Can Ear Infections Be Prevented
Some lifestyle choices can help protect kids from ear infections:
- Breastfeed infants for at least 6 months to help to prevent the development of early episodes of ear infections. If a baby is bottle-fed, hold the baby at an angle instead of lying the child down with the bottle.
- Prevent exposure to secondhand smoke, which can increase the number and severity of ear infections.
- Parents and kids should wash their hands well and often. This is one of the most important ways to stop the spread of germs that can cause colds and, therefore, ear infections.
- Keep children’s immunizations up to date because certain vaccines can help prevent ear infections.
What Causes Middle Ear Infections
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This mean mucus can’t drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections. Read more about removing adenoids.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are relatively much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome a genetic condition that typically causes some level of learning disability and a characteristic range of physical features
Why Do Kids Get Ear Infections
Kids get ear infections more than adults do for several reasons:
- Their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes let bacteria and viruses find their way into the middle ear more easily. The tubes are also narrower, so more likely to get blocked.
- Their adenoids, gland-like structures at the back of the throat, are larger and can interfere with the opening of the eustachian tubes.
Other things that can put kids at risk include secondhand smoke, bottle-feeding, and being around other kids in childcare. Ear infections are more common in boys than girls.
Ear infections are not contagious, but the colds that sometimes cause them can be. Infections are common during winter weather, when many people get upper respiratory tract infections or colds .
Read Also: Infection Control For Healthcare Professionals
Ear Infection Hearing Loss Is Often Temporary
Hearing loss caused by an ear infection is usually temporary and subsides after treatment. Your physician may choose to treat your ear infection with antibiotics. If the antibiotics successfully treat the infection, your hearing should return to normal. If you have a history of recurrent ear infections, your physician may insert a tube in your ear drum to help the fluid drain.
Eliminating the buildup of fluid relieves the pain and pressure that often accompanies an ear infection and can prevent the eardrum from rupturing. If fluid builds up without resolution, the pressure can cause your eardrum to rupture.
A history of recurrent ear infections can also lead to tympanosclerosis, which is the thickening or scarring of the tympanic membrane. A perforated eardrum and tympanosclerosis adversely affect the mobility of the eardrum and reduce hearing acuity. If your hearing does not return to normal following treatment, your physician and hearing professional may recommend hearing aids to treat the unresolved hearing loss.
Cause Of Ear Infections
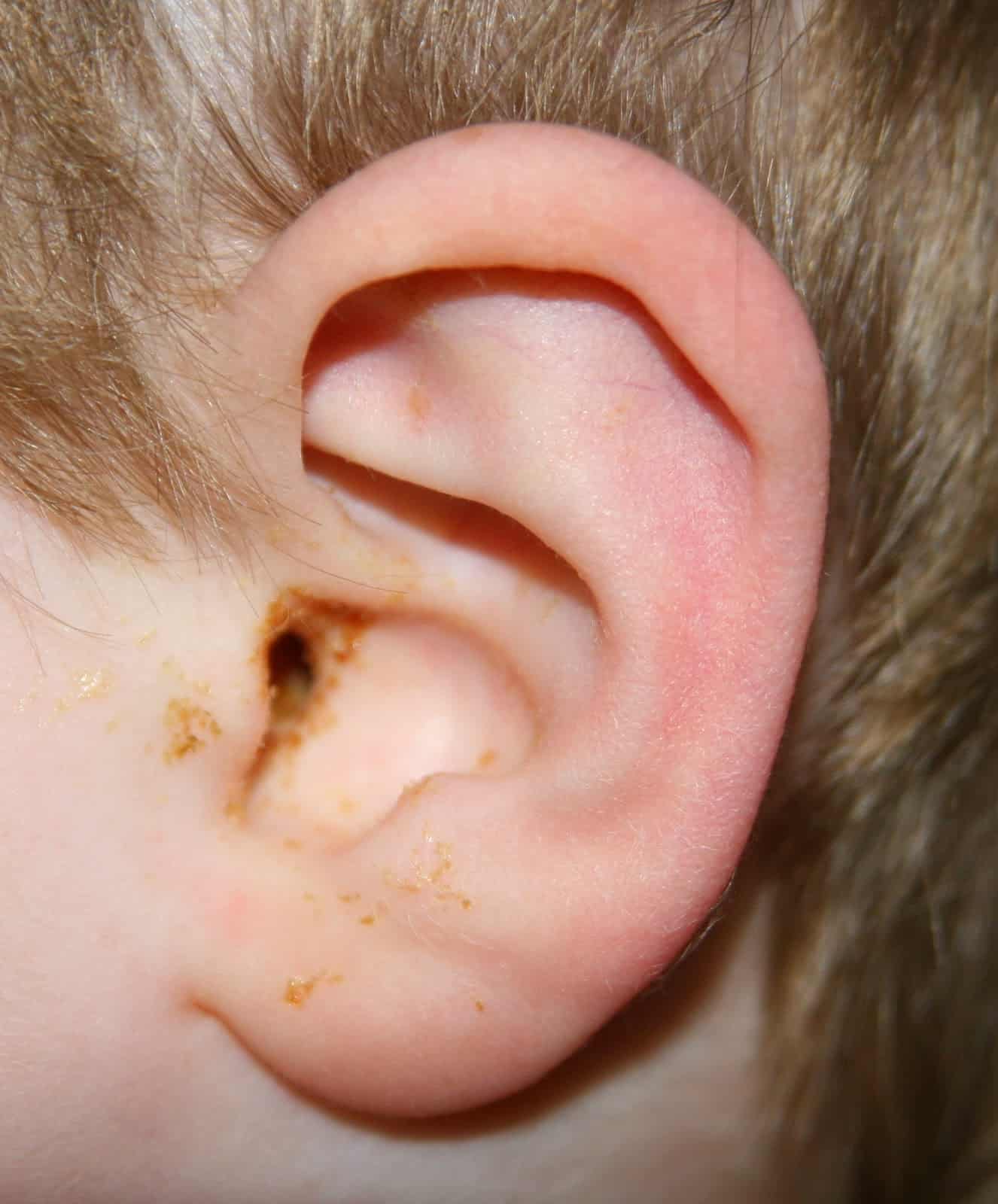
- A bacterial infection of the middle ear
- Blocked eustachian tube, usually as part of a common cold. The eustachian tube joins the middle ear to the back of the throat.
- Blockage results in middle ear fluid .
- If the fluid becomes infected , the fluid turns to pus. This causes the eardrum to bulge out and can cause a lot of pain.
- Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8.
