How To Get Vaccinated Against Hpv
HPV vaccines come as a single vaccine, not as a combination vaccine.
HPV vaccines include:
*Indicates National Immunisation Program vaccine.
Your vaccination provider will tell you which vaccine they will give you.
Find product information and consumer medicine information for each available vaccine from the Therapeutic Goods Administration.
How Does The Hpv Vaccine Work
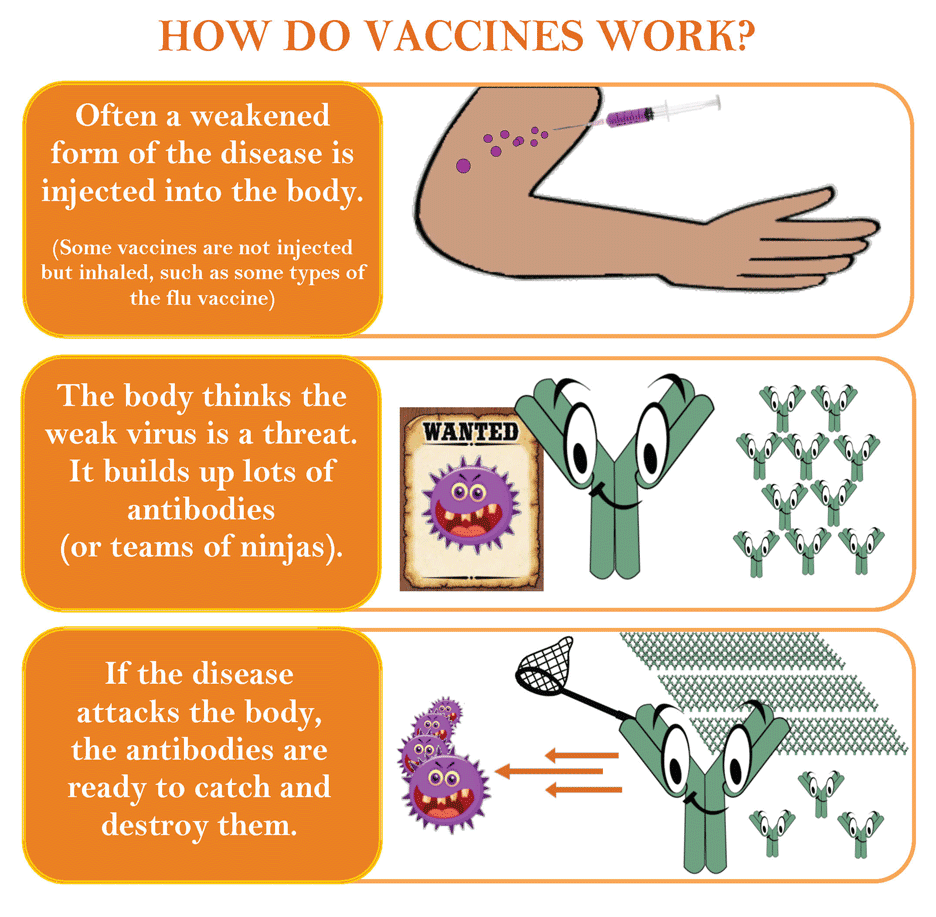
The HPV vaccine works in a series of two or three shots to protect your child from HPV infections. The vaccine signals the body to produce antibodies that will bind to the virus if encountered and prevent it from infecting cells.
The vaccine is most effective when it is administered before your child encounters the virus. Therefore, the most effective way to prevent an HPV infection is for your child or teen to get vaccinated before having sex for the first time. However, if your child is already sexually active, they should still receive an HPV vaccine because condoms do not fully protect against HPV infections.
Question: Why Is The 9
Answer: In accordance with current scientific studies, apart from HPV type 16 and 18, other high-risk HPV including type 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58 can potentially cause pre-cancerous changes. Therefore, the 9-valent HPV vaccine offers more protection against HPV than the quadrivalent HPV vaccine does and is as safe.
Don’t Miss: Ear Infection Treatment Adults Over The Counter
How Long Is The Hpv Vaccine Effective
Studies also show that the HPV vaccine gives long-lasting protection against HPV. The longer the vaccine is out, the more scientists will know about how long it works for. But so far the vaccines are being shown to last for many years.
Since the HPV vaccine was recommended in 2006 in the U.S., rates of infection, genital warts, and cervical precancers have gone down a lot.
