How Serious Is Influenza
This decrease in quality of life, the impact of symptoms, the shifting nature of the virus, and the danger of life-threatening complications, combine to make the flu a major public health problem.
Each year between 3,000 and 49,000 Americans die from flu and its complications. Although most people are back on their feet within a week after having the flu, certain people are more susceptible to complications. If you have asthma or other lung diseases, or other chronic conditions you are at higher risk of developing complications from the flu. Learn more about risk factors.
What Is The Flu
The flu, also called influenza, is a respiratory infection caused by viruses. Each year, millions of Americans get sick with the flu. Sometimes it causes mild illness. But it can also be serious or even deadly, especially for people over 65, newborn babies, and people with certain chronic illnesses.
Diagnosis Of Bacterial And Viral Infections
If you believe you have an infection other than the common cold, which is usually not life-threatening, consult your healthcare provider to make the proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
A healthcare provider will use your report of symptoms, medical history, and a physical examination to begin the diagnosis of a respiratory infection. Depending on possible exposures, they may refer you to testing for bacteria or viruses.
Tests that are frequently performed to diagnose respiratory bacterial infections include:
- Rapid strep test: A throat swab is analyzed for strep throat.
- Throat culture: A swab is taken and sent to the lab for culture.
- Sputum culture: Phlegm is collected and sent to the lab for culture.
- Blood culture: Blood is drawn into special bottles and incubated in the lab.
To see if you have a viral respiratory infection, commonly used laboratory tests that are used include:
- Nasal, cheek, or throat swab: This may be used for detection of viral antigens or for viral culture for influenza or COVID-19.
- Blood tests: Blood may be drawn to test for viral antigens or antibodies.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If A Sinus Infection Goes Untreated
How Are Bacterial Infections Transmitted
There are many modes of transmission of bacteria. Bacteria are transmitted to humans through air, water, food, parasites, animals, or contact with other humans.
Also, bacteria that normally are present in or on the body without causing illness can produce illness if a person’s immune system is weakened and they overgrow or are introduced to a different area of the body, such as the bloodstream, lungs, or urinary tract.
How Are Stomach Flu And Influenza Different
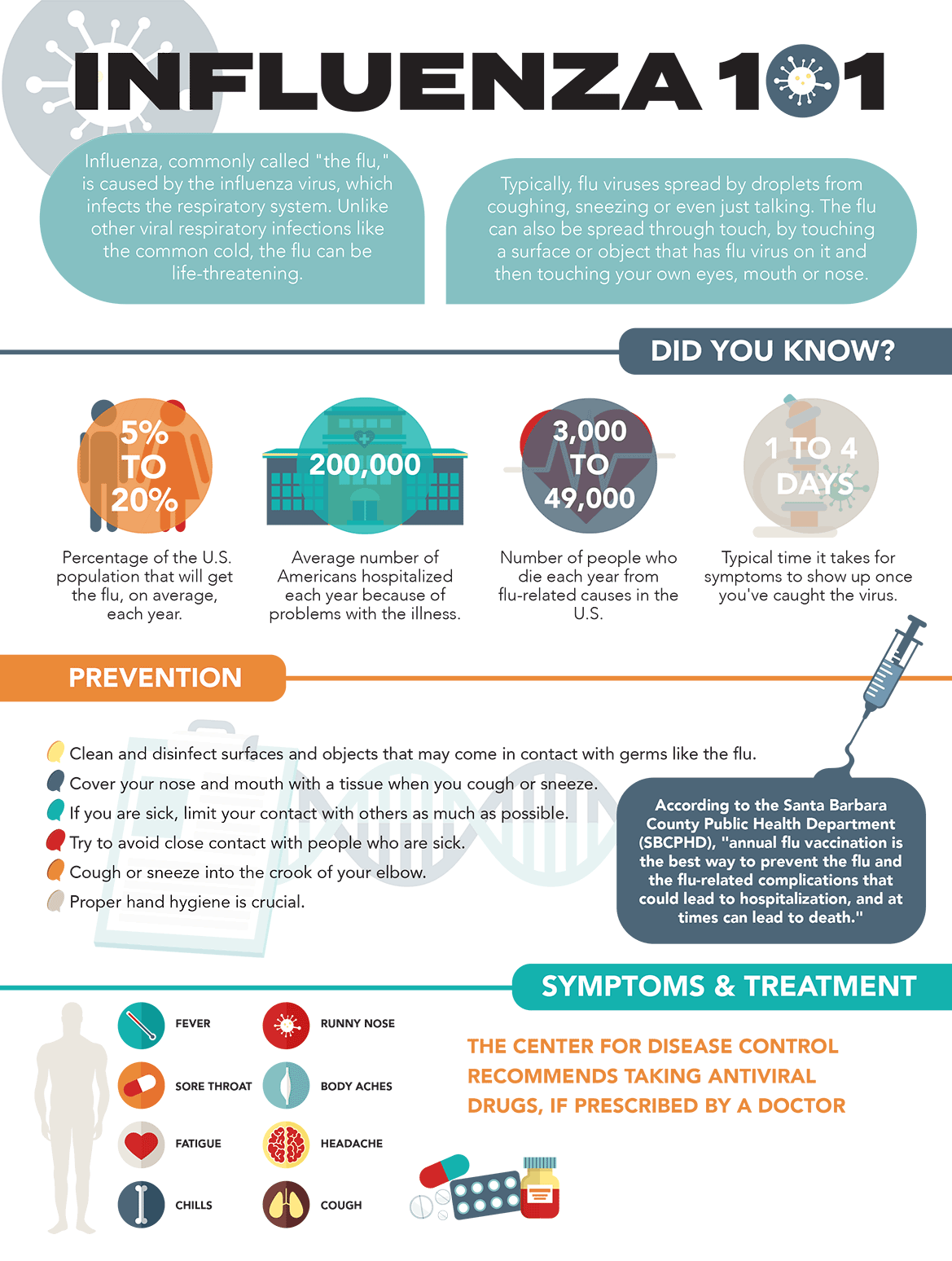
“Stomach flu” is a popular term, but not a true medical diagnosis. It’s not uncommon to mistake gastroenteritis, which is what stomach flu is, for the viral infection we commonly call the “flu.” Gastroenteritis refers to inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract . Viruses are the most common cause of stomach flu. With gastroenteritis, you may have symptoms such as fever, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
For more about gastrointestinal flu, read WebMD’s Stomach Flu or Influenza?
Don’t Miss: Is A Uti And Bladder Infection The Same
What Are The Symptoms Of The Flu In A Child
The flu is a respiratory disease, but it can affect the whole body. A child can become suddenly ill with any or all of these symptoms:
