New Hiv Diagnoses And People With Diagnosed Hiv In The Us And Dependent Areas By Area Of Residence 2020*
Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state and local jurisdictions.* Among people aged 13 and older.Source: CDC.Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2020. HIV Surveillance Report2022 33
Although Strides Have Been Made In The Hiv Response Children Are Still Affected By The Epidemic
Of the estimated 38.4 million people living with HIV worldwide in 2021, 2.73 million were children aged 019. Each day in 2021, approximately 850 children became infected with HIV and approximately 301 children died from AIDS related causes, mostly because of inadequate access to HIV prevention, care and treatment services.
As of 2021, roughly 14.9 million children under the age of 18 had lost one or both parents to AIDS-related causes. Millions more have been affected by the epidemic, through a heightened risk of poverty, homelessness, school dropout, discrimination and loss of opportunities, as well as COVID-19. These hardships include prolonged illness and death. Of the estimated 650,000 people who died of AIDS-related illnesses in 2021, 110,000 of them were children under 20 years of age.
Global trends
In 2021, around 160,000 children aged 09 were newly infected with HIV, bringing the total number of children aged 09 living with HIV to 1.02 million . Nearly 86 per cent of these children live in sub-Saharan Africa. One bright spot on the global horizon is the rapid decline of approximately 52 per cent in new HIV infections among children aged 09 since 2010 due to stepped-up efforts to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV. However, the number of new HIV infections among adolescents has declined at a slower rate of about 40 per cent.
Geographic disparity
Fewer And Fewer Children Affected By Hiv
The HIV virus may be transmitted sexually, by blood, or bymother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, birth, orbreast-feeding. In ten years the number of new infections amongchildren under 15 has been halved thanks to antiretroviraltreatment of HIV-positive pregnant women, which considerablyreduces mother-to-child HIV transmission. It is estimated that atthe end of 2012 approximately 63% of HIV-positive pregnant womenworldwide were receiving preventive treatment. A new strategy hasbeen implemented in some high-prevalence countries: providingsimple, lifelong antiretroviral treatment to all pregnant women whotest positive for HIV, regardless of the stage of their disease. Inaddition to preventing transmission to the child during thatpregnancy and any later ones, this strategy protects the mothershealth and reduces transmission to HIV-negative partners, thereforecontributing to containing the epidemic. However, the effectivenessof this strategy depends on several factors, namely the ability ofthe health systems to implement and maintain the treatmentprogramme over the long term and the ability of the HIV-positivewomen to continue the treatment throughout their lives.
Don’t Miss: Ear Infection Antibiotics List For Babies
Efforts Towards Reducing Hiv/aids Prevalence
Countries with the highest rates of HIV infection have taken several measures towards reducing the rate of infection among the population. Awareness programs are conducted to educate the public about HIV/AIDS. Antiretroviral therapies have been provided at low costs to treat HIV positive patients. Pregnant women who test positive for HIV are monitored strictly to prevent mother-to-child transmission of the infection. Other remedial measures have also been implemented to curb HIV/AIDS in these countries.
How Does Cdc Know The Number Of People Living With Hiv If Some Of Those People Are Unaware Of Their Status
CDC estimates the number of people living with HIV by using a scientific model. This model helps CDC estimate the number of new HIV infections and how many people are infected but dont know it. HIV prevalence is the number of people living with HIV infection at a given time, such as at the end of a given year. More information on HIV prevalence.
You May Like: Yeast Infection Clear On Its Own
Hiv Treatment And Antiretroviral Therapy
HIV can be controlled and treatedthough not fully curedthrough the use of antiretroviral therapy medicines, which can keep patients healthy for many years by reducing the amount of HIV present in the body. ART both helps slow the progression of the virus and also reduces the chances of transmitting the virus to other people. ART is typically taken as a combination of three or more medications, which can sometimes be combined into one pill.
Patients whose viral loads drop to fewer than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood are said to have entered viral suppression or viral load suppression. Some even achieve an HIV level so low it is unmeasurable via current tests. This is classified as an undetectable viral load and is the ideal condition for HIV patients.Approximatley 72% of the total population of those diagnosed with HIV are being treated with ART. Testing and treatment coverage of HIV has dramatically improved around the world. That said, poverty, gender inequality, and HIV stigma and discrimination are major barriers to HIV prevention and treatment in many countries.