- The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- How often do kids get ear infections? 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
Also Check: Get Yeast Infection Prescription Online
How Are Ear Infections Treated
Treating a middle ear infection usually involves two steps: Treating the pain, and then, if symptoms dont improve, prescribing antibiotic medication to fight the infection. Doctors sometimes wait to prescribe antibiotics because an otherwise healthy child may be able to fight the infection on their own, helping a child avoid side effects and other risks of antibiotics.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends focusing on pain management for the first 1 to 2 days before prescribing antibiotics. Over-the-counter ibuprofen and acetaminophen are recommended for pain relief, and occasionally ear drops that contain pain medicine.
Doctors sometimes wait to prescribe antibiotics, because the infection may clear up on its own.
If a doctor prescribes antibiotics to treat a middle ear infection, it is usually amoxicillin. This oral antibiotic works to destroy the infection. Over time, inflammation will get better, and the Eustachian tubes can properly ventilate the middle ear.
Until the backed-up fluids have cleared, your child is prone to recurrent infections. It is important to take the entire course of prescribed antibioticseven though the symptoms may have subsided. Older children may report being able to hear better several days after they have resumed normal activities. This is a sign that the fluid build-up has resolved.
Home Remedies For Clogged Ears Due To Sinus Infections
Here are some additional home remedies that can help alleviate ear problems associated with sinus infections and even wax build-up.
- Yawning helps redistribute the fluid in your ear.
- Take a hot, steamy shower.
- Make a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and warm water and pour it into the ear.
- Chew gum as it can help move wax out of the ear.
- Combine rubbing alcohol and vinegar and use the mixture as ear drops.
- Pinch your nose and blow to pop your ears.
- Drop warm olive oil into your ear once again this breaks up wax.
- Combine rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar as ear drops to help treat infection.
- Apply warm compresses to the ears.
- Gargle with warm water and salt.
You May Like: Can You Do A Root Canal On An Infected Tooth
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed
Ear exam
Your healthcare provider will look at your or your childs ear using an instrument called an otoscope. A healthy eardrum will be pinkish gray in color and translucent . If infection is present, the eardrum may be inflamed, swollen or red.
Your healthcare provider may also check the fluid in the middle ear using a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a small amount of air at the eardrum. This should cause the eardrum to move back and forth. The eardrum will not move as easily if there is fluid inside the ear.
Another test, tympanometry, uses air pressure to check for fluid in the middle ear. This test doesnt test hearing. If needed, your healthcare provider will order a hearing test, performed by an audiologist, to determine possible hearing loss if you or your child has had long lasting or frequent ear infections or fluid in the middle ears that is not draining.
Other checks
Your healthcare provider will also check your throat and nasal passage and listen to your breathing with a stethoscope for signs of upper respiratory infections.
