of values. This can help alert doctors if a drug like Retrovir is causing anemia or there are early signs of an opportunistic infection. The CBC is often the first clue that something is not right.
This article looks at the three major blood cell types in a CBC and what high or low counts of each can mean if you are living with HIV.
Also Check: How Soon After Hiv Infection Can You Infect Others
Hiv Effects On The Digestive System
More than half of people who have AIDS report digestive symptoms as the virus or an opportunistic infection targets the walls of their intestines. Diarrhea is the most common one. Over time, the virus can change how your digestive tract works and even how it looks.
Liver
Some HIV medications can damage your liver. Many people with HIV also have a form of inflammation called hepatitis.
Limit how much alcohol you drink, and don’t use recreational drugs. Having diabetes, high cholesterol, or triglycerides and being overweight can lead to fatty liver disease, so keep an eye on the carbs, fats, and calories you eat each day.
Talk to your doctor about getting the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines. Thereâs no vaccine against hepatitis C, but you should get tested for it.
Get regular blood tests to catch any liver problems early.
Mouth
Your mouth might be one of the first places where you notice signs of HIV. Things like dry mouth, fungal infections, gum disease, cold sores, and canker sores can make chewing or swallowing painful. If they go on too long, you might not be able to take your HIV medication or get the nutrients you need.
Good dental habits can help prevent these issues, so brush and floss regularly. See your dentist for checkups, and tell them if youâre having problems. Most mouth conditions tied to HIV are treatable.
Hiv Stigma And Discrimination
HIV can prompt intense feelings in people, regardless of their HIV status. It is sometimes viewed with a sense of unacceptability or disgrace. A person with HIV may feel shame and despair about their status. An HIV-negative person may be fearful or angry when they discover someone has HIV. The relationship of these feelings to HIV is referred to as stigma.Felt stigma refers to deep feelings of shame and self-loathing, and the expectation of discrimination. It can have serious negative impacts on the health and wellbeing of people living with HIV by discouraging them from getting tested, receiving support, or taking treatment. It may also lead people to engage in high-risk behaviours that harm their health, and contribute to new HIV infections.Enacted stigma is the experience of unfair treatment by others. For people living with HIV this can be in the form of being treated differently and poorly, or through rejection, abuse, or discrimination.HIV stigma is particularly harmful when it overlaps with other factors that are stigmatised such as if a person uses drugs, is a sex worker, is trans or gender diverse.Breaking down stigma is a community response where:
If you have experienced stigma or discrimination from a health care provider, and are unable to resolve your complaint with them directly, contact the Health Complaints Commissioner
Also Check: Can Bacterial Sinus Infection Treated Without Antibiotics
Strategies For Preventing The Transmission Of Hiv
|
Condoms made of latex provide good protection against HIV , but they are not foolproof. Oil-based lubricants should not be used because they may dissolve latex, reducing the condom’s effectiveness.
Other measures can help. For men, circumcision, an inexpensive, safe procedure, reduces the risk of becoming infected during vaginal intercourse with an infected woman by about half. Whether circumcision reduces the risk of HIV infection in other circumstances is unclear. Because circumcision provides only partial protection against HIV infection, people should also use other measures to prevent HIV infection. For example, if either partner has a sexually transmitted infection or HIV infection, it should be treated, and condoms should be used correctly and consistently.
Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
You can reduce the risk of spreading HIV by:
- Getting tested for HIV.
- Choosing less risky sexual behaviors. This includes limiting the number of sexual partners you have and using latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
- Getting tested and treated for sexually transmitted diseases .
- Not injecting drugs.
- Talking to your health care provider about medicines to prevent HIV:
- PrEP is for people who don’t already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk.
- PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. It is only for emergency situations. PEP must be started within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV.
NIH: National Institutes of Health
Recommended Reading: What To Do If Malware Infects Your Computer
Stages Of Hiv Infection
About a month after you get HIV, you might feel like you have the flu. This is the first stage, called primary or acute HIV infection. Symptoms include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
The next stage is called clinical latency, or chronic infection. You might have no symptoms, or only mild ones, for 10 years or more.
Without treatment, as HIV keeps multiplying inside your body, youâll move into the third stage, which is AIDS. A person who has HIV is diagnosed with AIDS when they have fewer than 200 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter of blood or when they get whatâs called an AIDS-defining condition.
AIDS-defining conditions are certain cancers and illnesses called opportunistic infections.
Hiv Transmission In Australia
In Australia, HIV is commonly transmitted through:
- Sharing any needles, syringes, or other injecting equipment.
- From mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding This can occur when the mother doesnt know she is HIV-positive, or is not on effective treatment.
- Tattooing or other procedures that involve unsterile or reused equipment.
- Needle stick injuries.
HIV is not transmitted by:
- kissing, hugging, massaging, mutual masturbation and other body contact
- social interaction
- sharing food, dishes, utensils, drinking glasses
- air, breath, or being coughed or sneezed on
- mosquito, insect or animal bites
- use of communal facilities .
It is perfectly safe to consume food and drinks prepared by someone who is HIV-positive even if theyre not receiving treatment.
People with HIV who are on treatment and achieve and maintain an undetectable HIV viral load cannot transmit HIV sexually.
Read Also: Diff Between Uti And Yeast Infection