Antibiotics For Dental Work
Certain types of dental work can cause infections elsewhere in the body. There are many different types of bacteria in the mouth. Depending on the patient, the bacteria can cause an infection in different organ systems. For example, some patients can become bacteremic, meaning they develop a bacterial infection in their blood. Others may develop pneumonia, cardiovascular infections, or inflammatory conditions. Different patients have different risk factors.
Dont Miss: Intellicast Aches And Pains
S To Take Before Surgery
In the weeks before surgery, see your dentist to check for cavities or other problems that need attention. This is because an infection from your mouth, or anywhere else in your body, can go to your knee.
Before your knee surgery, the following steps can help prevent infections:
- Antibiotics. Your healthcare team will usually give you antibiotics in the hour before surgery, and then at 24 hour intervals afterwards.
- Testing for and reducing nasal bacteria. There is some evidence that testing for Staphylococcus bacteria in the nasal passages, and using intranasal antibacterial ointment before surgery, could reduce infections.
- Washing with chlorohexidine. Some evidence says that washing with cloths soaked in chlorhexidine in the days leading up to surgery could help prevent infection. Brands include Betasept and Hibiclens.
- Avoid shaving. Opt not to shave your legs before surgery as this can increase the bacterial load.
The surgeon may recommend rescheduling your surgery if there are any changes in your medical condition, cuts or scratches on the skin, signs of a urinary tract infection, or symptoms of a cold.
Types Of Bone & Joint Infections
NYU Langone physicians are experienced in identifying and treating bone infections, known as osteomyelitis, and joint infections, or septic arthritis. These infections begin when disease-carrying bacteria enter the body, often after a trauma or a surgical procedure, and spread to the bones and joints through the bloodstream. Without prompt treatment, bone and joint infections can become long-term conditions.
Many types of bacteria can cause bone and joint infections, including Staphylococcus aureus, also called staph, Enterobacter, and Streptococcus.
Also Check: Does Keflex Treat Sinus Infection
Selection Of Oral Antibiotic Agent
Several factors should be considered when selecting oral antibiotics to treat bone and joint infections. These include the type of infection, the extent of debridement when applicable, the antibiotic susceptibility of the pathogen, antibiotic penetration into the bone and joint tissues, oral bioavailability and cost. The drug selected must have activity against the isolated organism and have a low risk for the development of adverse reactions and drugdrug interactions.
The presence of a foreign body may also be one of the most important factors in choosing the antibiotic regimen. In the presence of a foreign body, there are slow-growing or adherent organisms in biofilms, against which antibiotic efficacy is diminished. Therefore, for managing staphylococcal bone and joint infections, especially implant-associated infections, an optimal antibiotic agent should have activity against surface-adherent, slow-growing and biofilm-associated pathogens. It is notable that standard antibiotic susceptibility tests, which evaluate drug efficacy on freely growing bacteria in the logarithmic growth phase, are not reliable in predicting the outcome of implant-associated bone and joint infections. Their only use is to exclude antibiotic agents without in vitro efficacy.
Is The Infected Fluid Drained
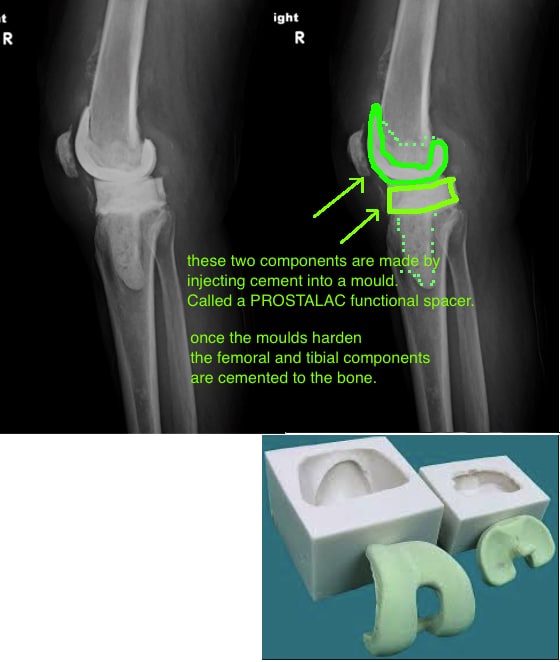
Drainage of the infected area is critical for rapid clearing of the infection. Drainage is performed by removing the fluid with a needle and syringe. Often the draining occurs daily or with multiple surgical procedures. The exact method depends on the location of the joint.