Fact : The Vaccine Is Safe
The HPV vaccine has been used since 2006. The vaccine went through extensive safety testing before becoming available. More than 270 million doses of the HPV vaccine have been given worldwide, including 120 million doses in the US. Scientists and health organizations around the world closely monitor HPV vaccine safety.
In the US, vaccine safety is watched by several national systems that work together to make sure that any harmful effects of vaccines can be found early. More than 100 studies in millions of people worldwide have all shown that the HPV vaccine is safe.
Like any vaccination, there may be common mild side effects from the HPV vaccine that go away quickly like headache or fever. There can be pain, redness, and/or swelling where the shot was given. A small number of people may have a more serious side effect that could occur with any vaccine, such as an allergic reaction or fainting when the vaccine is given. Anyone who has a severe allergy to yeast or any other ingredient in the vaccine should not receive the HPV vaccine.
Also Check: Can Bactrim Treat Bladder Infection
What Are The Side Effects
Many people have no side effects from the vaccines. For those that do, common side effects may include soreness, redness and swelling where the vaccine was given. Fever, fatigue, headache, and muscle or joint ache may also occur. As with other vaccines, fainting has occurred following HPV vaccination. Fainting can occur with any medical procedure – not just the HPV vaccine and people recover quickly.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is an extremely rare possibility of anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening allergic reaction. This may include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, tongue, or lips. The chance of true anaphylaxis is about 1 in 1 million vaccine doses. Should this reaction occur, your health care provider is prepared to treat it. Emergency treatment includes administration of epinephrine and transfer by ambulance to the nearest emergency department. If symptoms develop after you leave the clinic, call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number. Learn more about anaphylaxis on our vaccine side effects page.
It is important to always report serious or unexpected reactions to your health care provider.
How Well Do These Vaccines Work
HPV vaccination works extremely well. HPV vaccine has the potential to prevent more than 90% of HPV-attributable cancers.
- Since HPV vaccination was first recommended in 2006, infections with HPV types that cause most HPV cancers and genital warts have dropped 88% among teen girls and 81% among young adult women.
- Fewer teens and young adults are getting genital warts.
- HPV vaccination has also reduced the number of cases of precancers of the cervix in young women.
- The protection provided by HPV vaccines lasts a long time. People who received HPV vaccines were followed for at least about 12 years, and their protection against HPV has remained high with no evidence of decreasing over time.
Read Also: Embarrassed To Go To Doctor For Yeast Infection
Question: What Do I Need To Do If I Want To Be Vaccinated With The 9
Answer: Clinical studies have assured both efficacy and safety of the 9-valent HPV vaccine after receiving GARDASIL® or CERVARIX® longer than a year. However, there are some studies that ensure vaccine safety even though it has been given in less than 12 months after the administration of GARDASIL® or CERVARIX®.
In conclusion, the bivalent and quadrivalent HPV vaccines are aimed at protecting against high-risk HPV type 16 and 18, resulting in less chance of developing precancerous changes, defined as Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or cervical dysplasia. CIN is characterized by a premalignant condition of the cervix and usually detected by screening with cytological test and HPV testing. If left untreated, CIN can develop into invasive cervical cancer. However, the bivalent and quadrivalent HPV vaccines can only minimize the chance of developing high grade CIN e.g. CIN II-III, there are still some possibilities of developing low grade lesion e.g. CIN I. In addition, they do not prevent the infection of other HPV strains that possibly cause other diseases. Therefore, the novel 9-valent HPV vaccine covers broader spectrum, targeting 9 HPV strains grouped in high-risk HPV that most commonly cause cervical cancer and other cancers as well as genital warts. Nevertheless, individual benefits obtained from the 9-valent HPV vaccine should be further discussed among different females.
Information by
Why Is The Hpv Vaccine Given At Such A Young Age
HPV infections can be spread by any skin-to-skin contact and are usually found on the fingers, hands, mouth and genitals.
This means the virus can be spread during any kind of sexual activity, including touching.
The HPV vaccine works best if girls and boys get it before they come into contact with HPV .
So getting the vaccine when recommended will help protect them during their teenage years and beyond.
Most unvaccinated people will be infected with some type of HPV at some time in their life.
The virus does not usually do any harm because the person’s immune system clears the infection.
But sometimes the infection stays in the body for many years, and then it may start to cause damage.