Tips To Prevent Sinus Infections
In order to avoid ear pain and temporary hearing loss due to clogged ears as a result of sinus infections one must prevent sinus infections. Here are some tips to help you prevent sinus infections and avoid the complications associated with it.
- Control your allergies.
- Keep hydrated, which keeps mucus thin.
- Reduce alcohol consumption, which can worsen mucus.
- Minimize exposure to people with cold or flu.
- Always wash your hands and avoid germs.
- Avoid chlorinated swimming pools.
You May Like: Yeast Infection Urge To Urinate
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of otitis media pass within a few days, so there’s usually no need to see your GP.
However, see your GP if you or your child have:
- symptoms showing no sign of improvement after two or three days
- a discharge of pus or fluid from the ear some people develop a persistent and painless ear discharge that lasts for many months, known as chronic suppurative otitis media
- an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read more about diagnosing middle ear infections
Will I Get My Hearing Back After An Ear Infection
by Audiology & Hearing Care of SWFL | Aug 15, 2018 | Hearing Loss Articles
An ear infection is the typical name, but its medically called otitis media or AOM. Ear infections are especially common after a sinus infection or cold and they not only affect children but adults too. You can even get an ear infection if you have a bad tooth.
Just how long will hearing loss last after an infection of the middle ear? The answer to this question might be more complex than you might think. There are a lot of things going on with ear infections. To understand the potential risks, you should learn more about the injury these infections can cause and how they affect hearing.
Also Check: Strep Throat And Ear Infection
Signs In Young Children
As babies are unable to communicate the source of their discomfort, it can be difficult to tell what’s wrong with them. Signs that a young child might have an ear infection include:
- raised temperature
- pulling, tugging or rubbing their ear
- irritability, poor feeding or restlessness at night
- coughing or a runny nose
- unresponsiveness to quiet sounds or other signs of difficulty hearing, such as inattentiveness
- loss of balance
Conductive Hearing Loss Caused By Chronic Ear Infections
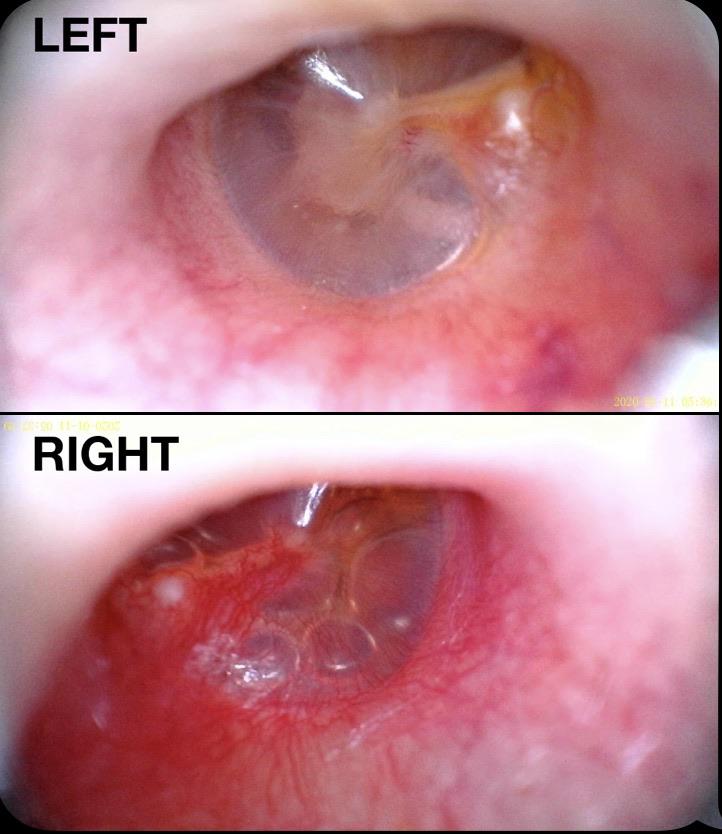
Conductive hearing loss can be brought on by repeated ear infections. In other words, sound waves dont get to the inner ear with enough strength. By the time the sound reaches the tiny hairs in the inner ear, they are amplified by the elements of the ear canal and reach their maximum power. When you have conductive hearing loss, something changes along that route and the sound isnt amplified as much.
Bacteria dont simply sit and behave themselves inside the ear when you have an ear infection. They need to eat to live and multiply, so they break down those mechanisms that amplify sound waves. The damage is in most cases done to the tiny little bones and the eardrum. The bones are very fragile and it doesnt take much to destroy them. If you lose these bones its permanent. When this happens your ears dont heal themselves. In certain cases, surgeons can install prosthetic bones to restore hearing. The eardrum can repair itself but it may have scar tissue influencing its ability to vibrate. This can also potentially be fixed with surgery.
