Third Stage: Aids Symptoms
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection. This is usually when your CD4 T-cell number drops below 200 and your immune system is badly damaged. You might get an opportunistic infection, an illness that happens more often and is worse in people who have weakened immune systems. Some of these, such as Kaposi’s sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia , are also considered âAIDS-defining illnesses.â
If you didn’t know earlier that you were infected with HIV, you may realize it after you have some of these symptoms:
- Being tired all the time
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck or groin
- Fever that lasts more than 10 days
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
At this stage, there are often no symptoms, but the virus continues to multiply at low levels. The virus can transmit from the individual to another person.
However, current treatment can reduce the level of the virus so effectively that a test can no longer detect it.
When this happens, the virus is still present in the body, but it cannot:
- cause damage to the immune system
- progress to stage 3, more commonly known as AIDS
- pass to another person
Chronic Infection Top Of Page
During chronic infection, immune activation occurs. The immune activation is likely to provide some restoration of CD4+ cells to the memory pool, Dr. Douek commented. You see that theres a good response, in an effort to maintain some kind of immunity. But theres trouble here too. The immune activation imposes a homeostatic strain that further drains the memory CD4+ cell pool that was initially depleted during acute infection.
The regenerative capacity of the memory CD4+ cell pool is limited, unlike the CD8+ cell pool. It is critically dependent on the input from the naïve CD4+ cell pool and the thymus. CD4+ cells start off as naïve T-cells, Dr. Douek reviewed. They divide and become memory T-cells. This is the pool that is depleted during acute infection. Eventually, they become further activated and they die. What happens in the chronic phase of HIV infection is that immune activation increases the flux of the system from naïve CD4+ cells through to memory and through to cellular death. Persistent rounds of activation and death is going to slowly and preferentially deplete the CD4+ cell pool. This is not going to affect the CD8+ cell pool. Thats why immune activation can cause CD4+ cell, but not CD8+ cell, depletion.
Read Also: How Much Amoxicillin For Sinus Infection
What Is Acute Hiv Infection
Acute HIV infection is the initial stage of HIV, and it lasts until the body has created antibodies against the virus.
Acute HIV infection develops as early as 2 to 4 weeks after someone contracts HIV. Its also known as primary HIV infection or acute retroviral syndrome. During this initial stage, the virus is multiplying at a rapid rate.
Unlike other viruses, which the bodys immune system can normally fight off, HIV cant be eliminated by the immune system.
Over a long time, the virus attacks and destroys immune cells, leaving the immune system unable to fight off other diseases and infections. When this happens, it can lead to late stage HIV, known as AIDS or stage 3 HIV.
Its possible to contract HIV from a person with an acute HIV infection because of the high rate of viral replication during this time.
However, most people with acute HIV infection dont even know theyve contracted the virus.
This is because the initial symptoms resolve on their own or may be mistaken for another illness such as the flu. Standard HIV antibody tests arent always able to detect this stage of HIV.
Acute HIV infection symptoms are similar to those of the flu and other viral illnesses, so people may not suspect that theyve contracted HIV.
In fact, the estimates that of the nearly 1.2 million people in the United States living with HIV, about 14 percent of them dont know they have the virus. Getting tested is the only way to know.