Using arthroscopy, your doctor can irrigate the joint and remove the infected tissue. If drainage cannot be accomplished with joint aspirations or arthroscopy, open joint surgery is often necessary to drain the joint. If the fluid buildup is significant, the drains are left in place to remove excess fluid that may build up after the surgery.
Don’t Miss: Otc Urinary Tract Infection Relief
Prevention Of Knee Infection
You can prevent a knee infection by following simple measures including:
- Discussing with your doctor various ways to prevent infection if you take medications for rheumatoid arthritis or HIV-AIDS, or if you are diabetic.
- Have your joints assessed by your doctor on a regular basis. Check for any sores or cuts which may further lead to infection.
- Do not ignore insect, spider or animal bites.
- Do not ignore any other infections in your body.
- Avoid intravenous drug use.
Why Patients With Joint Implants No Longer Need Antibiotics Before A Dental Visit
QUESTION: When my knee was replaced with an artificial joint, the surgeon said I should always take antibiotics before any dental procedure. He said the bacteria in my mouth could get into my bloodstream and cause an infection around the implant. But my dentist said not to worry and that I actually dont need antibiotics. Who is correct?
ANSWER: For several years, orthopaedic surgeons and dentists have given conflicting advice about whether a patient with a prosthetic joint implant needs antibiotics to prevent potential infections a practice known as antibiotic prophylaxis.
The surgeons believed that antibiotics were necessary because a joint infection could jeopardize the implant. Dentists, on the other hand, felt that mouth bacteria didnt pose a risk to the implants and patients shouldnt be taking the drugs needlessly.
The mixed messages have certainly caused confusion for a lot of patients. But, thankfully, the dentists and surgeons have finally settled their differences and come to a common position. After reviewing the available scientific evidence, they recently concluded that antibiotics arent needed before dental procedures after all.
The national bodies that represent the two professions , plus infectious disease specialists have issued a joint statement calling for an end to the practice.
To understand how we got to this point, its worthwhile reviewing the long history of this controversy.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Over A Yeast Infection Without Treatment
What Is The Difference Between Septic Arthritis And Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are both rare and serious conditions. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone. Septic arthritis is inflammation in the surface of the cartilage that lines the joint and the synovial fluid that lubricates the joint that is caused by an infection. Both conditions are usually caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis can be tricky to tell apart because they have similar symptoms, including pain, tenderness and swelling in the affected area. Septic arthritis can lead to osteomyelitis, and you can have both at the same time. If you have symptoms of osteomyelitis and/or septic arthritis, go to the nearest hospital immediately. Both conditions need medical treatment. Your healthcare provider will perform certain tests to determine which condition is causing your symptoms.
Antibiotics Used To Treat Mrsa Bone Infection
Teicoplanin has been particularly useful, enabling patients to be discharged from hospital while continuing with parenteral therapy as it can be given by bolus injection once daily or less frequently.,, Bone concentrations of a mean of 65% serum concentrations have been measured 3 h post injection during cardiac surgery. A summary of non-comparative studies has demonstrated between 50% and 100% efficacy for bone infections , although this would incorporate the initial studies using lower doses with decreased efficacy. While streptococcal infections are particularly amenable to treatment with teicoplanin, higher doses to give high trough serum concentrations appear necessary to treat deep-seated staphylococcal bone infection.,, Le Frock et al. used doses of 612 mg/kg to treat bone and joint infection in 90 evaluable patients. After an average of 6 weeks therapy for osteomyelitis and 3 weeks for septic arthritis, cure rates were 90%, 88% and 100% for acute and chronic osteomyelitis and septic arthritis, respectively. The reasons for selection of higher doses for some osteomyelitis patients in this study were not clear 12 mg/kg is recommended for septic arthritis.
Recommended Reading: Can Urgent Care Treat A Kidney Infection
How Long Does It Take For Antibiotics To Work For Knee Infection
A symptom can be relieved if the antibiotics are effective within 48 hours. For those with severe illnesses, IV antibiotics may be required for 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the severity of the condition. IV antibiotics are usually given to people at home as a routine measure by doctors. Following that, oral antibiotics may be prescribed for another two to six weeks.
