Turning The Tide Against Aids Will Require More Concentrated Focus On Adolescents And Young People
Adolescents and young people represent a growing share of people living with HIV worldwide. In 2020 alone, 410,000 young people between the ages of 10 to 24 were newly infected with HIV, of whom 150,000 were adolescents between the ages of 10 and 19. To compound this, most recent data indicate that only 25 per cent of adolescent girls and 17 per cent of adolescent boys aged 15-19 in Eastern and Southern Africa the region most affected by HIV have been tested for HIV in the past 12 months and received the result of the last test. The testing rates in West and Central Africa and South Asia are even lower. If current trends continue, hundreds of thousands more will become HIV-positive in the coming years, and without knowing their status, adolescents will miss out on life-saving treatment. Additionally, a large population of children infected with HIV perinatally over the last decade are growing into adolescence.
In 2015, UNICEF and UNAIDS, in partnership with other international health and development partners, launched ALL IN! to End Adolescent AIDS. This global initiative established 2020 targets towards ending the AIDS epidemic among adolescents by 2030. To achieve this, it is critical to accelerate efforts to address the epidemic among adolescents.
HIV in adolescents
Progress in reducing new HIV infections among adolescents
Interventions for HIV prevention among adolescents
Antiretroviral treatment among adolescents
Majority Of New Hiv Infections Among Key Populations Sexual Partners Unaids Release Says
UNAIDS: Worldwide, more than half of new HIV infections now among key populations and their sexual partnersIn 2018, the global distribution of new HIV infections in 2018 crossed a threshold: the majority of global new infections were among key populations and their sexual partners. This change is a result of the strong progress in settings with high HIV prevalence in eastern and southern Africa, combined with a mixture of progress and setbacks in lower prevalence regions. Key populations make up a small proportion of the general population, but they are at extremely high risk of acquiring HIV infection .
The KFF Daily Global Health Policy Report summarized news and information on global health policy from hundreds of sources, from May 2009 through December 2020. All summaries are archived and available via search.
Tags
The National Hiv/aids Strategy And Priority Populations
The National HIV/AIDS Strategy is the nationâs roadmap for ending the HIV epidemic in the U.S. by 2030. It recognizes racism as a serious public health threat that drives and affects both HIV outcomes and disparities. The Strategy also notes while HIV remains a threat in every part of the United States, certain populations bear most of the burden, signaling where our HIV prevention, care, and treatment efforts must be focused. It therefore designates five priority populations: Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men, in particular, Black, Latino, and American Indian/Alaska Native men Black women transgender women youth aged 13-24 years and people who inject drugs.
Learn more: View NHAS-at-a-Glance.
For in-depth information about the impact of HIV on different racial and ethnic populations, see these CDC fact sheets:
Don’t Miss: Does Yeast Infection Affect Pregnancy
Hiv Infection And Aids 2015
HIV Infection and AIDS The incidence of HIV/AIDS in Minnesota remains moderately low. In 2014, state-specific HIV infection diagnosis rates ranged from 1.9 per 100,000 population in Montana to 36.6 per 100,000 in Louisiana. Minnesota had the 16th lowest HIV infection rate at 7.0 cases per 100,000 population. In 2014, state-specific AIDS diagnosis rates ranged from 0.7 per 100,000 persons in Montana and Wyoming to 13.7 per 100,000 population in Louisiana. Minnesota had the12th lowest AIDS rate at 3.0 AIDS cases reported per 100,000 population.
As of December 31, 2015, a cumulative total of 11,007 cases of HIV infection had been reported among Minnesota residents. Of the 11,007 cases, 3,737 are known to have died. By the end of 2015, an estimated 8,215 persons with HIV/AIDS were assumed to be living in Minnesota.
The annual number of AIDS cases reported in Minnesota increased steadily from 1982 through the early 1990s, reaching a peak of 361 cases in 1992. Beginning in 1996, the annual number of new AIDS diagnoses and deaths declined sharply, primarily due to better antiretroviral therapies. In 2015, 141 new AIDS cases , and 89 deaths among persons living with HIV infection, were reported.
The number of HIV diagnoses has remained fairly constant over the past decade from 2005 through 2015, at approximately 247 cases per year. With a peak of 282 newly diagnosed HIV cases in 2009, 228 new HIV cases were reported in 2015 .