Symptoms of acute HIV infection can include:
What Are The Stages Of Hiv
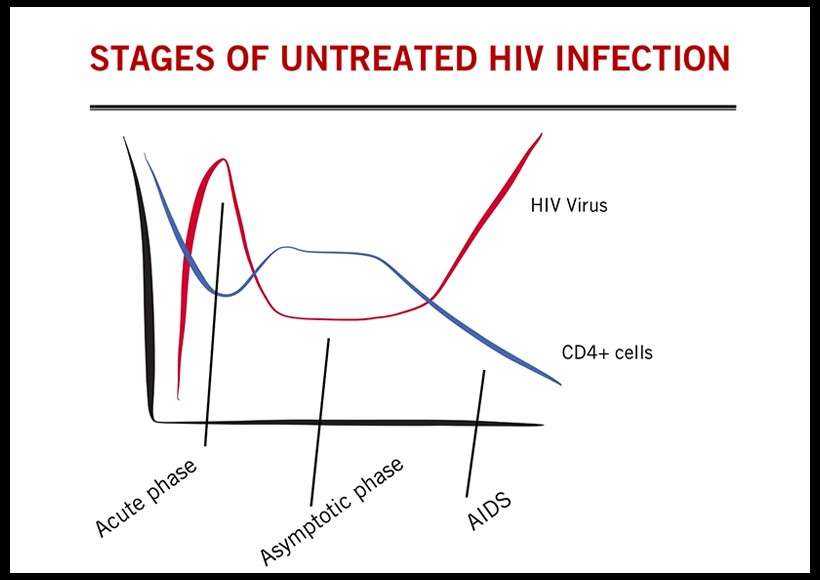
HIV disease has a well-documented progression. Untreated, HIV is almost universally fatal because it eventually overwhelms the immune systemresulting in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . HIV treatment helps people at all stages of the disease, and treatment can slow or prevent progression from one stage to the next.
A person can transmit HIV to others during any of these stages:Acute infection: Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, you may feel sick with flu-like symptoms. This is called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection, and its the bodys natural response to the HIV infection. During this period of infection, large amounts of HIV are being produced in your body. The virus uses important immune system cells called CD4 cells to make copies of itself and destroys these cells in the process. Because of this, the CD4 count can fall quickly.Your ability to spread HIV is highest during this stage because the amount of virus in the blood is very high.Eventually, your immune response will begin to bring the amount of virus in your body back down to a stable level. At this point, your CD4 count will then begin to increase, but it may not return to pre-infection levels.
Don’t Miss: How Do Doctors Check For Sinus Infection
Estimating Ehmacute From The Rakai Retrospective Cohort
We fit the couples transmission model to the Rakai retrospective cohort data using approximate Bayesian computation with sequential Monte Carlo to estimate transmission rates, RHacute, dacute, and hazard. We describe our approach in detail in S1 Text. Briefly, we used the model to simulate 4,875 couples for each of hundreds of thousands of parameter sets drawn from uninformative prior distributions . Parameter sets that generated retrospective cohorts sufficiently similar to the Rakai cohort, as measured by several summary statistics, were accepted, while others were rejected. Summary statistics included proportions of secondary partners seroconverting in incident and prevalent couples and the extent of individual heterogeneity as indicated by discrepancies between unadjusted and adjusted regression analyses . New parameter sets, sampled randomly around those accepted in the previous step, were simulated and then again filtered based on similarity to the Rakai data. This filtering procedure was repeated with increasingly strict criteria for similarity, until the distribution of parameters converged and the simulation summary statistics sufficiently matched the real data.
What Are The Treatments For Hiv/aids
There is no cure for HIV infection, but it can be treated with medicines. This is called antiretroviral therapy . ART can make HIV infection a manageable chronic condition. It also reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Most people with HIV live long and healthy lives if they get and stay on ART. It’s also important to take care of yourself. Making sure that you have the support you need, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular medical care can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Frequent Uti And Kidney Infections
Factors Associated With Higher Immune Activation
In the complete case analysis, we examined baseline factors associated with having levels of plasma or CSF immune activation markers within the highest tertile of observed values at week 0 and week 24. Examined variables were age at baseline, sex, estimated infection duration, Fiebig stage, and HIV subtype, as well as plasma viral load, CSF viral load, CD4+ T-cell count, CD8+ T-cell count, and ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ T cells at weeks 0 and 24. Baseline plasma viral load was associated with having a highest tertile value for plasma levels of neopterin , CXCL10 , and CCL2 and CSF level of neopterin . Baseline CSF viral load was associated with the highest tertile for baseline plasma CXCL10 level and CSF CXCL10 level . Baseline CD8+ T-cell count was associated with the highest tertile for plasma neopterin level . No baseline findings were associated with having a CSF CCL2 or CSF IL-6 level at week 0 in the highest tertile. Plasma IL-6 levels were not analyzed, owing to a similarity between values at week 0 and in the control group. No variables were associated with a highest tertile value at week 24.
