Tests For Other Abnormalities
In patients with HIV myopathy, EMG is a sensitive diagnostic test. The most common finding on muscle biopsy is scattered myofiber degeneration with occasional inflammatory infiltrates. Other pathologic findings include nemaline rod bodies, cytoplasmic bodies, and mitochondrial abnormalities. Serial creatine kinase levels are useful for monitoring the course of the disorder.
EMG is useful for evaluating mononeuritis multiplex. Results generally reveal multifocal axonal neuropathy. Biopsy of nerve tissue reveals inflammation and vasculitis. In some cases, CMV inclusions have been found.
In patients with elevated transaminases, acute viral hepatitis A, B, and C should be excluded with appropriate serologic testing.
Signs Of Kidney Problems During Pregnancy
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia affects only pregnant women after the 20th week of pregnancy and resolves shortly after the baby is delivered. Although it is by origin not a primary kidney problem, it does involve the kidneys. It is characterised by:
- Proteinuria, or protein in the urine
Other symptoms which may appear as part of preeclampsia or as preeclampsia progresses include:
- Headache that cannot be alleviated with painkillers
- Edema of hands, arms, face and/or feet
- Blurred vision, other visual disturbances or blind spots
- Confusion or disorientation
- Oliguria of 500ml or less over 24 hours
- Being unable to feel the baby move as much as previously
- Shortness of breath, possibly due to pulmonary edema
- Stroke. This is very rare
Good to know: If a pregnant person suddenly discovers that their watch, bracelets or rings no longer fit their arm or hand, or that their sleeves are suddenly tight, they should seek medical help immediately. Preeclampsia can lead to eclampsia and HELLP Syndrome and is considered a medical emergency.
For more information on, see this resource on preeclampsia, eclampsia and HELLP Syndrome.
If you are concerned that you or a loved one may have preeclampsia, eclampsia or HELLP Syndrome, download the Ada app for a free symptom assessment.
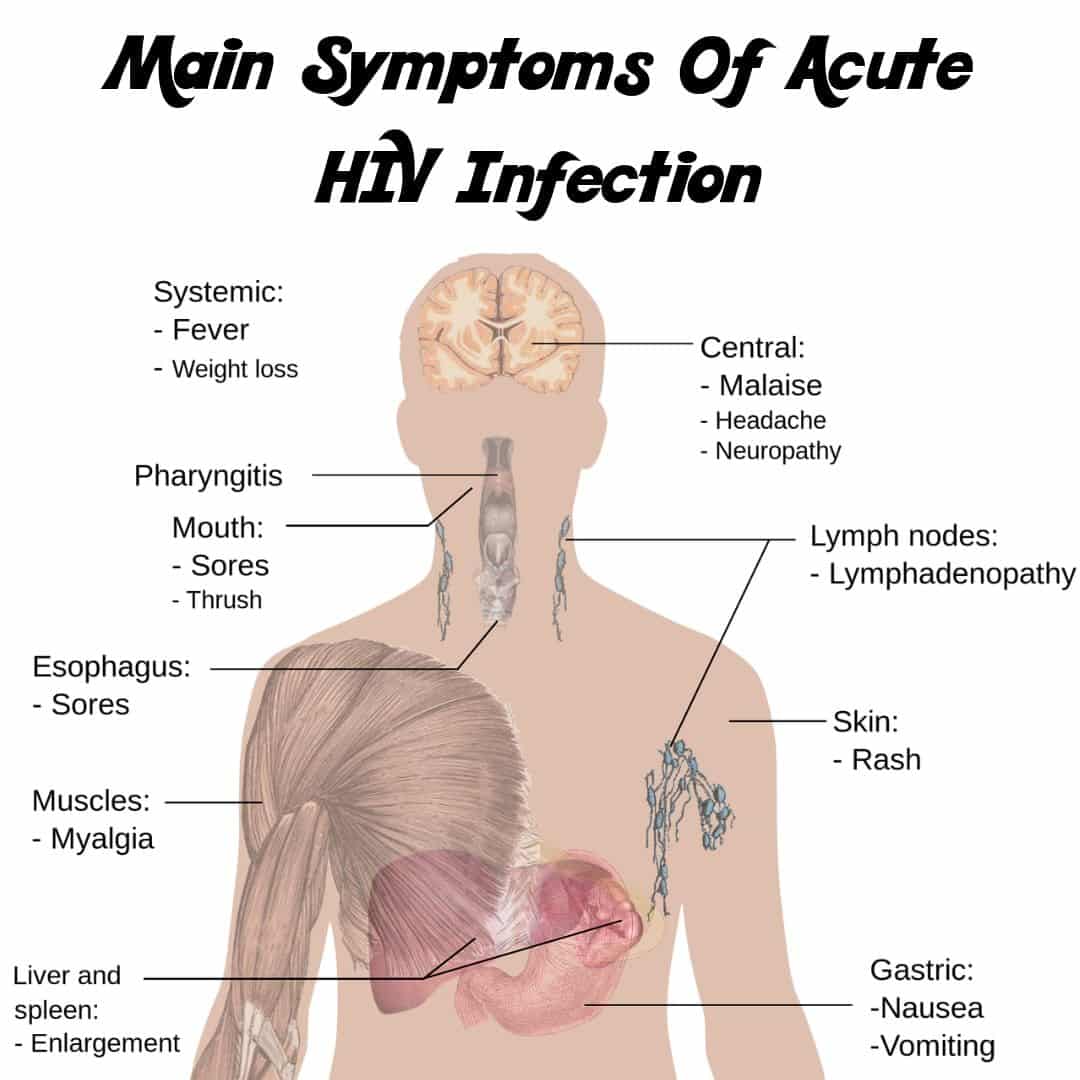
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-like illness. This is the bodyâs natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-like symptoms can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. But some people do not have any symptoms at all during this early stage of HIV.
Donât assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptomsâthey can be similar to those caused by other illnesses. But if you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Hereâs what to do:
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Wisdom Tooth Is Infected
Symptoms Of Hiv And Aids