Don’t Miss: Antibiotics For E Coli Infection
Can Ear Infections Cause Permanent Deafness
Ear infections are a common childhood malady. Fortunately, infections usually dont cause permanent damage in children or adults. If hearing returns to normal after treatment, the risk is lower for permanent deafness. You should discuss any concerns with your doctor. If there is temporary loss, you may be able to use a device to treat the condition until hearing returns.
To prevent recurrent ear infections, wear swim ear plugs when in the water. Dont smoke and limit your and the childs exposure to secondhand smoke. Try to prevent colds and flu, by following good hygiene. Get your flu vaccine. Ask your doctor about using antihistamines to prevent allergies from causing fluid in the ear.
How Long Does Hearing Loss Last In Adults
There are two main types of auditory loss, conductive impairment and sensorineural auditory loss. Conductive loss is often temporary. When the blockage is treated, the impairment usually goes away. Ear infections are typically easily treated with antibiotics. Recurrent ear infections may need further treatment. A doctor can insert a tube in the eardrum to keep the fluid from building up, known as a Eustachian tube. If your hearing doesnt get back to normal after treatment, you should discuss this with your doctor and an auditory professional.
Ear infections can also cause pressure to build up in the ear, which can cause the eardrum to rupture. Left untreated, this can cause damage to the eardrum which can reduce acuity. The tympanic membrane, which is another part of the ear that vibrates in response to sound, can also be scarred from chronic, recurrent ear infections. This, too, can affect hearing.
The second type of loss, sensorineural, occurs when there is damage to the auditory nerve or inner ear. The most common cause of this type of impairment is age-related, known as presbycusis. Sensorineural loss that is age-related is generally permanent, but the impairment can be mitigated with devices. When sensorineural loss occurs suddenly, within three days or less, a medical provider should be contacted immediately.
Don’t Miss: Yeast Infection Vs Chlamydia Discharge
What To Do When I Can’t Hear Out Of One Ear
1. Drain Your Earwax
If you are suspecting you have ear wax and you have no history of a hole in your eardrum or surgery, you can try out OTC wax irrigation and softener.
- Prepare a Wax-Softening Solution
You can buy or prepare your own. Mix warm water with a few drops of mineral or baby oil, a few drops of glycerin and 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Lie Down on Your Side
Lie on your side with the ear you want to drain facing downwards. Put a towel beneath your head for any excess water that spills. If you cannot lie down, tilt your head as much as you can. Pull the edge of your ear lobe upwards, making it perpendicular to your neck.
- Pour the Solution into Ear Canal
You can use a bulb syringe, glass measuring cup or a plastic syringe. If you are using a syringe, make sure you do not stick it in too deep. Lie down for 10-15 minutes to allow the solution to work. If you are using peroxide, you might hear some fizzing in your ear.
- Drain and Dry Your Ear
Put a bowl beneath your ear and tilt your head such that your canal drains into the bowl. Pull your ear lobe to make it tight. Dry your ear gently after all the wax has drained from the ear. You can use a paper towel or cloth to pat the ear gently. Hold a blow dryer on low heat a few inches from your ear to dry the skin.
2. Clear Your Ear Infection
- Apply a Warm Compress
Over the affected ear, place a warm moist cloth to ease the pain, but avoid sleeping with an electric heating pad as it may cause fire.
- Take Pain Relievers
Ear Infection And Hearing Loss: Everything You Need To Know
Ear infections, or otitis media, are the most common causes of earaches. People of all ages can develop ear infections, although they are more common in babies and young childrenâoften accompanying a cold, flu, or respiratory infection.
The Eustachian tube is a tiny channel that connects the middle ear to the upper respiratory tract. It is the place where the ear, nose and throat connect. This connection means that germs from the nose or sinus cavities can climb up the Eustachian tube to the middle ear and start growing. In children, the Eustachian tube is shorter and narrower, making it easier to become blocked by secretions.
Swimmerâs ear, or otitis externa, is another example of an ear infection that can cause hearing loss. This is an infection in the outer ear canal and usually happens when water remains in the ear after swimming.
âEar infections may sometimes cause a temporary hearing loss due to congestion and/or fluid,â Chrisanda Sanchez, AuD, FAAA, assistant professor of audiology at the University of Miami tells Web MD Connect to Care. When this happens, it can feel like youâre listening through fluid or hearing underwater. Usually, this type of hearing loss is temporary and goes away as soon as the infection is treated.
Don’t Miss: Otc Skin Yeast Infection Treatment
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.