Otitis Media With Effusion
Otitis media with effusion , also known as serous or secretory otitis media , is an ear infection in which fluid is present in the middle ear and swelling develops in the inner ear. The fluid is generally not troublesome and goes away on its own in 4 to 6 weeks. In case, the fluid does not drain on its own within this time frame, the patient would need to be treated with antibiotics. This type of ear infection happens as a result of cold, sore throat or an upper respiratory infection. OEM tends to develop in kids aged between 6 months to 3 years. Boys are more prone to this type of ear infection than girls and this ear condition commonly occurs during the fall and winter months.
Fluid Buildup And Hearing Problems
Fluid behind the eardrum after an ear infection is normal. And in most children, the fluid clears up within 3 months without treatment. If your child has fluid buildup without infection, you may try watchful waiting.
Have your childs hearing tested if the fluid lasts longer than 3 months. If hearing is normal, you may choose to keep watching your child without treatment.
If a child has fluid behind the eardrum for more than 3 months and has significant hearing problems, then treatment is needed. Sometimes short-term hearing loss occurs, which is especially a concern in children ages 2 and younger. Normal hearing is very important when young children are learning to talk.
If your child is younger than 2, your doctor may not wait 3 months to start treatment. Hearing problems at this age could affect your childs speaking ability. This is also why children in this age group are closely watched when they have ear infections.
If there is a hearing problem, your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to keep the fluid in the ear from getting infected. The doctor might also suggest placing tubes in the ears to drain the fluid and improve hearing.
What Are The Types Of Middle
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
-
Acute otitis media. This middle-ear infection occurs suddenly. It causes swelling and redness. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear. You can have a fever and ear pain.
-
Otitis media with effusion. Fluid and mucus build up in the middle ear after the infection goes away. You may feel like your middle ear is full. This can continue for months and may affect your hearing.
-
Chronic otitis media with effusion. Fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time. Or it builds up again and again, even though there is no infection. This type of middle-ear infection may be hard to treat. It may also affect your hearing.
You May Like: Describe The Relationship Between An Hiv Infection And Aids
How Do Adults Get Ear Infections
Adults with weakened immune systems and certain medical conditions are more likely to get ear infections. For example, if you have diabetes, it can cause an inflammatory response throughout your body including your middle and inner ear. Having skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis can increase the chance that you get an outer ear infection.
Home Remedies For Ear Pain
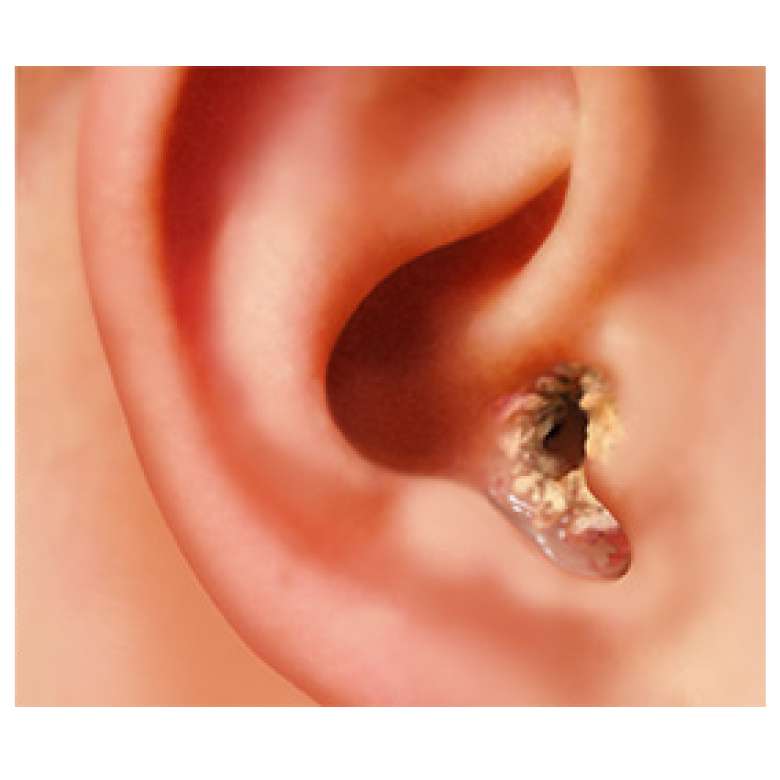
Before antibiotics, parents used home remedies to treat the pain of ear infections. Now, with current concern over antibiotic overuse, many of these simple remedies are again popular:
- Parents can press a warm water bottle or warm bag of salt against the ear. Such old-fashioned remedies may help to ease ear pain.