Recognizing The Signs Of A Blood Clot
Follow your orthopaedic surgeons instructions carefully to reduce the risk of blood clots developing during the first several weeks of your recovery. He or she may recommend that you continue taking the blood thinning medication you started in the hospital. Notify your doctor immediately if you develop any of the following warning signs.
Warning signs of blood clots. The warning signs of possible blood clots in your leg include:
- Increasing pain in your calf
- Tenderness or redness above or below your knee
- New or increasing swelling in your calf, ankle, and foot
Warning signs of pulmonary embolism. The warning signs that a blood clot has traveled to your lung include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sudden onset of chest pain
- Localized chest pain with coughing
Don’t Miss: Heal Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
What Are The Risk Factors For Developing Septic Arthritis
The risk factors for developing septic arthritis are different for children and adults. Risk factors for children include:
- Age: Newborn children are at a higher risk of getting septic arthritis because their immune systems arent as strong.
- Having hemophilia: Children who have hemophilia, an inherited bleeding disorder in which their blood does not clot properly, are at a higher risk of developing septic arthritis.
- Having a weakened immune system: Children who are immunocompromised from conditions like sickle cell anemia and HIV have a higher risk of getting septic arthritis.
- Being on chemotherapy: Chemotherapy weakens your immune system, which makes it more likely that people undergoing it will develop septic arthritis.
Risk factors for adults include:
How Do You Know If You Have An Infection In Your Knees
You may be unable to move your knee due to pain or stiffness. Its chills and nausea. This fever can cause severe problems for days or weeks. A knee swelling can cause discomfort.
Injury, surgery, infection, or infection elsewhere in your body can all lead to knee problems. Every year, an estimated 14 million people in the United States seek medical attention for soft tissue infections. There are certain joint conditions that can increase your chances of developing an infection, such as rheumatoid arthritis and immune-suppressing medications. When there is inflammation in your knee, you may have knee bursitis. An bursae is a fluid-filled sac in the knee that aids in the protection of the knee from infection. Bacteria can cause an infection in these sacs if they penetrate them. As the infection spreads throughout the rest of your body, you may experience swelling.
You will need to have fluid surrounding your joint removed if your knee is infected. When your infection has not improved, you can take intravenous antibiotics. Oral antibiotics can be given for up to six weeks. If you have more serious issues, you may require open surgery to remove infected fluid as well as damaged tissue.
Also Check: Can Men Get Yeast Infections From Women
Is There A Virus That Attacks Your Joints
Joint pain and swelling are common symptoms of viral infections in this type of patient. Parvovirus B19, also known as the fifth disease , is known to cause swelling, pain, and anemia in some people. Viruses such as enterovirus, rubevirus, HIV, and hepatitis B and C are also known to cause viral arthritis.
Treatment Of Knee Infection
Treatment involves the use of antibiotics which are either prescribed orally or intravenously. Joint drainage may be necessary to drain infected fluid surrounding your knee joint. A large needle may be used to drain the fluid. Very serious infections may be treated by arthroscopy or open surgery. This involves removal of infected fluid and tissue and changing out the prosthesis if needed.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Bladder Infection After Intercourse
If Youve Had Joint Replacement You May Need Antibiotics Before Dental Work
If youve had a total joint replacement or similar procedure, you will want your surgeon to decide if you need to take an antibiotic before you undergo dental work. This is a precaution to prevent a serious infection known as bacteremia.
Bacteremia occurs when bacteria become too prevalent in the bloodstream and cause infection in other parts of the body, especially in joints and bone with prosthetic substances. Its believed that during invasive dental procedures bacteria in the mouth can enter the bloodstream through incisions and other soft tissue disruptions.
Joint infections are a serious matter and can require extensive therapy to bring it under control. Out of this concern, the use of antibiotics as a prophylactic against bacteremia once included a wide range of patients for a variety of conditions and procedures. But after an in-depth study in 2007, the American Dental Association concluded that the risks for many of these patient groups for infection triggered by a dental procedure was extremely low and didnt warrant the use of antibiotic premedication therapy.