- For up to date information see> > HIV
The Global Hiv/aids Epidemic
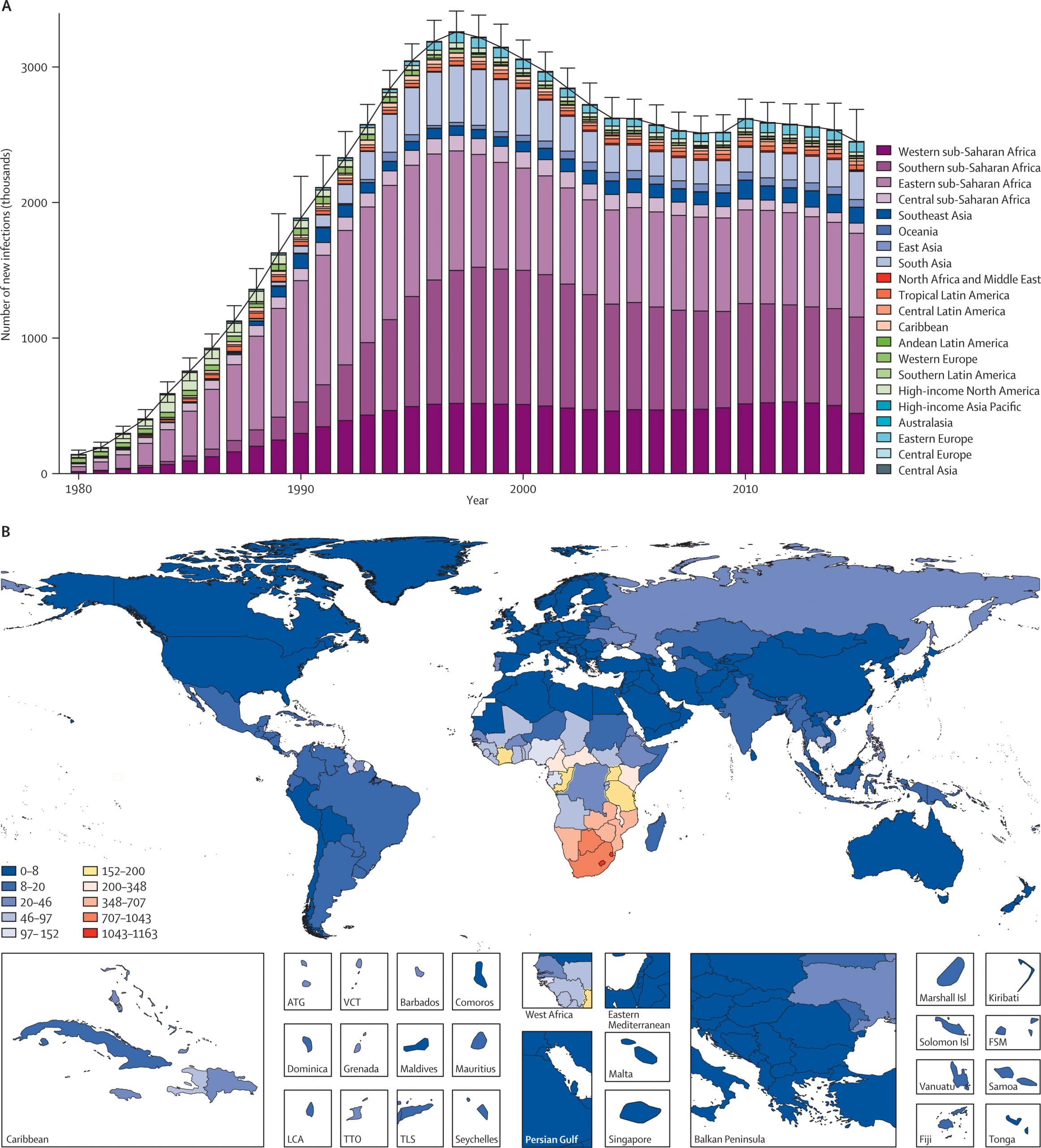
HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, is one of the worldâs most serious public health challenges. But there is a global commitment to stopping new HIV infections and ensuring that everyone with HIV has access to HIV treatment.
According to UNAIDSExit Disclaimer:
Number of People with HIVâThere were approximately 38.4 million people across the globe with HIV in 2021. Of these, 36.7 million were adults and 1.7 million were children . In addition, 54% were women and girls.