- Due to the high risk of burns, ear candles should not be used to remove wax from ears. These candles are not safe or effective for treatment of ear infections or other ear conditions.
- Researchers are studying the protective value of probiotics especially lactobacilli strains such as acidophilus. But it is important not to give your child any herbal remedies or dietary supplements without consulting with the pediatrician.
Read Also: Cvs Minute Clinic Ear Infection Cost
How To Use Ear Drops
Prior to using ear drops, you should always read the instructions provided to you with your prescription. You can also speak to your pharmacist or doctor for advice on using them. The following instructions will help you use ear drops correctly.
For adults:
- Lie down on a flat surface with a folded towel beneath your head and the affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Pull your earlobe up to straighten out the ear canal.
- Administer the appropriate number of drops into the ear.
- Push the ear flap gently to help ease the drops into the ear.
- Remain in this position for up to two minutes to ensure that the ear canal is fully coated with medicine.
For children:
- Have the child lie on the floor or bed with a towel beneath their head and their affected ear facing the ceiling.
- Hold their head still if they are squirming or fidgeting.
- Pull the earlobe out and down to straighten their ear canal..
- Administer the recommended number of drops
- Press on their ear flap or place a cotton ball gently into the ear and let it remain in position for several minutes to ensure that the medication coats the inside of their ear.
The process for infants is similar to children, but you can also cradle your infant while you administer the drops in an appropriate position that allows the medication to go into their ear properly.
Response To Antibiotic Treatment
Your child’s symptoms, including fever, should improve within 48 to 72 hours after beginning antibiotics. If symptoms do not improve it may be because a virus is present or the bacteria causing the ear infection is resistant to the prescribed antibiotic. A different antibiotic may be needed.
In some children whose treatment is successful, fluid will still remain in the middle ear for weeks or months, even after the infection has resolved. During that period, children may have some hearing problems, but eventually the fluid almost always drains away.
If your child fails to improve and middle ear fluid remains, your doctor may recommend consultation with an ear, nose, and throat specialist . This specialist may perform a tympanocentesis procedure in which fluid is drawn from the ear and examined for specific bacterial organisms. But this is reserved for severe cases.
You May Like: Does Zpack Cause Yeast Infection
Symptoms Of Acute Otitis Media
Ear pain is the most common symptom of ear infections. The ear pain associated with acute otitis media usually comes on very suddenly.
Babies and young children who haven’t yet learned to speak may express ear pain in various ways including:
- Pulling, tugging, rubbing, or holding the ear
- Excessive crying, especially when feeding
- Irritability, fussiness, and other changes in behavior
- Difficulty sleeping
Other symptoms associated with ear infections include:
- Fluid discharge from ear
- Cold symptoms such as nasal congestion, runny nose, or coughing
If the ear infection is severe, the tympanic membrane may rupture, causing the pus to drain from the ear. Pus in the ear may cause hearing loss in some children.
How To Know If You Have Earwax Buildup
Do you feel mild discomfort in your ear? There are some signs that can reveal if you have a buildup of earwax . It is advisable to clean your ears so you can look after your well-being and your hearing. Wax is a natural bodily mechanism that is created to keep your ear canals protected and to prevent any infection that may penetrate this area. However, when it is created in abundance, you can experience some discomfort which is easy to treat. In this OneHowTo article, we will explain how to know if you have earwax buildup by telling you some of this conditions most obvious symptoms so you can help them to clean naturally.