The symptoms of HIV and AIDS will vary depending on the individual and the phase of infection. Some individuals will have flu-like symptoms within 2-4 weeks after infection, usually lasting anywhere between a few days to several weeks. This phase, called acute HIV infection, is when the effects of HIV are the most difficult to detect. Not only are these symptoms shared by far more mundane illnesses like allergies or the common cold, but some HIV-positive patients may not feel sick at all during acute HIV infection.
Possible symptoms of HIV include:
Because these symptoms are shared by other illnesses, and because some patients dont experience any symptoms whatsoever, its all the more important to see a health care provider if you have any of these symptoms and think you may have been exposed to HIV. Getting tested is the only way to truly know whether you are positive for HIV.
Protecting Yourself From Hiv/aids
- Use a new condom every time you have sex. Ensure that you are always protected in any experience involving sexual contact. Women may use female condoms as well. When using lubrication, make sure it is water-based, as oil-based lubricants can weaken condoms and cause them to break or tear. Use nonlubricated, cut-open condoms or dental dams when engaging in oral sex.
- Use clean needles. If you use a needle for injection drugs, take steps to ensure the needle is sterile and do not share it with others. However, the best way to prevent contraction through illicit drug use is to seek help in quitting.
- Consider male circumcision. There is evidence to suggest that male circumcision can help to reduce the risk of contracting HIV.
- Take Pre-exposure Prophylaxis . If you are at high risk of contracting HIV, you can take this combination of drugs to help reduce your risk of contracting sexually transmitted HIV by more than 90% and injection-related HIV transmissions by more than 70%.
- Use Post-exposure Prophylaxis . If you think youve already been exposed to HIV through sex, needles or in the workplace, take PEP as soon as possible and within the first 72 hours after exposure to reduce your risk of becoming infected.
Don’t Miss: How Does Infection Cause Sickle Cell Crisis
What Is A Latent Hiv Reservoir
A latent HIV reservoir is a group of immune system cells in the body that are infected with HIV but are not actively producing new virus.
HIV attacks immune system cells in the body and uses the cells own machinery to make copies of itself. However, some HIV-infected immune cells go into a resting or latent state. While in this resting state, the infected cells do not produce new virus. HIV can hide inside these cells for years, forming a latent HIV reservoir but, at any time, cells in the latent reservoir can become active again and start making more virus.
To find out more about how HIV attacks cells, read the HIV Life Cycle fact sheet from HIVinfo.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Itâs important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Recommended Reading: Under Belly Yeast Infection Treatment
Assessment Of Organ Function
Assessing organ function is important to screen for HIV-associated complications, establish a baseline in order to monitor toxicity, and help select an ART regimen.
