Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome
Patients beginning ART sometimes deteriorate clinically, even though HIV levels in their blood are suppressed and their CD4 count increases, because of an immune reaction to subclinical opportunistic infections or to residual microbial antigens after successful treatment of opportunistic infections. IRIS usually occurs in the first months of treatment but is occasionally delayed. IRIS can complicate virtually any opportunistic infection and even tumors but is usually self-limited or responds to brief regimens of corticosteroids.
IRIS has two forms:
-
Paradoxical IRIS, which refers to worsening symptoms due to a previously diagnosed infection
-
Unmasked IRIS, which refers to the first appearance of symptoms of an infection not previously diagnosed
Paradoxical IRIS typically occurs during the first few months of treatment and usually resolves on its own. If it does not, corticosteroids, given for a short time, are often effective. Paradoxical IRIS is more likely to cause symptoms and symptoms are more likely to be severe when ART is started soon after treatment of an opportunistic infection is started. Thus, for some opportunistic infections, ART is delayed until treatment of the opportunistic infection has reduced or eliminated the infection.
Determining whether clinical deterioration is caused by treatment failure, IRIS, or both requires assessment of the persistence of active infections with cultures and can be difficult.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv And Aids
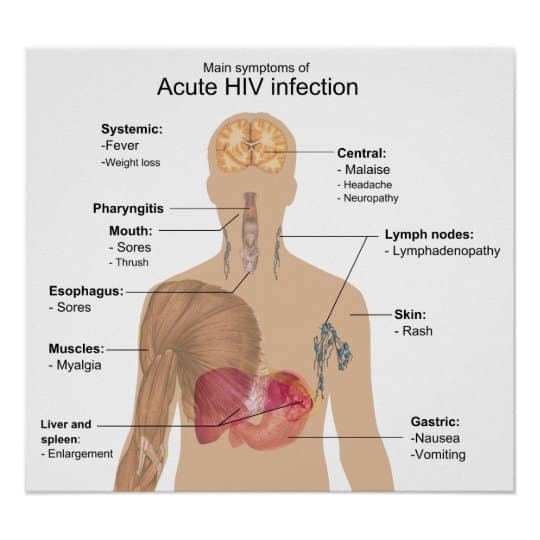
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, some people may have flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, or rash. The symptoms may last for a few days to several weeks. Other possible symptoms of HIV include night sweats, muscle aches, sore throat, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and mouth ulcers. Having these symptoms do not mean you have HIV. Other illnesses can cause the same symptoms. Some people may not feel sick during early HIV infection . During this earliest stage of HIV infection, the virus multiplies rapidly. After the initial stage of infection, HIV continues to multiply but at very low levels.
More severe symptoms of HIV infection, such as a badly damaged immune system and signs of opportunistic infections, generally do not appear for many years until HIV has advanced to AIDS. People with AIDS have badly damaged immune systems that make them prone to opportunistic infections.
Without treatment with HIV medicines, HIV infection usually advances to AIDS in 10 years or longer, though it may advance faster in some people.
HIV transmission is possible at any stage of HIV infectioneven if a person with HIV has no symptoms of HIV.
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
Recommended Reading: Infection Control And Epidemiology Certification
Interruption Of Antiretroviral Therapy
Interruption of ART is usually safe if all drugs are stopped simultaneously, but levels of slowly metabolized drugs may remain high and thus increase the risk of resistance. Interruption may be necessary if intervening illnesses require treatment or if drug toxicity is intolerable or needs to be evaluated. After interruption to determine which drug is responsible for toxicity, clinicians can safely restart most drugs as monotherapy for up to a few days. NOTE: The most important exception is abacavir patients who had fever or rash during previous exposure to abacavir may develop severe, potentially fatal hypersensitivity reactions with reexposure. Risk of an adverse reaction to abacavir is 100-fold higher in patients with HLA-B*57:01, which can be detected by genetic testing.
Prognosis For Hiv Infection
Risk of AIDS, death, or both is predicted by the
-
CD4 count in the short term
-
Plasma HIV RNA level in the longer term
For every 3-fold increase in viral load, mortality over the next 2 to 3 years increases about 50%. HIV-associated morbidity and mortality vary by the CD4 count, with the most deaths from HIV-related causes occurring at counts of & lt 50/mcL. However, with effective treatment, the HIV RNA level decreases to undetectable levels, CD4 counts often increase dramatically, and risk of illness and death falls but remains higher than that for age-matched populations not infected with HIV infection results from 1 of 2 similar retroviruses that destroy CD4+ lymphocytes and impair cell-mediated immunity, increasing risk of certain… read more ).