Worldwide Rates And Yearly Shifts
HIV diagnoses and mortality rates have continually decreased over the past decade. This is due to continuing public health efforts in HIV prevention, early recognition, and treatment. However, progress has been unequal among and within countries. Also, the pace of decline has varied widely by age, sex, and religion.
The disease burden of HIV remains entirely too high given the advances made in HIV screening and treatment.
Recent data have shown that there were about 1.7 million new HIV diagnoses in 2019, nearly 5,000 new diagnoses per day. This highlights the need for continued and sustained efforts.
In 2020, 37.7 million people globally were living with HIV, down from 39 million in 2019. HIV is now slightly more common in women than men53% of all people living with HIV worldwide are women and girls.
Black women, both cis and trans, are disproportionately affected by HIV and account for about 60% of all new infections among women. Black women also carry the largest burden of HIV globally.
But the most troubling statistic is the number of preventable deaths caused by HIV/AIDS. In 2020, 680,000 people died from AIDS-related illnessesa number far too high given the prevention and treatment options that exist.
You May Like: Does Cephalexin Treat Ear Infections
How Common Is Hiv
The global AIDS pandemic remains one of the greatest healthcare crises in human history. At the height of the epidemic in the United States in 1985, around 130,000 new infections were reported. By 2010, that number dropped to approximately 50,000 due largely to advances in HIV therapy.
While there continues to be a decline in the annual HIV infection rate, it is not as steep as some might have imagined. The causes of this are many.
According to updated statistics from the Department of Health and Human Services :
- Around 1.2 million people in the United States are currently living with HIV.
- In 2020, an estimated 30,635 new HIV infections occurred.
How Does Hiv Affect Different Groups Of People
There are different ways to answer this question.
In 2020, male-to-male sexual contactdaccounted for68% of all new HIV diagnoses in the United States and dependent areas.In the same year, heterosexual contact accounted for 22% of all HIV diagnoses.
Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state and local jurisdictions.NOTE: Does not include other and perinatal transmission categories.* Among people aged 13 and older.
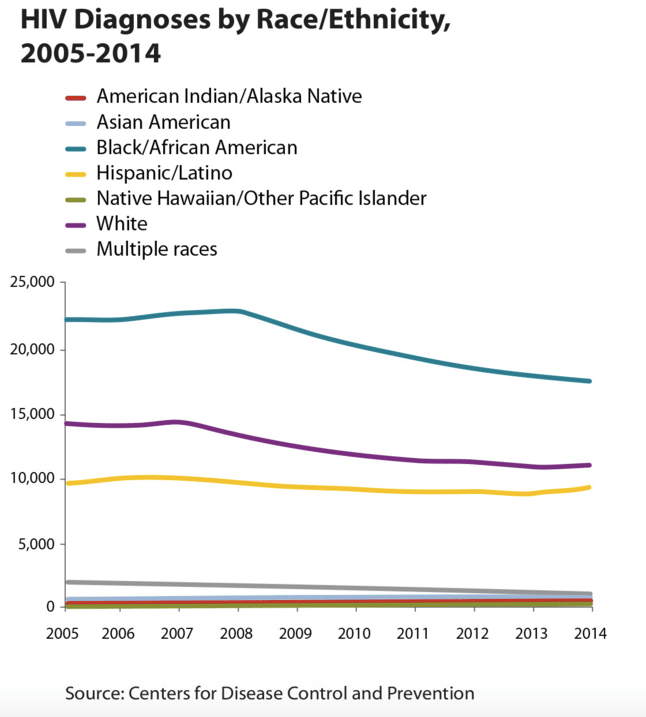
If we look at HIV diagnoses by race and ethnicity, we see that Black/African American people are most affected by HIV. In 2020, Black/African American people accounted for 42% of all new HIV diagnoses. Additionally, Hispanic/Latino people are also strongly affected. They accounted for 27% of all new HIV diagnoses.
Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state and local jurisdictions.* Among people aged 13 and older.Black refers to people having origins in any of the Black racial groups of Africa. African American is a term often used for people of African descent with ancestry in North America.Hispanic/Latino people can be of any race.