- HIV drugresistance testing: Genotypic assays are preferred over phenotypic assays.
- CD4+ count: correlates with overall immune function
- Normal values are > 500 cells/mm3, whereas in the advanced stages of HIV the CD4+ count is often < 200 cells/mm3.
- Critical measurement to determine when to initiate opportunistic infection prophylaxis
- CD4+ counts increase in response to successful ART therapy.
Measurement of CD8 cell count and CD4:CD8 ratios is not routinely recommended, as the results are not used to guide treatment.
Common Cold: Stage By Stage
A sore throat Joint and muscle aches Diarrhea A rash These signs and symptoms of acute HIV infection can begin a few days after you are exposed to HIV and usually last for about 14 days. They could last for just a few days, or they could last for several months. You might not realize your illness is acute HIV infection Stage 2 Hip Osteoarthritis. At this stage, you will probably be experiencing some pain and discomfort in your hip area. You might notice that you are stiff, especially when you first get up in the morning or after sitting for a long time. Those first few steps will be tough on whichever hip has arthritis, but once you get going, it.
Dont Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Don’t Miss: Severe Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
Indications For Hiv Testing
HIV testing should be offered to patients who have signs that raise concern for HIV infection, prior exposure, and as part of routine screening.
- Routine screening
- All individuals > 13 years of age in all health care settings
- Any individuals :
- Starting treatment for tuberculosis
- Attending STI clinics or diagnosed with an STI
In most US states, HIV testing requires patient consent in the majority of locations, oral consent is sufficient, but check local guidance.
What Impact Does Hiv Have On The Body
HIV weakens the bodys natural defences, and over time it damages the immune system.
The impact of HIV on the body depends on a persons general health, such as:
-
how quickly they are diagnosed
-
how quickly they start antiretroviral treatment
-
how consistently they take their treatment
The HIV lifecycle is made up of four stages. Each of these involve a number of processes which happen in and around a human CD4 cell.
Don’t Miss: I Have A Urinary Tract Infection And Im Bleeding
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people dont have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that youre infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
Dont Miss: How To Tell Your Boyfriend You Have A Yeast Infection
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
Other names for this stage are the asymptomatic stage or clinical latency. At this stage, you still have the virus in your body but at low levels. Itâs possible you wonât notice any symptoms. But as long as the virus is at detectable levels, you can pass the infection to another person.
Without treatment, this stage can last 10 years or longer. Some people will get worse and progress to the next stage faster than others. If you take medicine, this stage can last for a long time. You may never move to the next stage.
Also Check: Can An Ear Infection Heal On Its Own
Stage : Symptomatic Hiv Infection/aids
It takes about 10 years of going untreated for HIV to develop into what is known as HIV/AIDS. At this point, symptoms of ongoing destruction of the immune system may develop, such as recurring fever, persistent and extreme fatigue, chronic diarrhea, and neurological disorders such as depression and memory loss.
Other distinctive symptoms that may occur at this time include:
People with HIV/AIDs also may develop diseases such as shingles pneumonia, and many others.
Prevention And Treatment Of Hiv And Aids
There is currently no vaccine to prevent HIV infection, nor is there currently a cure for AIDS. However, there are ways to protect yourself and your partner from infection. Here are some ways to protect yourself from developing HIV and AIDS, as well as some ways to protect others if you are HIV-positive.
You May Like: How To Know If Eczema Is Infected
The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that attacks the bodys immune system, interfering with the bodys natural ability to fight off infection and disease. This most commonly spreads through sexual contact, however, it can also spread through contact with infected blood or breast milk.
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition that develops as a progression of HIV. This is the most severe phase of HIV infection, wherein the bodys immune system is so badly damaged that the person is at an increased risk of developing severe illnesses.
There is currently no cure for HIV and AIDS. Once contracted, the affected individual will have it for life, and it will become more severe and potentially life-threatening if left untreated. However, with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled, allowing patients to live long, healthy lives.
