The Difference Between Aids
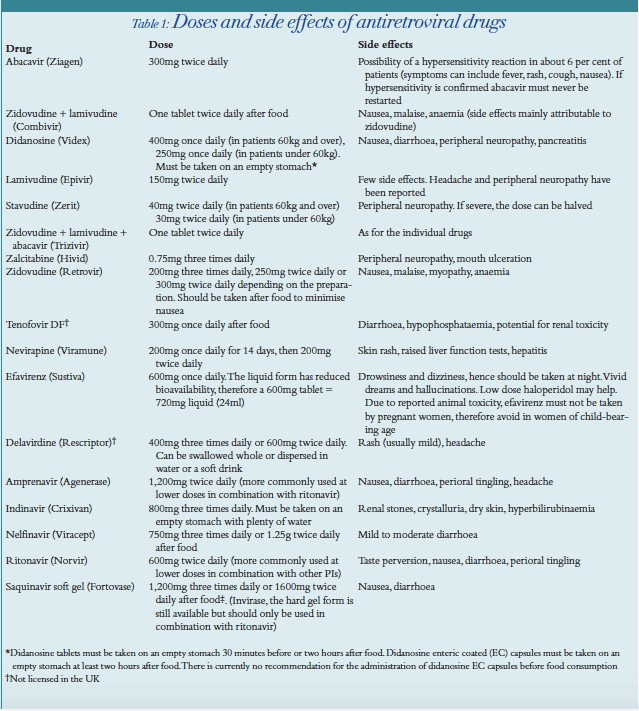
AIDS-defining illnesses are directly linked with the damage of the immune system as a result of HIV infection. AIDS-defining illnesses tend to occur in the later stages of the disease in patients who have not received antiretroviral treatment for HIV infection and who have a very low CD4 count. HIV may be initially diagnosed when these patients present to the doctor to the first time with one of these infections or cancers. When a person gets one of these illnesses, he or she is diagnosed with the advanced stage of HIV infection known as AIDS.
Opportunistic infections occur more often or more frequently when the immune system is weak, as with HIV/AIDS. People with weakened immune systems include people living with HIV/AIDS, but might also include people with cancers of the immune system like leukemia or multiple myeloma, or immune-complex diseases like viral hepatitis.
What Is Hepatitis And How Can I Prevent It
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are common co-infections for people with HIV, especially people who inject drugs. Both are preventable and treatable. Talk to your healthcare provider about how often you should test for them.
Using a condom and not sharing needles can prevent hepatitis. You can also get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Primary Prophylaxis As The Standard Of Care
P jiroveci pneumonia
Indications for PCP prophylaxis include a CD4 count of fewer than 200 cells/L or less than 14% of lymphocytes . The preferred regimen is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 1 double-strength tablet orally daily or 1 double-strength tablet orally 3 times weekly. Alternatives include dapsone 100 mg orally daily , aerosolized pentamidine 300 mg administered via the Respirgard II nebulizer monthly , or atovaquone suspension 750 mg orally twice daily).
Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and exposure
Tuberculosis is both the leading cause of death from infectious disease globally and the leading cause of morbidity and mortality among people living with HIV. Screening for TB in the HIV-infected population has been suboptimal, with only 47% to 65% of patients completing screening. The most common predisposition for TB is birth or residence outside of the United States. All persons with HIV should be tested for LTBI regardless of their epidemiologic risk for TB exposure . All newly-diagnosed patients with HIV infection should be screened with a tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma release assay , and re-screened once the CD4 count rises to 200 if initially less.
Active TB should be excluded by lack of symptoms and negative chest radiograph before prophylactic regimens are started. Active TB may be more likely in a patient with previous active TB than in a patient without a history of TB.
M avium complex infection
Toxoplasma gondii infection
Syphilis
Don’t Miss: Does Monistat Clear Up Yeast Infections
Mycobacterium Avium Complex In Hiv
Mycobacterium avium complex is a common AIDS infection caused by a bacterium related to tuberculosis, as well as Mycobacterium intracellulare or Mycobacterium kansasii. The mycobacteria are present in the soil and rarely cause issues for those with a healthy immune system.
Normally, the bacterium causes an infection of the respiratory tract but, in advanced HIV or AIDS, an infection can affect almost any internal organ, including the bone marrow, liver or spleen. MAC causes nonspecific symptoms such as cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue, stomach pain, and diarrhea.
MAC is particularly dangerous in those with a CD4 count of 50 cells/mm3 or less.
You May Like: Z Pack Vs Amoxicillin For Sinus Infection
Are Opportunistic Infections Common In People With Hiv
OIs are less common now than in the early days of HIV and AIDS when there was no treatment. Todays HIV medicines reduce the amount of HIV in a persons body and keep the immune system stronger and better able to fight off infections.
However, some people with HIV still develop OIs for reasons such as:
- they do not know they have HIV and so they are not on treatment
- they know they have HIV but are not taking ART
- they had HIV for a long time before they were diagnosed and so have a weakened immune system
- they are taking ART, but their drug combination is not working as expected and is not keeping their HIV levels low enough for their immune system to fight off infections
You May Like: Middle Ear Infection Over The Counter
How Aids May Lead To An Opportunistic Infection
Because people with AIDS have weakened immune systems, theyre more prone to infections, called opportunistic infections. Opportunistic infections are caused by organisms that typically dont cause disease in healthy people but affect people with damaged immune systems . These organisms attack when theres an opportunity to infect.