Read Also: Why Do You Bleed When You Have A Bladder Infection
Can Getting The Hpv Vaccine Help If I Already Have Genital Warts
Can vaccination for HPV virus help someone who already has genital warts? Will it help to protect my partner? Mel*
Getting the HVP vaccine is definitely still a good idea for you. That’s because there are different types of HPV some that cause warts, and others that cause cancer. Even if you have already been infected with the type of HPV that causes genital warts, you can still protect yourself against the types that can cause cancer since you may not be infected with those types yet.
If you get vaccinated now, it won’t protect your partner, though. But your partner can be vaccinated too. People of all genders should be vaccinated against HPV to help prevent the spread of the disease.
Even if you and your partner have both been vaccinated, always use condoms for any type of sex . Condoms help prevent the spread of the types of HPV that are not covered by the vaccine. And, of course, condoms also help protect against other sexually transmitted diseases .
*Names have been changed to protect user privacy.
A Boost For Vaccinations
The Swedish study does have some limitations. For example, it couldnt account for factors such as the extent to which women followed in the study were screened for cervical cancer, the study team reported. The researchers also couldnt capture the number of vaccine doses each person in the vaccination group received.
But thats not a big limitation for this type of study. Its not a dose question, Dr. Kreimer said. For this study, she continued, They were saying, We established a vaccine program in a population, and this is how it worked.
Although rates of HPV vaccination have increased among adolescents and teens in the United States, they still are lower than public health officials would like. Dr. Berenson said shes hopeful that the findings from the Swedish study can provide a boost.
provide a very good discussion point around age of vaccination, she said. And thats needed, she added, because parents sometimes are reluctant to have their daughters receive the HPV vaccine at the recommended age, which is 11-12 years old.
They often tell us they want to wait until shes olderuntil shes 18saying, She can make the decision for herself, Dr. Berenson said. This study gives good evidence to say, We understand why you may feel that way, but you are missing the opportunity of much higher efficacy if she gets vaccinated at a younger age.
Read Also: Sickle Cell Anemia Bacterial Infection
Age Range For Two Doses
A two-dose regimen is recommended for people ages 9 to 14. The first dose must be initiated before a person turns 15 to fall under the two-dose schedule.
Research shows that children in the 9-14 age range who receive two doses of the vaccine at least six months apart have equal or greater protection than people over the age of 15 who receive three doses.
What Are The Advantages Of Getting The Hpv Vaccine
The biggest advantage is reducing your risk for cancers caused by HPV infection. HPV is so common that around 80% of people in the United States will encounter it at some point in their lives. There is no way to know which infection can lead to cancer. Vaccinating against HPV is the best protection available at this time.
You May Like: Cranberry Pills For Yeast Infection
Possible Side Effects Of Hpv Vaccination
You may experience minor side effects following vaccination. Most reactions are mild and last no more than a couple of days and you will recover without any problems.
Common side effects of HPV vaccines include:
- pain, redness and swelling at injection site
Talk to your vaccination provider about possible side effects of HPV vaccines, or if after having a HPV vaccine you or your child have symptoms that worry you.
The Consumer Medicine Information available on the Therapeutic Goods Administration website lists the ingredients and side effects of each vaccine.
Why Is Hpv Vaccination Important
The combination of HPV vaccination and cervical screening can provide the greatest protection against cervical cancer. Also, HPV vaccination reduces the risk of developing cancers caused by HPV at sites other than the cervix.
Not only does vaccination protect vaccinated individuals against infection by the HPV types targeted by the vaccine that is used , but vaccination can also reduce the prevalence of the vaccine-targeted HPV types in the population, thereby reducing infection in individuals who are not vaccinated . For example, in Australia, where a high proportion of girls are vaccinated with Gardasil, the incidence of genital warts went down during the first 4 years of the vaccination program among young maleswho were not being vaccinated at the timeas well as among young females .
Further evidence that large-scale HPV vaccination confers protection for unvaccinated individuals comes from a 2019 meta-analysis of girls-only HPV vaccination programs in 14 high-income countries that included 60 million vaccinated people . That analysis showed that, up to 8 years after the start of vaccination, diagnoses of anogenital warts decreased by 31% among women aged 2529 years, by 48% among boys aged 1519 years, and by 32% among men aged 2024 years, compared with the period before vaccination began.
Don’t Miss: Can I Go To Urgent Care For A Yeast Infection
Effects That Influence The Vaccine Coverage And Efficacy
There are many potential effects that influence vaccine coverage and efficacy, such as vaccine age, geographical regions, and education. The ideal time for the best protection against HPV-related diseases is prior to HPV exposure . Studies demonstrated that vaccination before first sexual contact could protect more than 90% of targeted HPV-related infections, abnormalities, and precancerous lesions, while vaccination after HPV exposure only protects about 5060% infections . Taira et al. developed a disease transmission model and suggested that vaccination of 12-year-old girls provides the best and most cost-effective solution against cervical cancer . The earlier the HPV vaccination is provided to the population before the sexual-behavior transition, the more effective the results are likely to be .