New HIV InfectionsâAn estimated 1.5 million individuals worldwide acquired HIV in 2021, marking a 32% decline in new HIV infections since 2010. New HIV infections, or âHIV incidence,â refers to the estimated number of people who newly acquired HIV during a given period such as a year, which is different from the number of people diagnosed with HIV during a year. Of these 1.5 million new HIV infections:
- 1.3 million were among adults
- 160,000 were among children
HIV TestingâApproximately 85% of people with HIV globally knew their HIV status in 2021. The remaining 15% did not know they had HIV and still needed access to HIV testing services. HIV testing is an essential gateway to HIV prevention, treatment, care, and support services.
- 85% knew their HIV status
- 75% were accessing ART
- 68% were virally suppressed
Perinatal TransmissionâIn 2021, 81% of pregnant people with HIV had access to ART to prevent transmitting HIV to their babies during pregnancy and childbirth and to protect their own health.
You May Like: Why Do I Constantly Get Sinus Infections
Men Who Have Sex With Men
Gay or bisexual MSM are the most severely affected population. MSM account for just a small fraction of the total U.S. population, yet nearly two-thirds of all new infections occurred within this group in 2009, and one-half of all people living with HIV in 2008 were MSM. MSM within ethnic minority populations are at greatest risk .
National Hiv Surveillance System Reports
May 27, 2021 Hopeful signs of progress in HIV prevention, but gains remain uneven
New CDC data show new HIV infections fell 8% from 2015 to 2019, after a period of general stability in new infections in the U.S. Much of this progress was due to larger declines among young gay and bisexual men in recent years. From 2015 to 2019, new infections among young gay and bisexual men dropped 33% overall, with declines in young men of all races, though African Americans and Hispanics/Latinos continue to be severely and disproportionately affected.
The data suggest recent progress is likely due to increased uptake of key prevention and treatment strategies. In 2019, nearly23% of people eligible for pre-exposure prophylaxis were prescribed it. This represents substantial progress a previous CDC report showed that percentage was roughly 3% in 2015. In 2019, 66% of people with diagnosed HIV were virally suppressed and 81% of people with diagnosed HIV were rapidly linked to care within one month of diagnosis in 45 U.S. jurisdictions. While not directly comparable due to a differing number of jurisdictions with complete data , a previous CDC report showed that 60% of people were virally suppressed and 75% were rapidly linked to care in 2015.
You May Like: Will Teladoc Treat Ear Infection
If I Am Pregnant And Have Hiv Will My Baby Also Have Hiv
Most women with HIV can protect their baby from becoming infected during pregnancy. Proper pre-natal treatment can reduce the risk that an HIV-positive mother will pass the virus to her child to less than 1 percent. The only way these special treatments can be provided is if the health care professionals know the mother is living with HIV. Treatment is most effective when started early in pregnancy. HIV-positive moms should not breastfeed their babies because HIV is sometimes passed this way.
Us Response To The Global Epidemic
The U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief is the U.S. Governmentâs response to the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and represents the largest commitment by any nation to address a single disease in history. Through PEPFAR, the U.S. has supported a world safer and more secure from infectious disease threats. It has demonstrably strengthened the global capacity to prevent, detect, and respond to new and existing risksâwhich ultimately enhances global health security and protects Americaâs borders. Among other global results, PEPFAR provided HIV testing services for more than 50 million people in Fiscal Year 2021 and, as of September 30, 2021, supported lifesaving ART for nearly 18.96 million men, women, and children. PEPFAR also enabled 2.8 million babies to be born HIV-free to parents living with HIV.
In addition, the National Institutes of Health represents the largest public investment in HIV/AIDS research in the world. NIH is engaged in research around the globe to understand, diagnose, treat, and prevent HIV infection and its many associated conditions, and to find a cure.
Read more about the U.S. Governmentâs global HIV/AIDS activities.
Read Also: Why Do I Get Sinus Infections So Much
Hiv Testing And Access To Prevention & Care
- In 2014, three quarters of Black people over age 18 report ever having been tested for HIV and they are more likely than Latino people or White people to report having been tested .39
- Among those who are HIV positive, 20% of Black people were tested for HIV late in their illness that is, were diagnosed with AIDS within 3 months of testing positive for HIV by comparison, 22% of White people and 21% of Latino people were tested late.40
- Looking across the care continuum, from HIV diagnosis to viral suppression, missed opportunities are revealed. Eight-five percent of Black people with HIV are diagnosed, 60% are linked to care, and 46% are virally suppressed.41 Compared with White people, Black people are less likely to have reached each of these goals in the continuum diagnosis, linkage to care and viral suppression and thus disparities are likely to persist.42
Endnotes
What Is The Impact Of Hiv On Racial And Ethnic Minorities In The Us
HIV can affect anyone regardless of sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, gender, age, or where they live. However, in the United States, some racial/ethnic groups are more affected than others, given their percentage of the population. This is because some population groups have higher rates of HIV in their communities, thus raising the risk of new infections with each sexual or injection drug use encounter. Additionally, a range of social, economic, and demographic factors such as stigma, discrimination, income, education, and geographic region can affect peopleâs risk for HIV as well as their HIV-related outcomes.