In order to know if you have earwax buildup, it is essential that you familiarize yourself with the symptoms that may occur in relation to this condition. The most common symptoms include:
- Hearing loss: Wax buildup can produce a sensation of a plug in the ear and consequently, a loss in hearing. This usually occurs suddenly and not gradually, i.e. from one day to the next, you get up feeling like you are deaf and are unable to hear clearly.
- Hearing your own voice: It is also common for people with a plug of earwax to hear their own voice echoing when they speak.
- Pain in the ear area: It is also possible that an accumulation of wax can produce some pain in the area which is usually mild but can become worse if not treated immediately. So if you feel any discomfort, see your doctor so they can remove the wax and restore your health.
Read Also: Blood Test For H Pylori Infection
So We Should Not Insert Cotton Swabs Into Our Ears To Try To Clean Them Or Remove Earwax Right
Dr. Wang: Correct. Use of Q-Tips can cause not only outer ear infections, but also trauma of the ear canal or eardrum, which can affect hearing and cause other types of infection and ear pain. Also, part of the swab can break off, leaving a foreign body in your ear that needs to be removed. It’s a common reason for ER visits, actually. If you feel you have a buildup of ear wax, I recommend applying a tissue or soft thin cloth to your finger and wiping gently around the entrance to the ear. There are also over-the-counter ear wax removal kits from Debrox® that are safe to use, when used as directed.
Did You Know Different Types Of Ear Infections
Did you know that there are different types of ear infections? Each have their own symptoms and treatments. Take a look below to explore the inner ear.
Acute Otitis Media
Acute Otitis Media is what is commonly called an ear infection. It is the collection of fluid behind the eardrum that has become infected by bacteria. Common symptoms include: pain, fever, fussiness, and hearing loss. Severe infections can cause rupture of the eardrum resulting in drainage from the ear canal. Infections often respond well to oral antibiotics. Patients who have had multiple episodes of AOM are often candidates for ear tube placement. This procedure drastically reduces the severity and frequency of infections. Infections can still occur after placement of ear tubes, but are much less painful, and can be easily treated with placement of antibiotic ear drops directly into the ear canal.
Serous Otitis Media
Serous Otitis Media is more commonly known as ear fluid. This condition is often a result of AOM. After an infection is treated, non-infected fluid can persist behind the eardrum. Often, there is hearing loss as a result of the fluid. Patients may feel a pressure in the ear, but usually no pain. Fluid that persists for longer than 3 months is often treated with placement of ear tubes. It is important to identify this condition in children as hearing loss can sometimes result in speech delay.
Chronic Otitis Media
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Health Topics:
Recommended Reading: Can Men Get Yeast Infections From Women
What Are The Causes Of Labyrinthitis
Viral infectionsâViral infections of the inner ear or activation of a virus that is has hibernated within nerve endings are thought to be the most common cause of labyrinthitis. The specific virus that causes this is usually unknown in most cases. A unique type of labyrinthitis may be caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus , called Ramsay Hunt syndrome, or herpes zoster oticus. Patients may experience ear pain, facial weakness, and blisters around the ear, ear canal, and/or eardrum in addition to hearing loss and dizziness.
Bacterial infectionâA bacterial infection of the middle ear can spread to the inner ear and cause bacterial labyrinthitis. Children with inner ear deformities are at a higher risk for bacterial labyrinthitis either from a middle ear infection or from the spread of bacterial meningitis to the inner ear. Severe bacterial labyrinthitis can occur with ear pain, ear infection, drainage of pus from the ear, fevers, or chills. Patients may require hospitalization. This type of infection has a higher risk for permanent hearing loss and may also lead to labyrinthitis ossificans, where there is bone formation in the inner ear after the infection.
AutoimmuneâAutoimmune labyrinthitis is a rare cause of labyrinthitis and may come and go. It is often associated with other autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune disorders.