The New Hiv Pathogenesis Top Of Page
The new HIV disease pathogenesis, as summarized by Dr. Douek, essentially involves four mechanisms: 1) early, rapid, and massive memory CD4+ cell infection and depletion in acute HIV infection 2) chronic activation imposes homeostatic strain on maintenance of vulnerable CD4+ cell pools 3) destruction of the lymph node microenvironment preferentially affects CD4+ homeostasis and 4) suppression of thymic output preferentially affects CD4+ cell reconstitution. In other words, the new HIV disease pathogenesis reflects a much more detailedand altogether complicatedversion of the initial tap-and-drain model proposed by Dr. Ho and his colleagues.
For Dr. Douek, the answer likely resides in the mucosa. The immune system is usually activated by external agents that enter at mucosal surfaces, he explained. The ability to partially reconstitute mucosal CD4+ cells after the acute depletion predicts progression, as shown recently by Dr. Louis Picker and his colleagues in the SIV model .
Read Also: Can I Infect Someone While On Prep
Effectiveness Of Antiretroviral Therapy During Acute Hiv Infection
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : June 27, 2008Last Update Posted : August 31, 2017 |
| Drug: Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Other: No treatment | Phase 1 |
Antiretroviral therapy for the treatment of HIV infection has been remarkably successful in reducing morbidity and mortality in HIV infected people. This treatment still has its shortcomings, however. Individuals receiving ARV treatment are at risk of toxicity, developing drug resistance, and unknown long-term side effects. Therefore, development of alternative treatment strategies is important. A short course of ARV treatment that is initiated during the acute period of HIV infection, followed by treatment cessation may have a substantial impact on controlling infection and delaying the need for lifelong potent ARV therapy. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether treatment initiated during acute HIV infection and followed by a terminal treatment interruption is effective in lowering the viral load set point and raising CD4 cell counts in people with HIV, as compared to those measures in people with HIV who have received no treatment.
Chronic Hiv Infection With Antiretroviral Treatment
If you take effective HIV treatment, you can live with HIV as a chronic, manageable condition. A chronic health condition is one which continues for a long period of time.
This stage is not included in most descriptions of the stages of infection, which only describe disease progression in the absence of treatment.
However, most people living with HIV who have access to good healthcare are living with HIV as a chronic condition and will continue to do so for the rest of their lives. They are unlikely to fall ill or die as a direct result of HIV.
In order to reach this stage and to remain in it, you need to take HIV treatment and continue to take it, on an ongoing basis. These medications reduce levels of HIV in your body and strengthen the immune system. This usually prevents the symptoms and opportunistic infections described above from occurring.
One of the benefits of effective HIV treatment is that is stops HIV from being passed on. Treatment drastically reduces the amount of HIV in body fluids to the point where there is not enough HIV to transmit the virus to sexual partners.
The chronic infection phase can last for decades. People who start HIV treatment as soon as possible, are able to stick with it and have access to good healthcare are likely to have a similar life expectancy to their peers who dont have HIV.
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Itchy At Night
Rationale For Treatment Of Acute Hiv Infection
The potential benefits of initiating antiretroviral therapy for patients with acute and recent HIV infection include accelerated resolution of symptomatic acute retroviral syndrome, minimized immunologic damage, diminished size of the latent HIV reservoir pool, and prevention of HIV transmission to others.