-
Fever, which may be as high as 103°F to 105°F
-
Body aches, which may be severe
-
Headache
| Extreme tiredness that can last weeks | |
| Sore throat | Sore throat in some cases |
A cold is usually mild and often goes away after a few days. The flu can cause severe symptoms and lead to problems such as pneumonia and even death. The symptoms of the flu can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
What Is Being Done About Mrsa Infections Associated With Influenza
CDC is working with state and local public health authorities to monitor and investigate infections with MRSA, including pneumonias and other types of MRSA infections that occur in patients with influenza. CDC also acts as a technical advisor to state and local health departments and various professional organizations that are working to control MRSA.
You May Like: Gynecologist Recommended Yeast Infection Treatment
How Are Upper Respiratory Infections Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider may diagnose the infection based on a physical exam and your symptoms. Theyll look in your nose, ears and throat and listen to your chest to examine your breathing. You often dont need other tests.
If your provider is concerned you may have a lung infection or another infection, you may need a:
- Sputum test, when you cough up some sputum for examination.
Viral Adaptations Needed For Host Switch And Determinants Of Pathogenicity
To successfully adapt to humans as a new hosteither via the direct transmission from birds to humans or a possible further adaptation process in swineIAVs need to ensure efficient replication and interspecies transmission. Contrary to birds, where IAV replicates in the gastrointestinal epithelia, the primary target cells of IAV in humans as well as in pigs are found in the epithelium of the respiratory tract. Consequently, a successful adaption to the human host requires mutations in the viral replication machinery.
Don’t Miss: Will Vagisil Cure Yeast Infection
How Long Do Upper Respiratory Infections Last
Upper respiratory infections typically last one to two weeks. Most of the time, they go away on their own. Over-the-counter pain medications can help you feel better. Make sure you drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
If your symptoms last longer than two weeks, talk to your healthcare provider. You may have another condition that is causing the symptoms, such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
Are There Carriers Of Influenza
No, not in the sense of people going around for days unwittingly spreading influenza. Some people may become infected with an influenza virus without experiencing any symptoms or only having mild symptoms for a short period. This may be how some people catch influenza without recalling having been in contact with anyone with the disease. However, it is thought that those without symptoms, or with minor symptoms, are generally less infectious than those with stronger symptoms.
You May Like: Apple Cider Vinegar Vaginal Yeast Infection
Should I Worry About An Upper Respiratory Infection
Most of the time, these infections go away on their own. Youll likely make a full recovery. However, some higher-risk groups should take extra precautions when it comes to upper respiratory infections. These infections can be more dangerous for:
- Children, especially babies.