The most affected subpopulation is Black/African American gay and bisexual men.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Cure A Bladder Infection
Us Response To The Global Epidemic
The U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief is the U.S. Governments response to the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and represents the largest commitment by any nation to address a single disease in history. Through PEPFAR, the U.S. has supported a world safer and more secure from infectious disease threats. It has demonstrably strengthened the global capacity to prevent, detect, and respond to new and existing riskswhich ultimately enhances global health security and protects Americas borders. Among other global results, PEPFAR provided HIV testing services for more than 50 million people in Fiscal Year 2021 and, as of September 30, 2021, supported lifesaving ART for nearly 18.96 million men, women, and children. PEPFAR also enabled 2.8 million babies to be born HIV-free to parents living with HIV.
In addition, the National Institutes of Health represents the largest public investment in HIV/AIDS research in the world. NIH is engaged in research around the globe to understand, diagnose, treat, and prevent HIV infection and its many associated conditions, and to find a cure.
Is The World Making Progress In Its Fight Against Hiv/aids
The 1990s saw a substantial increase in the number of people infected with HIV and dying of AIDS.
Between 1996 and 2001 more than 3 million people were infected with HIV every year. Since then the number of new infections began to decline and in 2019 it was reduced to below 2 million. The lowest number of new infections since 1990.
The number of AIDS-related deaths increased throughout the 1990s and reached a peak in 2004, 2005 when in both years close to 2 million people died. Since then the annual number of deaths from AIDS declined as well and was since halved. 2016 was the first year since the peak in which fewer than 1 million people died from AIDS.
The chart also shows the continuing increase in the number of people living with HIV. The rate of increase has slowed down compared to the 1990s, but the absolute number is at the highest ever with more than 36 million people globally living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Antibiotics For Ear Infection
A Major Health Crisis
Since the early 1980s, when the first cases were diagnosed in the USA, an estimated 78 million people have been infected by HIV and 39 million people have died of AIDS and AIDS-related illnesses. There are currently 36.9 million cases worldwide, according to UNAIDS.
Every year the number of people living with HIV increases, a fact that can be interpreted both positively more people have access to antiretroviral treatment and negatively the HIV/AIDS pandemic continues.
Breakthroughs but no stop to the rise in new infections
The availability of triple antiretroviral therapy in the mid-1990s marked the transition from fatal disease to chronic infection. But despite the enormous progress achieved with HIV, global efforts to prevent and control new infections continue to encounter obstacles.
Worrying numbers of people contract the virus each year: 2 million people were infected in 2014 and 1.2 million people die from HIV every year.
A global health problem
Some 80% of people living with the virus areconcentrated in just 20 countries: South Africa, Nigeria, India, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Tanzania, Uganda, Kenya, the USA, Russia, Zambia, Malawi, China, Brazil, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Thailand and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
However, HIV/AIDS continues to be a global health problem. The rate of new infections and deaths has seen an increase in recent years in some regions of Asia, the Pacific, the Middle East and North Africa.
The Global Distribution Of Deaths From Hiv/aids
In some countries HIV/AIDS is the cause of more than a quarter of all deaths
Globally, 1.5% of deaths were caused by HIV/AIDS in 2019.
This share is high, but masks the wide variations in the toll of HIV/AIDS across the world. In some countries, this share was much higher.In the interactive map we see the share of deaths which resulted from HIV/AIDS across the world. Across most regions the share was low: across Europe, for example, it accounted for less than 0.1% of deaths.
But across some countries focused primarily in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa the share is very high. More than 1-in-4 of deaths in South Africa were caused by HIV/AIDS in 2019. The share was also very high across Botswana Mozambique Namibia Zambia Kenya and Congo .
Death rates are high across Sub-Saharan Africa
The large health burden of HIV/AIDS across Sub-Saharan Africa is also reflected in death rates. Death rates measure the number of deaths from HIV/AIDS per 100,000 individuals in a country or region.
In the interactive map we see the distribution of death rates across the world. Most countries have a rate of less than 10 deaths per 100,000 often much lower, below 5 per 100,000. Across Europe the death rate is less than one per 100,000.
