Prevention Of A Kidney Infection
Preventing kidney infections usually starts with preventing UTIs in the lower urinary tract. Steps you can take to help prevent UTIs include:
- Drink lots of water throughout the day.
- Urinate when you feel the urge to do so dont wait.
- Urinate after having sex.
- Dont use unnecessary cleansing or deodorizing products in the genital area.
- Steer clear of birth control methods that can raise the risk of a UTI.
If you do develop a UTI, get it treated as soon as possible. See your primary healthcare provider for treatment, or visit an urgent-care facility for diagnosis and a prescription for antibiotics.
Treating a UTI promptly may prevent it from spreading from your bladder to your kidneys.
What Can Happen If A Uti Is Not Treated
If treated right away, a UTI is not likely to damage your urinary tract. But if your UTI is not treated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and other parts of your body. The most common symptoms of kidney infection are fever and pain in the back where the kidneys are located. Antibiotics can also treat kidney infections.
Sometimes the infection can get in the bloodstream. This is rare but life-threatening.
What Are The Common Causes Of Urinary Tract Infection
Treatment for kidney infections can vary depending on the cause and severity of an infection. Infections in the urinary tract most commonly occur when bacteria travel through the urethra to the bladder to use urine as food for growth and multiplication. Excess levels of bacteria can lead to infections that, when they migrate to the kidneys, are known as kidney infections.
The most common cause of an infection in the urinary tract is from the bacteria Escherichia coli, also commonly referred to as E.coli. They are found in our colon and feces.
Certain sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, and mycoplasma, can also lead to an infection that spreads to the kidneys. Holding your urine for six hours or more can give time for bacteria that enter the bladder to overgrow without being flushed out, increasing the risk of infection.
Dehydration can also increase the risk of infection. Without the proper fluids, your body can not properly flush out bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections . Constipation, a possible result of dehydration, can make it difficult to empty your bladder and allow trapped bacteria to grow as well.
Infections can also be caused by any condition in the urinary tract that prevents urine from flowing naturally. For instance, pregnant women are likely to get bladder infections when the baby puts pressure on the ureters, slowing urine flow.
Recommended Reading: Otc Products For Yeast Infection
When Will I Begin To Feel Better
Once you start treatment, you should start to feel better in a few days.
Can I have sex while being treated for a kidney infection?After you have started treatment and your symptoms have gone away, it is usually safe to have sex. Remember to urinate after sex to avoid getting more bacteria in your urinary tract.
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically respond very well to treatment. A UTI can be uncomfortable before you start treatment, but once your healthcare provider identifies the type of bacteria and prescribes the right antibiotic medication, your symptoms should improve quickly. Its important to keep taking your medication for the entire amount of time your healthcare provider prescribed. If you have frequent UTIs or if your symptoms arent improving, your provider may test to see if its an antibiotic-resistant infection. These are more complicated infections to treat and may require intravenous antibiotics or alternative treatments.
Recommended Reading: Can You Buy Antibiotics Over The Counter For Tooth Infection
How Do You Get Urinary Tract Infections
The design of the human body makes it so it isnt hard to get a bacterial UTI, because the infection comes from outside, through the urethra. Bacteria in the genital area can enter the urethra and the urinary tract, either because wiping after going to the bathroom, sexual activity, or unsanitary conditions. Once the bacteria have entered the urethra, the body tries fight them off, but sometimes the bacteria multiply and cause an infection.
In the case of a fungal infection, usually the fungus gets to the urinary tract through the blood stream. Those who develop this type of infection are usually ill with a disease that has compromised their immune system, such as AIDS.
In general, women get more UTIs than do men and this increases with age. Statistics show that many women get more than one. Almost 20% of women who have had one UTI will go on to have a second. Of this 20%, 30% of those will have a third, and in turn, 80% of these women will have more.
Utis And Menstrual Bleeding: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Delay Or Affect Your Period
While science now shows that men have a hormonal cycle of sorts, much as women do, they dont menstruate meaning that most women between puberty and menopause deal with monthly bleeding that men do not.
As if that isnt enough of an issue for women, with cramps in their uterus and ovaries that can range from annoying to debilitating, women are also more prone to urinary tract infections, or UTIs, with about 50 percent of women experiencing at least one UTI in their lifetime. Of course, a UTI can have complications that eventually affect more than just the urinary tract.
Recommended Reading: Urinary Incontinence And Overactive Bladder
You May Like: Will A Bladder Infection Go Away On Its Own
How To Wash Hands To Avoid Infection
While opting for a hand sanitizer may seem like a smart choice when no running water is close by, know that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not approved any products claiming to prevent E. coli infection.
Its also very important to follow certain food preparation and cooking rules. Here is what the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urges people to do:
- Wash produce. Wash well under running water. Be sure to open up leafy greens, since E. coli can hide in the crevices.
- Cook beef thoroughly. Cook to an internal temperature of at least 145 degrees F for beef steak and roasts and at least 160 degrees F for ground beef and pork.