Black/African American and Hispanic/Latino communities are disproportionately affected by HIV compared to other racial/ethnic groups. For example, in 2019, Blacks/African Americans represented 13% of the US population, but 40% of people with HIV. Hispanics/Latinos represented 18.5% of the population, but 25% of people with HIV.
Source: CDC, Estimated HIV incidence and prevalence in the United States, 2015â2019.
Among women, disparities also exist. Black women are disproportionately affected by HIV as compared to women of other races/ethnicities. Although annual HIV infections remained stable overall among Black women from 2015 to 2019, the rate of new HIV infections among Black women is 11 times that of white women and four times that of Latina women.
Also Check: Is Vaginal Yeast Infection Contagious
Cdph 2021 Data Shows Small Uptick In New Hiv Diagnoses Historic Drop In New Aids Diagnoses
CDPH also releases trailer of HIV Journey Toward Zero documentary for World AIDS Day
CDPH Public Information
CHICAGO In 2021, the second year Chicago faced COVID-19, new HIV cases in Chicago residents rose by just under 2 percent, while new AIDS diagnoses dropped to their lowest level since 1985, the Chicago Department of Public Health announced today. Additionally, there was a double-digit percentage decrease in primary and secondary syphilis cases in 2021, according to CDPH.
The 1.9 percent increase over 2020 in new HIV diagnoses bucked a decades-long trend of decreasing numbers of new HIV diagnoses in Chicago. Chicago reported 639 new HIV cases in 2021 up from 627 in 2020. However, the 2021 report represents the second-lowest number of new HIV diagnoses reported locally since the late 1980s. The minimal increase in diagnoses between 2020 and 2021 is not unexpected and likely reflects disruptions in health care services and reporting during the first year of the COVID pandemic, rather than a major change in disease patterns. Consequently, CDPH continues to urge caution when comparing data from 2020 and 2021 to other years.
The 246 new diagnoses of AIDS among Chicagoans in 2021 are the fewest since 1985.
Additional Resources and Links:
CDPH HIV & STI Resources. Includes information on CDPH Specialty Clinics, where Chicagoans can get HIV and STI services including testing, treatment, and information on prevention, PrEP.
Intimate Partner Violence And Hiv
- Women living with HIV are disproportionately affected by intimate partner violence , including physical, sexual, and emotional abuse compared to the general population. 44,45 Intimate partner violence , sometimes referred to as domestic violence, has been shown to be associated with increased risk for HIV among women, as well as poorer treatment outcomes for those who are already infected.46,47
- Among all U.S. women, 36% report having experienced IPV, including rape, physical violence, and/or stalking in their lifetime among HIV positive women in the U.S., IPV is even more prevalent, with 55% reporting having experienced IPV.48,49,50
- In many cases, the factors that put women at risk for contracting HIV are similar to those that make them vulnerable to experiencing trauma or IPV women in violent relationships are at a 4 times greater risk for contracting STIs, including HIV, than women in non-violent relationships, and women who experience IPV are more likely to report risk factors for HIV.51 These experiences are interrelated and can become a cycle of violence, HIV risk, and HIV infection.
- It has also been suggested that women are at risk of experiencing violence upon disclosure of their HIV status to partners.52
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Yeast Infection Without Antibiotics
What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
The term AIDS refers to the most advanced stages of HIV infection. Most of the conditions affecting people with AIDS are opportunistic infections that generally do not affect healthy people. In people with AIDS, these infections are often severe and sometimes fatal because the immune system is so ravaged by HIV that the body cannot fight off the infection. Symptoms of opportunistic infections common in people with AIDS include:
- coughing and shortness of breath
- seizures and lack of coordination
- difficult or painful swallowing
- severe headaches
People with AIDS also are particularly prone to developing various cancers. These cancers are usually more aggressive and difficult to treat in people with AIDS.