Across Sub-Saharan Africa the rates are much higher. Most countries in the South of the region had rates greater than 100 per 100,000. In South Africa and Mozambique, it was over 200 per 100,000.
Read Also: Will Azithromycin Treat Yeast Infection
Countries With The Highest Rates Of Hiv/aids
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that weakens the human immune system, sometimes leading to AIDS. If detected early, HIV can be managed to prevent it from progressing to the final stage of AIDS. HIV attacks CD4 cells exposing the infected person to opportunistic infections. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and medical care are essential factors to effective management and control of AIDS which has no permanent cure. While HIV is majorly a sexually transmitted disease, the virus can be transmitted through blood transfusion and during birth or breastfeeding, as well as through a few other means.
Ensuring Equal Access To Treatment
A number of challenges contribute to the global HIV disparities and unequal access to testing and treatment, including:
- Lack of access to healthcare
- Higher rates of some STIs
- Smaller sexual networks
- Lack of awareness of HIV status
- Little or no education about HIV prevention
- Cultural stigma
The number of people who need antiretroviral therapy is much greater than the resources that are available to help them in many countries. Therefore, additional investments are needed to properly identify and prioritize those who need critical lifesaving treatment.
Public health organizations around the world are encouraged to establish policies that clearly and objectively identify and prioritize groups disproportionately impacted when making healthcare decisions. Policies should ensure access for women and the most vulnerable, poor, and marginalized populations.
Recent advances in treatment technologies mean that ART can be provided successfully in settings in which basic health services are weak. However, decision-makers in each country need to carefully design policies that address financial and other barriers and give access to the poor and marginalized while supporting essential health services.
These efforts on the community, national, and federal levels must be coordinated so that the cost of care is offset for underserved populations.
Don’t Miss: Can I Get A Yeast Infection From Sex
Key Points: Hiv Incidence
- HIV incidence declined 8% from 2015 to 2019. In 2019, the estimated number of HIV infections in the U.S. was 34,800 and the rate was 12.6 .
- , the annual number of HIV infections in 2019, compared with 2015, decreased among persons aged 1324 and persons aged 45-54, but remained stable among all other age groups. In 2019, the rate was highest for persons aged 25-34 , followed by the rate for persons aged 35-44 .
- , the annual number of HIV infections in 2019, compared with 2015, decreased among persons of multiple races, but remained stable for persons of all other races/ethnicities. In 2019, the highest rate was for Blacks/African American persons , followed by Hispanic/Latino persons and persons of multiple races .
- , the annual number of new HIV infections in 2019, as compared to 2015, decreased among males, but remained stable among females. In 2019, the rate for males was 5 times the rate for females .
- , the annual number of HIV infections in 2019, compared with 2015, decreased among males with transmission attributed to male-to-male sexual contact, but remained stable among all other transmission categories. In 2019, the largest percentages of HIV infections were attributed to male-to-male sexual contact
For more details on recent HIV incidence statistics, see Estimated HIV Incidence and Prevalence in the United States, 2015-2019.
The Global Hiv Epidemic: What The Pathologist Needs To Know
1Hubert Department of Global Health, Rollins School of Public Health of Emory University
2Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine
3Emory Center for AIDS Research
Source: .
Trends in new infections and mortality over time reflect the impact of prevention and care services. Primarily because of scale up in antiretroviral treatment, mortality from HIV/AIDS has decreased by 45% since its peak in 2005 but still, with 1.1 million people dying of AIDS in 2015 . However, HIV/AIDS remains the leading cause of death worldwide and the number one cause of death in Sub-Saharan Africa. The reduction in deaths since 2010 has been greater among women than men , reflecting higher treatment coverage for women. There were approximately 2.1 million new infections in 2015, which is a 35% decline in the number of new infections over the past decade however, the number of new infections is now rising in some regions. Because of a steeper decline in mortality than in new infections, the number of people living with HIV continues to raise globally. Besides HIV prevalence, what determines the burden of HIV in a country is the size of its population. India, with an HIV prevalence of only 0.3% but a population of 1.31 billion, has 2.1 million people living with HIV, which is the third largest number of any country behind South Africa and Nigeria.
Read Also: French Bulldog Yeast Infection Treatment