Another, less well-understood prognostic factor is the level of immune activation as determined by evaluating the expression of activation markers on CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes. Activation, which may be caused by leakage of bacteria across the HIV-damaged colonic mucosa, is a strong prognostic predictor but is not used clinically because this test is not widely available and antiretroviral therapy changes the prognosis, making this test less important.
Recommended Reading: Can A Urinary Tract Infection Affect Your Eyes
Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
You May Like: Ways To Cure Bladder Infection
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Am I at high risk for HIV?
- What can I do to reduce my risk of HIV?
- How can I make sure I take my medications correctly?
- What can I do to protect myself from other illnesses?
- How can prevent the spread of HIV?
- What do my test results mean?
- What do my blood counts mean?
- What vaccinations should I get?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Treatments have come a long way since the height of the AIDS epidemic. You have the best chance of living a long life if youre diagnosed early and are able to get on and stick with ART medications. People living with HIV today are able to work, have active social lives and families, and pursue fulfilling relationships. In fact, this can have a positive impact on your well-being.
While weve come a long way with treatments, unfortunately, social stigmas around HIV still persist. In addition to the feelings of fear and uncertainty a new diagnosis can bring, you may wonder how those around you will respond. If youre hesitant to get tested or get treatment, or if you just arent sure what your next steps are, you can reach out to a community organization that specializes in HIV. Remember that you are deserving of support, compassion and high-quality healthcare.
Hiv Effects On The Nervous System
About half of people with AIDS have nerve problems related to the virus. Infection or inflammation can damage your spinal cord or brain and keep your nerve cells from working the way they should. Some medications can also affect your nervous system.
Brain
Inflammation in your brain and spinal cord can lead to confusion and other thinking problems as well as weakness, headaches, seizures, and balance problems.
When AIDS is far along, you might get dementia and have problems remembering things.
Having HIV can also affect your mental health. Many people living with it have depression or anxiety. Mental health professionals and support groups can help you work through your concerns and manage your life with HIV.
Nerves
The opportunistic infection cytomegalovirus can attack your nerves, making it hard for you to control your arms and legs or your bladder.
Itâs common for tiny holes to form in spinal fibers when people with AIDS donât get treatment. This is called vacuolar myelopathy and causes trouble walking.
HIV or the drugs that treat it can also damage nerves all over your body, causing neuropathy. You might have pain, numbness, weakness, burning, stiffness, or tingling.
Antiretroviral therapy to treat HIV can lower your risk of getting these conditions or complications. If a medication is causing the problems, your doctor might switch you to a different one.
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Clear On Its Own
The Effects Of Hiv On The Body
Most people are likely familiar with HIV, but they may not know how it can affect the body.
HIV destroys CD4 cells , which are critical to the immune system. CD4 cells are responsible for keeping people healthy and protecting them from common diseases and infections.
As HIV gradually weakens the bodys natural defenses, signs and symptoms will occur.
Find out what happens when the virus enters the body and interrupts its systems.
Once HIV enters the body, it launches a direct attack on the immune system.
How quickly the virus progresses will vary by:
- how quickly theyre diagnosed
The timing of their treatment can make a huge difference as well.
HIV targets the types of cells that would normally fight off an invader such as HIV. As the virus replicates, it damages or destroys the infected CD4 cell and produces more virus to infect more CD4 cells.
Without treatment, this cycle can continue until the immune system is badly compromised, leaving a person at risk for serious illnesses and infections.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is the final stage of HIV. At this stage, the immune system is severely weakened, and the risk of contracting opportunistic infections is much greater.
However, not everyone with HIV will go on to develop AIDS. The earlier a person receives treatment, the better their outcome will be.
Early on, HIV symptoms may be mild enough to be dismissed.
Hiv Symptoms In Men: Is There A Difference
Symptoms of HIV vary from person to person, but theyre similar in men and women. These symptoms can come and go or get progressively worse.
If a person has been exposed to HIV, they may also have been exposed to other sexually transmitted infections . These include:
- human papillomavirus , which can cause genital warts and lead to cervical cancer
While not related to HIV symptoms, another risk for women with HIV is that the virus can be transmitted to a baby during pregnancy. However, antiretroviral therapy is considered safe during pregnancy.
Women who are treated with antiretroviral therapy are at very low risk for transmitting HIV to their baby during pregnancy and delivery. Breastfeeding is also affected in women with HIV. The virus can be transferred to a baby through breast milk.
In the United States and other settings where formula is accessible and safe, its recommended that women with HIV not breastfeed their babies. For these women, use of formula is encouraged.
Options besides formula include pasteurized banked human milk.