Other Types Of Ear Infections
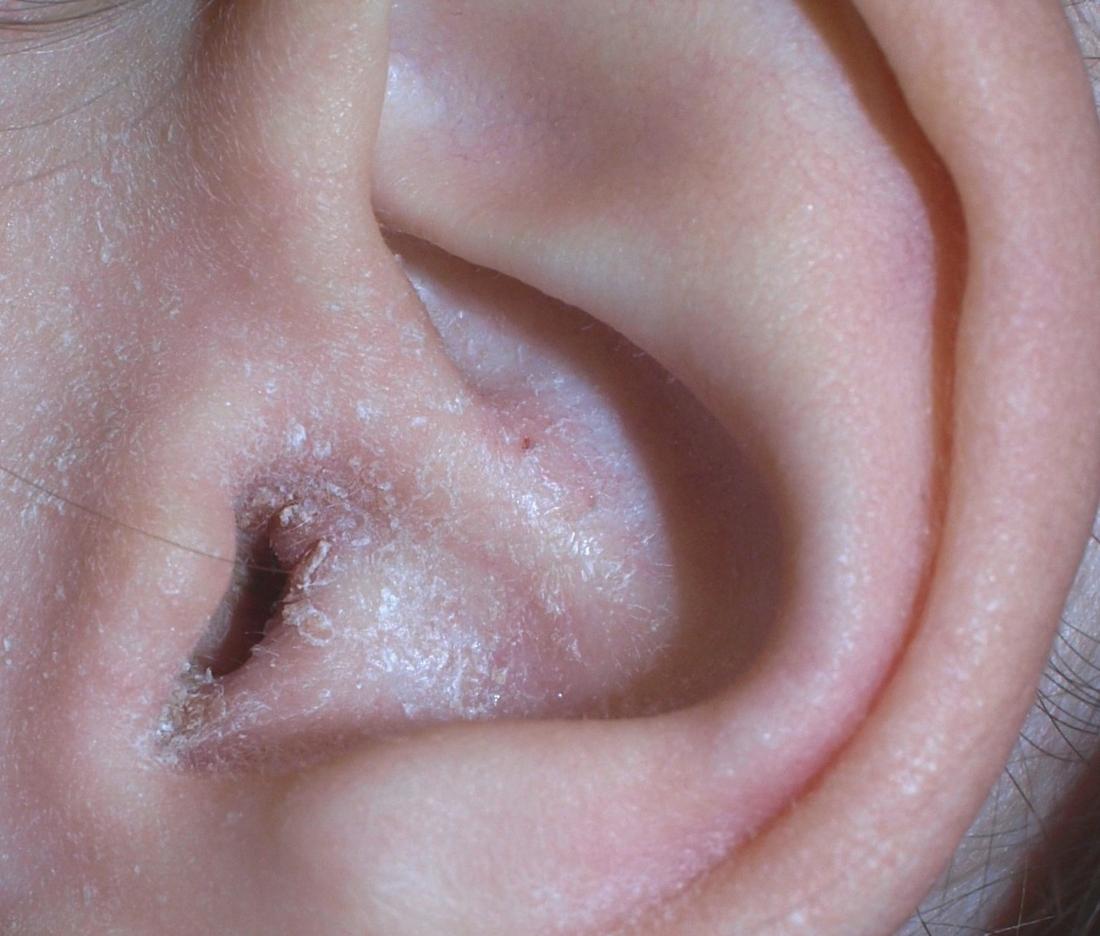
Swimmer’s Ear
Acute otitis externa is an inflammation or infection of the outer ear and ear canal. It can be triggered by water that gets trapped in the ear. The trapped water can cause bacteria and fungi to breed. Otitis externa can also be precipitated by overly aggressively scratching or cleaning of ears or when an object gets stuck in the ears.
Otitis externa is generally treated with topical antibiotics, which will cure the infection and help relieve pain. With eardrops, most cases will clear up within 2 to 3 days. If the condition persists, the doctor will need to evaluate and rule out other possible causes.
You May Like: Yeast Infection After Bv Treatment
Why Do Kids Get Ear Infections
Kids get ear infections more than adults do for several reasons:
- Their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes let bacteria and viruses find their way into the middle ear more easily. The tubes are also narrower, so more likely to get blocked.