Key Points: Hiv Diagnoses
In 2020, MSM were the population most affected by HIV in the U.S.:
- In 2020, MSM accounted for 71% of new HIV diagnoses in the United States.f
- In 2020, Black/African American MSM accounted for 26% of new HIV diagnoses and 39% of diagnoses among all MSM.
- In 2020, Hispanic/Latino MSM made up 21% of new HIV diagnoses and 31% of diagnosis among all MSM.
- From 2016 to 2019, HIV diagnoses decreased 7% among gay and bisexual men overall. But trends varied for different groups of gay and bisexual men.
Transgender people accounted for approximately 2% of the 30,635 new HIV diagnoses in 2020.
- Transgender womeng accounted for 2% of new diagnoses.
- Transgender menh accounted for less than 1% of new diagnoses.
People who acquired HIV through heterosexual contact made up 22% of HIV diagnoses in the U.S. in 2020.
- People assigned male sex at birth who acquired HIV through heterosexual contact accounted for 7% of new HIV diagnoses.
- People assigned female sex at birth who acquired HIV through heterosexual women accounted for 15%.
- From 2016 to 2019, HIV diagnoses from heterosexual contact decreased 13% overall.
People who inject drugs accounted for 7% of new HIV infections in the U.S. and 6 dependent areas in 2020.
- Men who inject drugs accounted for 4% of new HIV diagnoses.
- Women who inject drugs accounted for 3% of new HIV diagnoses.
Blacks/African Americans and Hispanics/Latinos continue to be disproportionately affected by HIV:
Don’t Miss: Oral Medication For Yeast Infection Prescription
The Differential Hiv Experience Of African
While African-Americans make up 12 percent of the U.S. population, they accounted for 46 percent of new HIV infections in 2010, substantially higher than the rate for Whites or Hispanics. The majority of these were men however, African-American women also have a high rate of HIV diagnosis nearly 20 times that of White women . More disheartening is that 1 in 16 African-American men and 1 in 32 African-American women will eventually be diagnosed with HIV.
The causes of this HIV health disparity are complex. HIV infection prevalence is higher and more broadly represented in the African- American community compared to the White population thus African-Americans are at increased risk of infection simply by choosing intimate partners within their own ethnic communities.24 Additionally, African-American communities experience high rates of other sexually transmitted infections, and some of these infections can significantly increase the risk of contracting HIV. African-Americans also tend to be diagnosed at later stages in the disease and therefore begin therapy later, increasing the length of time of their infectivity. Once engaged in HAART, African-Americans are more likely to discontinue therapy prematurely,25 risking resurgence of HIV infectivity and further health complications.
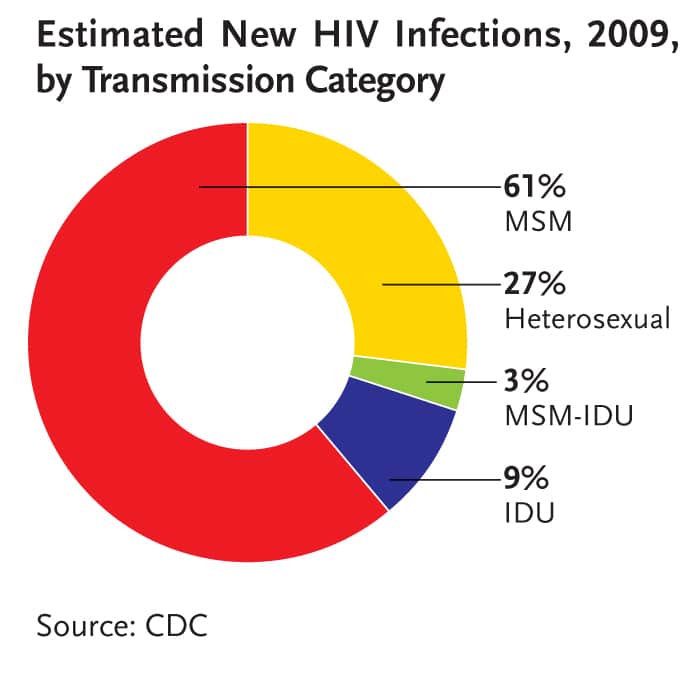
- Text Description: Diagnosis of HIV Infection Among Adults and Adolescents, by Transmission Category Graph
-
Male-to-male sexual contact: 61%