- Avoid cross-contamination. Use separate cutting boards for meats and produce, and clean counters and utensils after contact with raw meat.
Finally, do not consume any unpasteurized dairy products, unpasteurized juices, or raw milk. And avoid swallowing water when swimming in lakes, ponds, streams, swimming pools, and even backyard kiddie pools.
Dont Miss: What Could Cause Urinary Tract Infection
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are most commonly caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, which you might know as simply E. coli.
These bacteria are responsible for about 90% of all uncomplicated urinary tract infections. E. coli are found in the colons of humans and animals and in their fecal waste. When E. coli or other bacteria end up in the urethra, they cause a urinary tract infection.
There are other types of bacteria also known to cause UTIs. According to a study by The National Center for Biotechnology Information the most common bacteria to cause UTIs are:
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Streptococcus spp. , Staphylococcus epidermidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococci were each found to be the third pathogens in different periods during the two-year study.
Don’t Miss: How Long For Urinary Tract Infection To Clear
Why Do I Need Urinalysis
Healthcare providers order urinalysis tests for several reasons since a urine sample can provide many insights into your health. Your provider may order a urinalysis for you for one or more of the following reasons:
- As part of your routine medical exam to screen for early signs of certain health conditions.
- If youre experiencing and signs and symptoms of certain health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
- To monitor certain health conditions you’re receiving treatment for, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
- To diagnose a urinary tract infection .
- If youve been admitted to a hospital.
- As a preparatory checkup for surgery.
Should I Be Concerned If I Have An Abnormal Result On My Urinalysis
If one of your urinalysis test results is abnormal, it doesn’t necessarily mean that you have a medical condition. Several factors can affect or interfere with urinalysis test results, including:
- Certain medications and supplements, such as metronidazole and vitamin C supplements.
- Contamination of germs or other substances, such as vaginal discharge or menstrual blood, during the urine sample collection.
- Error in the processing of the test.
Your healthcare provider will consider your medical history, current medications and your results and let you know if you need to repeat the test or undergo further testing.
Don’t Miss: Can You Do Root Canal On Infected Tooth
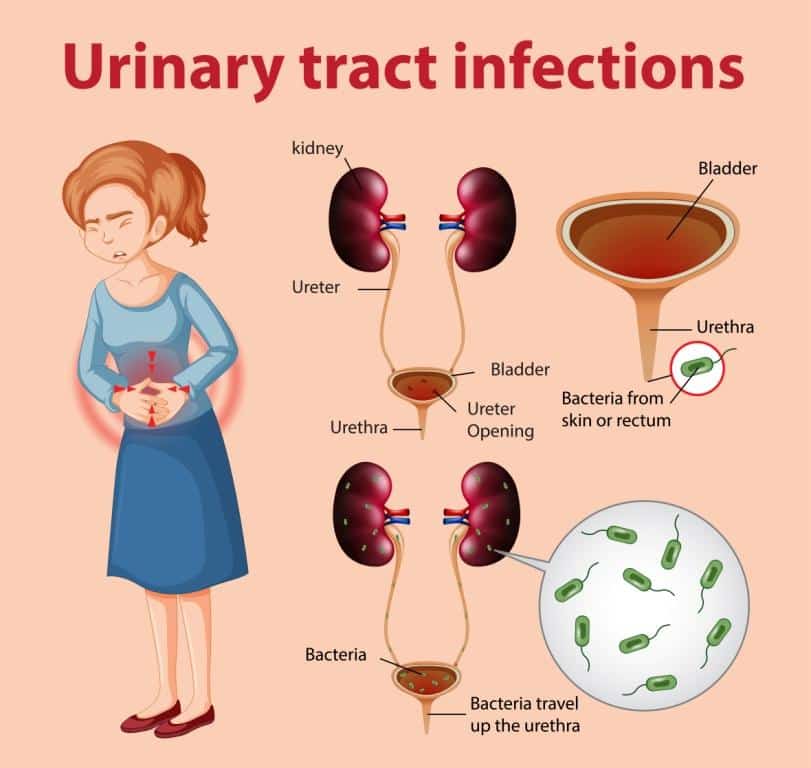
Basic Facts: The Components Of The Urinary Tract
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on the back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body.
- The kidneys remove waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before leaving the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
How Can I Prevent A Kidney Infection
You may be able to lower your chance of getting a kidney infection by:
- Drinking plenty of water
- Urinating as soon as you feel the need to
- Urinating after having sex
- Avoiding the use of deodorant sprays or douches in your genital area
- Getting treatment for constipation . Constipation is not a symptom of kidney infection but it can increase your chance of having bacteria in your urinary tract because it can make it difficult to empty your bladder fully.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotics To Treat Skin Infections
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Infection
If you have a kidney infection, you may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Pain in your back, side or groin
- Feeling like you have to urinate often, even if you just went
- Pain or burning when urinating
- Pus or blood in your urine
- Cloudy or bad-smelling urine
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your health care provider as soon as possible. If you are currently taking medicine to treat a urinary tract infection , but you are still having any of these symptoms, contact your health care provider.