Protein Chip Analysis And Depletion Of The 86
Surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry Protein chip arrays were used according to the manufacturers recommendations. Briefly, serum samples were diluted 10-fold in a binding buffer ) and applied to a strong anion exchanger chip. After incubation for 1 h at room temperature, unbound proteins were removed by three successive washes of 5 min each with a buffer containing 1 mM NaCl and 50 mM HEPES . Chip-captured proteins were air-dried and covered with a matrix , used as an absorbent for laser energy. The ionized and desorbed proteins were detected and their molecular masses displayed on the proteogram peaks were determined using SELDI-TOF-MS analysis with the Protein-Chip Biology System II software and Ciphergen Peaks software. Depletion of the 8.6-kDa protein from EU plasma was achieved as follows: 25 l of magnetic beads were washed three times with PBS, added to 25 g of a rat anti-acute-phase serum amyloid A or an isotype-matched control mAb and incubated for 1 h at 4°C with orbital shaking. After rigorous washing of the mAb-coated magnetic beads with PBS, they were incubated with a pool of five EU plasma samples at 4°C for 3 h with orbital shaking. After removal of the beads by a magnetic device, 5 l of EU plasma was analyzed by SELDI-TOF under the conditions described above.
Recommended Reading: Can You Remove An Infected Tooth
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles.
- Gay and bisexual men.
- Black/African Americans and Hispanic/Latino Americans. They make up a higher proportion of new HIV diagnoses and people with HIV, compared to other races and ethnicities.
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms.
Factors such as stigma, discrimination, income, education, and geographic region can also affect people’s risk for HIV.
Rationale For The Treatment Of Acute Hiv Infection: For The Individual
The principal rationales to treat acute HIV with ART, when considering the individual patient, are 1) to treat highly symptomatic patients as they are more likely to progress rapidly, 2) to preserve CD4 T + cell counts and reduce the viral set point, 3) to limit the size of viral reservoirs, 4) to preserve HIV-specific immunity, and 5) time to CD4 T + cell count 500 is short, why wait?
1. Treat Symptomatic Acute HIV Infection
Acutely HIV-infected patients who are symptomatic tend to progress more rapidly than those without symptoms. Antiviral therapy in acute infection rapidly reduces viral loads and alleviates symptoms as well . The most recent IAS-USA guidelines recommend considering ART in the setting of symptomatic acute HIV .
2. Preserve CD4 T-Cell Counts and Reduce Viral Set Point
You May Like: Amoxicillin For A Sinus Infection
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Treatment Indication And Duration
All persons with acute or recent HIV infection should promptly receive antiretroviral treatment . Several studies have examined the strategy of starting antiretroviral therapy for acute HIV infection and then discontinuing therapy after approximately 6 months. Although this strategy has shown beneficial impact on immune status when compared with no treatment during acute HIV, other studies have shown that treatment interruption in patients with chronic HIV results in increased in laboratory markers of inflammation, immune activation, and coagulation, as well as an increase in risk of clinical AIDS and non-AIDS-related events. In addition, persons with HIV at any stage of disease will reduce their risk of transmitting HIV to others if they are consistently taking recommended antiretroviral therapy. For these reasons, experts recommend continuing antiretroviral therapy indefinitely if started in the acute or early phase.
You May Like: Oral Medication For Yeast Infection
How Can You Tell If You Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. You cant rely on symptoms to tell whether you have HIV.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information so you can take steps to keep yourself and your partner healthy:
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV. People with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long and healthy lives and will not transmit HIV to their HIV-negative partners through sex. An undetectable viral load is a level of HIV in the blood so low that it cant be detected in a standard lab test.
- If you test negative, you have more HIV prevention tools available today than ever before, like pre-exposure prophylaxis , medicine people at risk for HIV take to prevent getting HIV from sex or injection drug use, and post-exposure prophylaxis , HIV medicine taken within 72 hours after a possible exposure to prevent the virus from taking hold.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If you have HIV and take HIV medicine as prescribed throughout your pregnancy and childbirth and give HIV medicine to your baby for 4 to 6 weeks after giving birth, your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby can be less than 1%. HIV medicine will protect your own health as well.
Use the HIV Services Locator to find an HIV testing site near you.