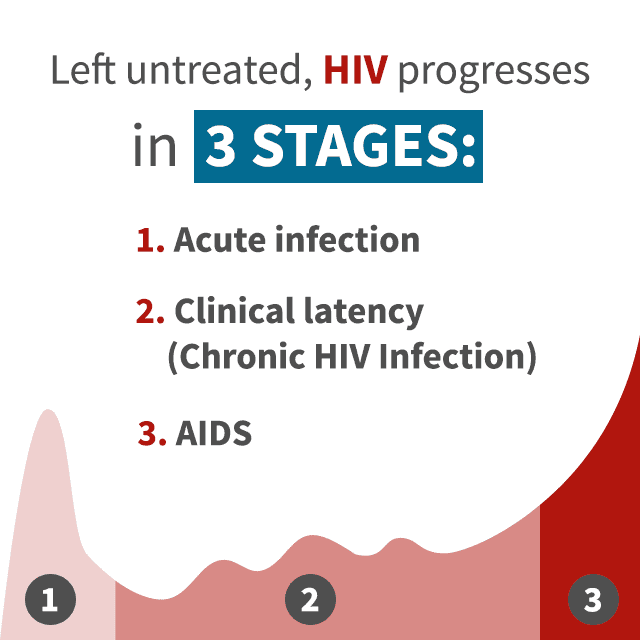
The Three Stages Of Hiv
When people with HIV are left untreated, the virus will generally phase through three stages, getting more severe and life-threatening with each new stage. However, its important to note that HIV treatment and medications can slow and even prevent further progression of the disease. Thanks to modern advancements in medicine, progression all the way to Stage 3 is far less common than it was when HIV first found its way to the United States.
Recommended Reading: Ear Infection Can T Hear
Third Stage: Aids Symptoms
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection. This is usually when your CD4 T-cell number drops below 200 and your immune system is badly damaged. You might get an opportunistic infection, an illness that happens more often and is worse in people who have weakened immune systems. Some of these, such as Kaposis sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia , are also considered âAIDS-defining illnesses.â
If you didnt know earlier that you were infected with HIV, you may realize it after you have some of these symptoms:
- Being tired all the time
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck or groin
- Fever that lasts more than 10 days
Protecting Others From Hiv/aids
- Tell your sexual partners you have HIV. It is important to tell all of your current and past sexual partners that you are HIV-positive and encourage them to get tested. This is essential to keep your partner and former partners safe and prevent further spread of the disease.
- Use treatment as prevention . If youre living with HIV, taking HIV medication will not only help slow the progression of the disease, but it can also help keep your partner from becoming infected with the virus. If your viral load becomes undetectable through treatment, you will not be able to transmit the virus to anyone else.
- If youre pregnant, seek medical care immediately. Women who are HIV-positive may pass the infection on to their baby. However, if you receive treatment during pregnancy, you can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting the disease to your child.
If you or someone you know is seeking testing or treatment for HIV/AIDS, contact Washington Health Institute for care either online or over the phone at 202-525-5175.
Also Check: Can An Ear Infection Cause Strep Throat
Should Pregnant Women Get Tested For Hiv
CDC recommends that all pregnant women get tested for HIV so that they can begin taking HIV medicines if they are HIV positive. Women with HIV take HIV medicines during pregnancy and childbirth to reduce the risk of perinatal transmission of HIV and to protect their own health. For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on Preventing Perinatal Transmission of HIV.
Screening For Associated Complications
- Screening for latent TB via PPD or IGRA
- Additional tests to consider in select patient groups:
- Chest x-ray: advised in patients with positive TB screen or as a baseline in patients with preexisting lung abnormalities
- CMVIgG: tested in patients with a low risk of prior infection
- All individuals with HIV infection, regardless of CD4 count, should begin antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible
- Antiretroviral drugs are combined to prevent resistance.
- All antiretroviral drugs are able to target both HIV-1 and HIV-2, except for enfuvirtide and NNRTIs.
Early treatment is particularly critical in patients with a low CD4 count , high viral load, or an AIDS-defining illness.
In the US, HIV/AIDS is a notifiable disease in every state.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Treatment For Ear Infection
What Drugs Are Approved For Prep
There are two oral medications approved for daily use as PrEP. They are combinations of two anti-HIV drugs in a single pill:
- Truvada®Exit Disclaimer is for all people at risk for HIV through sex or injection drug use. Generic productsExit Disclaimer are also available.
- Descovy®Exit Disclaimer) is for sexually active men and transgender women at risk of getting HIV. Descovy® has not yet been studied for HIV prevention for receptive vaginal sex.
A long-acting injectable form of PrEP, Exit Disclaimer, has also been approved by the FDA. It is administered by a health care provider every two months instead of daily oral pills.