If your health care provider thinks you might have a kidney infection, he or she might ask you for a urine sample to look or bacteria or other signs of infection. You might also need to have a blood test or imaging tests, such as an X-ray, ultrasound or CT scan.
Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
Don’t Miss: How To Get Ear Infection To Drain
Warning Disclaimer Use For Publication
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
DISCLAIMER: All material available on eHealthMe.com is for informational purposes only, and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. All information is observation-only. Our phase IV clinical studies alone cannot establish cause-effect relationship. Different individuals may respond to medication in different ways. Every effort has been made to ensure that all information is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. The use of the eHealthMe site and its content is at your own risk.
If you use this eHealthMe study on publication, please acknowledge it with a citation: study title, URL, accessed date.
You May Like: Signs Bladder Cancer Has Spread
How Is Kidney Infection Diagnosed
A kidney infection is usually diagnosed based on your symptoms, a physical exam, and the results of urine tests, indicating bacteria in your urinary tract.
Your doctor will likely ask about your health history and any conditions that might place you at higher risk of a kidney infection, such as having an enlarged prostate gland or a medical condition that can cause urinary retention, such as multiple sclerosis.
Sometimes a doctor will order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or computerized tomography scan, to look for signs of swelling or other abnormalities in your kidneys or bladder.
You May Like: Do I Need Meds For A Sinus Infection
What Is A Silent Uti
The majority of UTIs happen without symptoms. A UTI is called as silent UTI or asymptomatic UTI when the patient has no symptoms. A UTI is called as symptomatic UTI when the patient has symptoms of UTI. It becomes a silent UTI when patient does not have any symptoms of UTI. The first sign of UTI is usually a feeling of urgency to urinate, followed by frequency and burning sensation during urination. If you ignore symptoms and continue with your daily routine, the bacteria can spread inside the urethra or bladder, causing serious damage and ultimately, kidney infection. Therefore, if you encounter any symptoms of UTI, you should visit your doctor as soon as possible. An examination and urine culture test can help to diagnose UTI. If the UTI is not treated on time, it can lead to permanent kidney damage..
Treatment Options For Utis
Drinking water and cranberry juice are two common recommendations for lower UTIs. However, research has shown the methods to be inconclusive. Extra liquids make urination easier but do not treat the root cause. Speaking with a doctor is the first step. Doctors will then prescribe antibiotics. As bacteria could stay in the cells of the bladder, removing the infection can be difficult. However, when caught early, antibiotics can be effective.
You May Like: What Causes Frequent Bladder Infections
Recommended Reading: Swollen Chin From Tooth Infection
Understanding Your Urinary Tract
Your urinary tract, or urinary system, comprises several different organs designed to extract, hold, and transport waste from your system in the form of urine. The main organs involved in the urinary system include:
- The kidneys: These two organs sit on each side of your body, generally around the waist. They filter out excess water and waste from your blood to create urine.
- The ureters: These two thin tubes run between the kidney and bladder, transporting urine to the bladder.
- The bladder: This organ stores urine until it reaches a certain level, at which point you feel the need to pee. The body voluntarily contracts the muscles that line the bladder to urinate.
- The urethra: This thin tube connects the bladder to the outside of the body. When you urinate, a muscle called the urinary sphincter relaxes as your bladder contracts to remove urine from your body.
Urinary tract infections happen when bacteria infect any part of your urinary system, but they are most common in your lower urinary tract, comprising the urethra and bladder.
Symptoms In Children And Elderly People
While the typical range of symptoms for a kidney infection applies to most adults, older adults and young children may have different symptoms.
If youre over age 65, you may experience none of the typical symptoms of a kidney infection summarized above. Instead, you may only experience problems with your thinking, such as:
Children under 2 years old with a kidney infection may only have a high fever.
Caregivers of very old and very young individuals should know to seek help when these signs or symptoms occur.
Recommended Reading: Can Bladder Infection Clear Up On Its Own
You May Like: Swollen Mouth From Tooth Infection
Duration Of Antimicrobial Therapy
There are no valid published data from randomized trials determining the optimal duration of treatment of UTI in patients with CKD and in dialysis patients. It is customary to treat even uncomplicated cystitis for at least 7 days and to continue for 21 days or more, depending on clinical severity , . However, the response to even longer courses of antibiotics in higher dosage may only be transitory. Even if the urinary concentration of the antibiotic is adequate, the underlying infection may not be eradicated, thus leading to a relapse after the end of antimicrobial treatment.
Recurrent UTI presumably occur due to bacterial regrowth from colonies of non-planktonic bacteria residing in a protected biofilm environment. Persistent microbial niches may develop and colonize deeply within damaged renal parenchymal or urothelial tissue. Furthermore, antibiotic therapy may select highly resistant intracellular, ecologically stable bacterial communities living temporarily as commensals, so-called small colony variants .
Importantly, recent studies have confirmed again that any infection irrespective of severity is an independent risk factor for increased adverse events in the CKD population .