- Older adults.
- People with immune system disorders.
If you are in a high-risk group and get a cold or other respiratory infection, contact your healthcare provider.
How Is The Flu Diagnosed
To diagnose the flu, health care providers will first do a medical history and ask about your symptoms. There are several tests for the flu. For the tests, your provider will swipe the inside of your nose or the back of your throat with a swab. Then the swab will be tested for the flu virus.
Some tests are quick and give results in 15-20 minutes. But these tests are not as accurate as other flu tests. These other tests can give you the results in one hour or several hours.
Also Check: Over The Counter Yeast Infection Male
How Can You Tell The Difference Between A And The Flu
The flu is also a viral infection caused by the Influenza virus, but there are important differences between influenza and the common cold. Unlike a simple Upper Respiratory Infection , the flu usually causes a higher fever , as well as body aches and headaches. While there is no test for a common cold, there is a test for flu that can be run in your doctors office. If you do have the flu, your doctor can treat you with an antiviral medication that targets the influenza virus. Unfortunately, there is no similar antiviral treatment for a Upper Respiratory Infection .
Influenza And Other Respiratory Viruses
Influenza is a viral infection that affects mainly the nose, throat, bronchi and, occasionally, lungs. Infection usually lasts for about a week and is characterized by sudden onset of high fever, aching muscles, headache, and severe malaise, non-productive cough, sore throat, and rhinitis.
The virus is transmitted easily from person to person via droplets and small particles produced when infected people cough or sneeze. Influenza tends to spread rapidly in seasonal epidemics.
Most infected people recover within one to two weeks without requiring medical treatment. However, in the very young, the elderly, and those with other serious medical conditions, infection can lead to severe complications of the underlying condition, pneumonia, and death.
All age groups can be affected but there are groups that are more at risk than others.
- People at greater risk of severe disease or complications when infected are: pregnant women, children under 59 months, the elderly, individuals with chronic medical conditions and individuals with immunosuppressive conditions .
- Health care workers are at high risk of acquiring influenza virus infection due to increased exposure to the patients and risk further spread particularly to vulnerable individuals.
In temperate climates, seasonal epidemics occur mainly during winter, while in tropical regions, influenza may occur throughout the year, causing outbreaks more irregularly.
Also Check: Over The Counter For Bv Infection
Treatment And Home Remedies
If youre sick, be sure to drink plenty of liquids and get plenty of rest. You can also take over-the-counter pain and fever relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen , to help relieve your symptoms.
Stay at home while youre sick and for at least 24 hours after your fever has gone down.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication. Antiviral medications can reduce the length of your illness and may help prevent complications. They dont kill the influenza virus, however.
Antiviral medications must be taken within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms in order to be effective.
I Think I Have Influenza Should I See A Doctor
Most people who are generally healthy wont need to see their doctor for the flu. As symptoms of the flu are similar to COVID-19, talk to your doctor about testing for COVID-19 infection.
If you have the flu, try to rest, maintain a good fluid intake, and manage your symptoms. This will help you recover and prevent dehydration. Your immune system will fight the infection and symptoms will usually clear up on their own.
If you do need to see a GP for your symptoms, make sure you call ahead first so they can make sure theres no one in an at-risk group around when you have your appointment.
You May Like: Where To Go For Bladder Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Influenza
The most common symptoms of influenza are an abrupt onset of fever, shivering, headache, muscle or body ache, runny nose, fatigue and dry cough. Some people may experience vomiting and diarrhoea, although this is more common in children than adults. People can confuse influenza with a heavy cold. However, influenza is usually a more severe illness than the common cold.
For most people influenza infection is just an unpleasant illness, but for some it can become severe. The most common complications of influenza are bronchitis and pneumonia due to bacterial infections following an infection with the influenza virus.
Rarer but more severe complications are encephalitis and generalised infections. These complications often require treatment in hospital and can be life-threatening, especially for the very young, the elderly, and those in poor health.
Can The Flu Be Prevented
There’s no guaranteed way to avoid the flu. But getting the flu vaccine every year can help. Everyone 6 months of age and older should get it each year.
Most doctor’s offices, clinics, and drugstores offer the flu vaccine from September to mid-November. It’s best to get it before the end of October. But even if you don’t get it at the start of the flu season, it’s not too late to get one while the flu is still going around.
If your child is sick, has a fever, or is wheezing, talk to your doctor to see if you need to reschedule the flu vaccine.