The guidelines for antibiotic premedication can be complex. Its best, then, to speak with both your orthopedic surgeon and us about whether you should undergo antibiotic therapy before you undergo a dental procedure. The ultimate goal is to reduce the risks of any disease and to keep both your mouth and your body safe from infection.
Knee Pain Caused By Infection
Infection can cause knee pain in a few ways. The first is when an infection develops in or around the knee joint itself. This is called , and it can be extremely painful. The second way is when an infection elsewhere in the body, such as in the lungs or urinary tract, spreads to the knee through the bloodstream. This is called osteomyelitis, and it can also be quite painful. Treatment for both types of infection usually involves antibiotics.
Bacteria and other microorganisms commonly infect the tissues surrounding or inside the knee joint. Joint pain can be caused by a separate infection, such as a stomach virus, causing an auto-immune reaction. If you have septic arthritis, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. You will feel a sensation of tender tissue and swelling if you have a swollen bursa. Acute knee pain does not typically result in fever or other flu-like symptoms. Joint pain can be caused by late-stage Lyme disease or other infections, though it is less common. A knee joint brace can be used to relieve pressure and joint pain.
Hydroxyquinolone antibiotics, statin medications, and aromatase inhibitors are among the most common medications that cause joint and muscle pain. If you think you are experiencing joint or muscle pain as a result of taking a medication, you should consult with your healthcare provider.
You May Like: Eye Infection In Dogs Medication
What Kind Of Infection Makes Your Joints Hurt
There are many different types of infections that can cause joint pain. Some common infections that may cause joint pain include: bacterial infections, such as Lyme disease or septic arthritis viral infections, such as hepatitis C or parvovirus and fungal infections, such as candidiasis or histoplasmosis. In some cases, joint pain may also be caused by autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis. Treatment for joint pain will vary depending on the underlying cause.
If bone and joint infections are not treated quickly, they can lead to long-term problems. Disease-carrying bacteria enter the body and spread through the bloodstream, starting these infections. An infection elsewhere in the body, such as a urinary tract infection or pneumonia, is responsible for osteomyelitis, which spreads through the bloodstream to the bones. It is defined as the inflammation of a joint as a result of bacterial or fungal infection. Older people are more likely than infants to develop septic arthritis because their anatomy and blood supply to their joints are weak. The joint can become severely damaged if septic arthritis causes severe damage to its cartilage and bone.
Implants And The Biofilm
The implantation of prostheses itself predisposes to infections and makes it more difficult to control already established infections. In Zimmerlis classic animal model experiment , a population of guinea pigs had subcutaneous, rigid and perforated polymethacralate and polytetrafluoroethylene tubes implanted. In those which had the tubes removed, no abscesses developed, whilst those in which the implants remained developed infection in 95% of the population. The same experiment also suggested a decreased ability for opsonization in the presence of the implant as well as decreased bactericidal properties of polymorphonuclear leukocytes . The avascular nature of the implant prevents the access of cells facilitating the immunological response to bacteria. Furthermore, the presence of the implant reduced the minimal dose of Staph Aureus required to form an abscess by 10,000 folds from 106 to 102. Surrounding the implant is an area described as the immuno-incompetent fibroinflammatory zone . Within this zone, any cellular immune responses initiated result in the formation of superoxide radicals and cytokine mediated activity causing damage to the surrounding tissues and bringing about implant loosening .
As the biofilm increases in size, planktonic bacteria are released, subsequently forming secondary colonies .
Don’t Miss: My Ear Infection Is Getting Worse
How Is Septic Arthritis Diagnosed
A procedure called arthrocentesis is commonly used to make an accurate diagnosis of septic arthritis. This procedure involves a surgical puncture of the joint to draw a sample of the joint fluid, known as synovial fluid. Normally, this fluid is sterile and acts as a lubricant.
During arthrocentesis, a needle is inserted into the affected joint to collect fluid from the joint. The fluid sample is sent to a lab for evaluation. The lab will perform a white cell count on the fluid, which will usually be very high. The lab will also try to culture bacteria or other organisms. This will help the doctor determine if an infection is present and which organism is causing it.
X-rays are typically done to look for joint damage. Blood tests can also be used to monitor inflammation. MRI scanning is sensitive in evaluating joint destruction but is less useful in the early stages . Blood tests can also be taken to detect and monitor inflammation.