For women who may have been exposed to HIV, its important to know what symptoms to look for.
AIDS refers to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. With this condition, the immune system is weakened due to HIV thats typically gone untreated for many years.
If HIV is found and treated early with antiretroviral therapy, a person will usually not develop AIDS.
Symptoms of AIDS can include:
- recurrent fever
HIV does NOT transfer through:
Read Also: Which Antibiotic Is Best For Kidney Infection
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for a reduced cost or for free.
Ses Impacts The Lives Of People With Hiv/aids
Both domestically and internationally, HIV is a disease that is embedded in social and economic inequity , as it affects those of lower socioeconomic status and impoverished neighborhoods at a disproportionately high rate. Research on SES and HIV/AIDS suggests that a persons socioeconomic standing may affect his or her likelihood of contracting HIV and developing AIDS. Furthermore, SES is a key factor in determining the quality of life for individuals after they are affected by the virus.
SES Affects HIV Infection
A lack of socioeconomic resources is linked to the practice of riskier health behaviors, which can lead to the contraction of HIV. These behaviors include substance use, which reduces the likelihood of using condoms .
HIV Status Affects SES
HIV status often has a negative impact on socioeconomic status by constraining an individuals ability to work and earn income.
SES Affects HIV Treatment
Get Involved
- Consider SES in your education, practice and research efforts.
- Stay up to date on legislation and policies that explore and work to eliminate socioeconomic disparities . Visit the Office on Government Relations for more details.
Recommended Reading: Does Tooth Infection Go Away
What Does Hiv Do To A Person
HIV infects white blood cells of your immune system called CD4 cells, or helper T cells. It destroys CD4 cells, causing your white blood cell count to drop. This leaves you with an immune system that cant fight off infections, even those that wouldnt normally make you sick.
HIV initially makes you feel sick with flu-like symptoms. Then it can hide in your body for a long time without causing noticeable symptoms. During that time, it slowly destroys your T-cells. When your T-cells get very low or you begin to get certain illnesses that people with healthy immune systems dont get, HIV has progressed to AIDS.
AIDS can cause rapid weight loss, extreme tiredness, mouth or genital ulcers, fevers, night sweats and skin discolorations. Other illnesses and cancers often happen in people living with AIDS and can cause additional symptoms.
Whats a retrovirus?
A retrovirus is a virus that works backward from the way human cells do. Human cells have instructions that send a message to make building blocks for your body .
Retroviruses have their instructions written on RNA. When a retrovirus invades your cells, it changes its RNA to look like your cells instructions . Then it cuts your cells DNA and inserts its instructions into them. Your cell then acts as though the virus instructions are its own.
What Is The Treatment For Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
Human immunodeficiency virus is usually treated with different combinations of antiretroviral medicines to help control HIV infection.
Early HIV infection is often treated with one of the following antiretroviral therapy regimens:
- Dolutegravir plus tenofovir and either emtricitabine or lamivudine
- Bictegravir-tenofovir alafenamide-emtricitabine
- Ritonavir-boosted darunavir plus tenofovir and either emtricitabine or lamivudine
There is no cure for acquired immune deficiency syndrome but medications are used to reduce the amount of HIV virus in the body, keep the immune system healthy, and decrease the complications of the disease that can occur.
Types of medication used to treat AIDS include:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- Protease inhibitors
Recommended Reading: Will Urgent Care Treat Yeast Infection
What Are The Factors That Affect Disease Progression
The most important factor affecting HIV progression is the ability to achieve viral suppression. Taking antiretroviral therapy regularly helps many people slow the progression of HIV and reach viral suppression.
However, a variety of factors affect HIV progression, and some people progress through the phases of HIV more quickly than others.
Factors that affect HIV progression can include:
- Ability to achieve viral suppression. Whether someone can take their antiretroviral medications and achieve viral suppression is the most important factor by far.
- Age when symptoms start. Being older can result in faster progression of HIV.
- Health before treatment. If a person had other diseases, such as tuberculosis, hepatitis C, or other sexually transmitted diseases , it can affect their overall health.
- Timing of diagnosis. Another important factor is how soon a person was diagnosed after they contracted HIV. The longer between their diagnosis and treatment, the more time the disease has to progress unchecked.
- Lifestyle. Practicing an unhealthy lifestyle, such as having a poor diet and experiencing severe stress, can cause HIV to progress more quickly.
- Genetic history. Some people seem to progress more quickly through their disease given their genetic makeup.
Some factors can delay or slow the progression of HIV. These include:
Living a healthy lifestyle and seeing a healthcare provider regularly can make a big difference in a persons overall health.