Also Check: Medicine For Kids Ear Infection
Antigenic Drift And Shift
Two key processes that influenza viruses evolve through are antigenic drift and antigenic shift. Antigenic drift is when an influenza virus’s antigens change due to the gradual accumulation of mutations in the antigen’s gene. This can occur in response to evolutionary pressure exerted by the host immune response. Antigenic drift is especially common for the HA protein, in which just a few amino acid changes in the head region can constitute antigenic drift. The result is the production of novel strains that can evade pre-existing antibody-mediated immunity. Antigenic drift occurs in all influenza species but is slower in B than A and slowest in C and D. Antigenic drift is a major cause of seasonal influenza, and requires that flu vaccines be updated annually. HA is the main component of inactivated vaccines, so surveillance monitors antigenic drift of this antigen among circulating strains. Antigenic evolution of influenza viruses of humans appears to be faster than influenza viruses in swine and equines. In wild birds, within-subtype antigenic variation appears to be limited but has been observed in poultry.
What About Influenza Complications

In some cases of the flu, severe illness, and complications can develop. This can result in hospitalisation and even death.
People at higher risk of severe complications associated with the flu include:
- people with chronic medical conditions.
The flu can also make some existing medical conditions worse.
Also Check: Ear Infection For 3 Months
How Are Viral Infections Transmitted
Viruses replicate within the hosts cells to create copies that can be passed on, or transmitted, to others. Like bacteria, virus transmission can occur through multiple pathways. Some viruses can be transmitted by respiratory droplets when a person talks, coughs, or sneezes.
Viruses can be transmitted when you touch a surface that is contaminated and then touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. They can also be transmitted by contaminated water or food. Some viruses are spread through sexual contact or through contact with blood via needle or transfusion.
The Host Response To Influenzakey Players In Antiviral Defense And In Driving Epithelial Injury
In patients who succumb to IAV infection, lung autopsies almost always show diffuse alveolar damage, but viral RNA is present in only a subset of patients.73 These results and findings from published studies of IAV infection in animals suggest that mortality due to IAV infection may rather result from an overly exaggerated immune response than from uncontrolled viral spread. Several subsets of immune cells were found to contribute to damaging host responses, and some of the underlying molecular mechanisms have been recently defined, providing novel targets for therapeutic intervention6474 .
Key players in influenza A virus -induced lung injury. While upper respiratory tract infection results in mild symptomatic IAV infection, severe cases of IAV usually involve spread of the virus to the lower respiratory tract. Here, resident alveolar macrophages and dendritic cells sense IAV infection of alveolar epithelial type I and type II cells. Cytokine release and establishment of a proinflammatory milieu in the alveolar lumen lead to recruitment of additional monocyte-derived macrophages as well as neutrophils from the blood vessels to the site of infection. DC migration to the lymph nodes further induces generation of antigen-specific T cells into the vessel. An exuberant immune response with massive release of proinflammatory and proapoptotic mediators contributes to IAV-induced lung injury.
You May Like: Where To Go For Kidney Infection
How Is The Flu Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. The goal of treatment is to help prevent or ease symptoms.
Treatment may include medicines such as:
-
Acetaminophen. This is to help lessen body aches and fever. Don’t give aspirin to a child with a fever.
-
Cough medicine. This may be prescribed by your childs healthcare provider.
-
Antiviral medicine. This may help to ease symptoms, and shorten the length of illness. This medicine does not cure the flu. The medicine must be started within 2 days after symptoms begin.
Antibiotics arent effective against viral infections, so they are not prescribed. Instead, treatment focuses on helping ease your childs symptoms until the illness passes.
Talk with your healthcare providers about the risks, benefits, and possible side effects of all medicines.
Also make sure your child:
-
Gets lots of rest in bed
-
Drinks plenty of fluids
Who Is At Greatest Risk From Influenza Which Risk Groups Need Vaccination
Children under 18 years are more than twice as likely to become infected with influenza because they have not developed immunity to the virus. For this reason, some countries recommend routine immunisation of young children. However, with the exception of the very young, healthy children generally do not become severely ill with influenza.
The immune response in the elderly is less effective than in young people and therefore if infected, they have on average a greater risk of developing severe complications from influenza . They also more often have underlying diseases than younger adults, which increases their risk of becoming severely ill.
Other high-risk groups are people of any age with chronic medical conditions , pregnant women, and children under five years. These people are more likely to suffer from severe illness than those who are otherwise healthy.
As a result, most countries recommend annual influenza vaccination of the elderly and of those with chronic illnesses. The specific policies vary from country to country. Some countries offer vaccination against influenza to everyone over the age of 65 years, while other countries offer to everyone aged over 60, or even 55 years.
Also Check: How To Tell If Tooth Infection Is Spreading