- Their adenoids, gland-like structures at the back of the throat, are larger and can interfere with the opening of the eustachian tubes.
Other things that can put kids at risk include secondhand smoke, bottle-feeding, and being around other kids in childcare. Ear infections are more common in boys than girls.
Ear infections are not contagious, but the colds that sometimes cause them can be. Infections are common during winter weather, when many people get upper respiratory tract infections or colds .
What Is An Ear Infection
There are different types of ear infections. Middle ear infection is an infection in the middle ear.
Another condition that affects the middle ear is called otitis media with effusion. This condition occurs when fluid builds up in the middle ear without causing an infection. Otitis media with effusion does not cause fever, ear pain, or pus build-up in the middle ear.
Swimmers ear is an infection in the outer ear canal. Swimmers Ear is different from a middle ear infection. For more information, visit Swimmers Ear .
Also Check: Cdc Nursing Home Infection Preventionist Training
Can Ear Infections Affect Hearing
Fluid buildup in the middle ear also blocks sound, which can lead to temporary hearing problems. Kids having a problem might:
- not respond to soft sounds
- need to turn up the TV or radio
- seem inattentive at school
In kids who have otitis media with effusion, the fluid behind the eardrum can block sound, so mild temporary hearing loss can happen, but might not be obvious.
A child whose eardrum has ruptured might have ringing or buzzing in the ear and not hear as well as usual.
What Does An Ear Infection Feel Like
Symptoms depend on which part of your ear is infected and can include:
- ear pain or itch
- discharge from your ear
- redness or swelling of your ear
Babies and small children might:
- pull or rub their ear
- have a high temperature
- have redness around the ear
- be restless or irritable
- not respond to noises that would normally attract their attention
Don’t Miss: What To Do If Malware Infects Your Computer
The Role Of Eustachian Tubes
The eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. The ends of these tubes open and close to regulate air pressure in the middle ear, resupply air to this area, and drain normal secretions.
A respiratory infection or allergy can block the eustachian tubes, causing a buildup of fluids in the middle ear. Infection can occur if this fluid becomes infected bacterially.
The eustachian tubes of young children are smaller and more horizontal than in older children and adults. This means that fluid is more likely to collect in the tubes rather than drain away, increasing the risk of an ear infection.
Risk Factors For Ear Diseases
While these types of ear diseases can affect anyone, several factors might put you at a higher risk.
- Family history: If your relatives have a history of frequent ear infections and disease, you may be prone to experience similar symptoms.
- Allergies: Frequent colds and stuffy noses can lead to fluid buildup, increasing your odds of developing ear inflammation and infection.
- Preexisting medical conditions: Individuals with underlying medical conditions such as compromised immune systems or craniofacial abnormalities may experience a higher rate of ear infection and disease.
- Smoking: Exposure to cigarette smoke can cause fluid buildup in the middle ear, potentially affecting hearing loss and leading to recurring ear infections.
If one or more of these risk factors applies to you, an ear disease is not inevitable. However, youll want to pay closer attention to any ear disease signs and symptoms and seek care quickly.
You May Like: Urine Infection Not Getting Better With Antibiotics
What Should I Do About An Ear Infection
If its only been a couple of days and the only symptom has been ear pain, you dont need to head to the doctor right away. Because many ear infections go away on their own, its likely your doctor will want to wait and see how the symptoms improve before providing prescription medicines.
In the meantime, focus on getting lots of rest. Sleeping strengthens the immune system and helps the body fight off infections and other sickness.
If the ear infection is causing pain or discomfort, there are treatments for ear infections you can try at home. One of the simplest is using a warm compress to dull the pain. Just soak a washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess water and then hold it against the infected ear for up to 20 minutes. If it helps, reapply the compress throughout the day.
If your child is over 3 months old, an over-the-counter medication like acetaminophen can also help with the pain just make sure youre using an age-appropriate dose. If you have questions, contact your doctor or nurse line.