The number of sexual partners, one of the most important risk factors for HPV infection, has also been demonstrated as a strong predictor of CIN 2 and 3 regression . Women with no lifetime or past-year sexual partners had significantly lower HPV vaccine initiation as compared with those with male sexual partners . Notably, HPV vaccination did not show any comparative increase in sexual activity between vaccinated and unvaccinated men and women .
Fact : The Hpv Vaccine Works Best When Given Between Ages 9 And 12
Since vaccines are used to help prevent diseases, children are vaccinated before being exposed to an infection. Most people in the US are exposed to HPV in their teens and early twenties, so its best to get the vaccine before then, between ages 9 and 12. The body also produces the most antibodies to HPV when the vaccine is given in this age range. Teens and young adults age 13 through 26 who have not been vaccinated, or who havent gotten all their doses, should get the vaccine as soon as possible. ACS does not recommend HPV vaccination for anyone older than 26 years.
Don’t Miss: If I Touch Hiv Infected Blood
Are There Different Types Of Hpv Vaccines
HPV is a group of more than 200 viruses. About 40 of these are spread through sexual contact. Of these 40, about 12 types can cause certain cancers. There are three safe and effective HPV vaccines available worldwide:
- Gardasil® 9: This is the only vaccine currently being used in the United States. Gardasil 9 protects against nine types of cancer-causing HPV, including high-risk strains. It can prevent up to 90% of cervical cancers.
- Cervarix® and Gardasil®: These two HPV vaccines are used in other countries and treat certain high-risk strains of HPV. They can prevent around 70% of cervical cancer.
Hpv Vaccination For Transgender People
Trans women are eligible in the same way as MSM if their risk of getting HPV is similar to the risk of MSM who are eligible for the HPV vaccine.
Trans men are eligible if they have sex with other men and are aged 45 or under.
If trans men have previously completed a course of HPV vaccination as part of the girls’ HPV vaccine programme, no further doses are needed.
Also Check: Can A Tooth Implant Get Infected
How Has The Hpv Vaccination Programme Changed
In July 2018, it was announced that the HPV vaccine would be extended to boys aged 12 to 13 years in England.
This decision was based on advice from the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation , the independent body that advises UK health departments on immunisation.
Since the 2019 to 2020 school year, both 12- to 13-year-old boys and girls in school Year 8 have been eligible for the HPV vaccine.
A catch-up programme for older boys is not necessary as evidence suggests they’re already benefiting greatly from the indirect protection that’s built up from 10 years of the girls’ HPV vaccination programme.
Hpv Vaccine Boosts Immune Memory

Itâs long been known that the vaccine against the human papilloma virus offers protection when administered to those whoâd never experienced HPV infection. But new research suggests the possibility that it could also help those whoâd been previously infected to guard against re-infection, according to results recently published in EBioMedicine.
Vaccines are designed to create immunity, also known as immune memory, to keep infection at bay. Researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center have found that the HPV vaccine helps the immune system ârememberâ the virus better than natural HPV infection itself. A single dose of the vaccine appears to improve immune memory in those previously infected with HPV, raising the possibility that the vaccine could help prevent re-infection.
Until now, whether the vaccine could benefit those who had already experienced HPV infection was unknown, said senior author Dr. Denise Galloway, a virologist at Fred Hutch whose work linking HPV to cervical cancer and development of virus-like particles helped pave the way to the vaccine.
âWe wondered if we gave vaccine, could you boost that immunity?â said Galloway. âAnd the answer to that was definitely yes.â
A memorable vaccine
The researchers found that in most of the individuals, vaccination increased the quantity and quality of HPV immunity. Levels of antibodies against HPV16 in four of the vaccinated individuals increased, an average of 77-fold.
Also Check: Tooth Infection Cause Sinus Infection
Side Effects Of Hpv Vaccine
The most common side effects of the HPV vaccine are usually minor and experienced with other routine vaccinations. Side effects can include:
- Tenderness, swelling and/or redness at the injection site
Like other vaccines, there is a rare chance of an allergic reaction. However, most people have no trouble with the vaccine. For answers to more common questions about the HPV vaccine, visit our FAQs & Myths page.