Why does AIDS cause death by opportunistic diseases?
The infections are called opportunistic because they take the opportunity to attack you when your immune system is weak. The cancers are called AIDS related because they appear mostly in people who have advanced, later-stage HIV infection, known as AIDS. Most people who die of AIDS do not die from the virus itself.
Recommended Reading: Is Ampicillin Good For Tooth Infection
How Can You Prevent Getting Opportunistic Infections
If you have HIV, the best thing you can do to stay healthy and prevent OIs is to take ART exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral loadâa level of HIV in your blood so low that a standard lab test canât detect it.
It is also important to stay in HIV medical care and get lab tests done. This will allow you and your health care provider to know when you might be at risk for OIs and discuss ways to prevent them.
Some of the ways people with HIV can reduce their risk of getting an OI include:
- avoiding exposure to contaminated water and food
- taking medicines to prevent certain OIs if your CD4 count is below 200
- getting vaccinated against some preventable infections
- avoiding cat litter
Recommended Reading: How To Heal A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
List Of Common Opportunistic Infections In Hiv And Aids
The symptoms of AIDS are primarily the result of infections known as opportunistic infections that do not normally develop in individuals with healthy immune systems. OIs are less common today because of advances in HIV treatments and the ability to help keep a persons immune system stronger.
These are some of the most common HIV-related opportunistic infections seen in clinical practice, as noted by the CDC.
Recommended Reading: Eye Infection Doctor Or Optometrist
Will I Get Other Health Conditions Because I Have Hiv
Not necessarily. Having HIV does not automatically mean you will get other health conditions . But you are more at risk of developing them if you do not look after yourself. Its important to take your antiretroviral treatment and to have a healthy lifestyle.
If you have HIV, your doctor will look for signs of other health conditions in your check-ups. They can also give you more information about conditions that are linked to HIV that will help you make sense of it all.
You May Like: Can Urgent Care Treat A Kidney Infection
Fungal Or Yeast Infections
According to current NIH guidelines, Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida infections do not warrant primary prophylaxis. In the case of Cryptococcus infection, primary prophylaxis has not been shown effective in Thailand. New WHO guidelines recommend cryptococcal antigen testing and preemptive therapy in antigen-positive patients with a CD4 count < 100 cells/uL in Africa and other areas of high prevalence. Prolonged suppressive therapy for Candida is not recommended owing to risk of resistance. However, if necessary because of frequent recurrence or severe disease, fluconazole 100 mg PO thrice weekly for thrush , fluconazole 100-200 mg daily , or fluconazole 150 mg PO once weekly are the first recommended drugs.
Fortunately, aspergillosis and phycomycosis are rare in individuals infected with HIV. These infections should be considered in patients with invasive sinusitis and focal pulmonary lesions but do not warrant prophylaxis.
Travelers to malaria-prone areas should have malaria prophylaxis, and those who live in such areas should practice preventative measures, such as the use of treated mosquito netting.
Can You Prevent Opportunistic Infections
Opportunistic infections are less common in the U.S. now than they were in the past due to advances in detection times and treatment options. If you have been diagnosed with HIV, the best way to prevent complications is to visit your doctor on a regular basis, take your medications as prescribed, and learn to help to protect your immune system.
- Continue to use safe sex practices to help avoid getting other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Do not share needles or other equipment that has been used by others. This can increase your risk for contracting hepatitis.
- Get vaccinated – speak to your doctor about which vaccines you should get, and if you need them only once or on a regular basis.
- Avoid foods that might be contaminated, such as unpasteurized or raw milk and cheese, unpasteurized fruits juices, raw seed sprouts, undercooked eggs , undercooked or raw meats and seafood, or untreated water.
- Do not touch animal feces that may spread germs that can lead to OIs. If you touch feces, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
Recommended Reading: When To See A Doctor For Yeast Infection
Cd4 Counts And Infections
CD4 cells are white blood cells that fight infection. CD4 cell count is an indicator of immune function and disease progression and one of the key determinants for the need of opportunistic infection prophylaxis. CD4 cell counts are obtained from bloodwork as part of laboratory monitoring for HIV infection.
Studies have shown that starting HIV medicines soon after you are diagnosed, and ideally when your CD4 cell count is high, will greatly help your health and will reduce the risk of OIs. Regularly checking your CD4 cell count will allow you to begin necessary prophylactic medications to reduce your risk of opportunistic infections.
Predictors Of Oi Among Patients Living With Hiv On Art
Residency, functional status, disclosure status, WHO clinical stage, drug adherence, taking CPT, BMI, hemoglobin level, and CD4 count were variables for multivariable analysis. Of these: functional status, WHO clinical staging, CD4 counts, and ART drug adherence were found to be significant predictors of OI. In this study, the hazard of developing OI among PLWHIV classified as bedridden at baseline was 1.6 times higher than those classified as working functional status. Similarly, the hazard of developing OI among PLWHIV classified as WHO clinical stage IV at baseline was 2.1 times higher than those classified as WHO Stages I.
On top of that, the hazard of developing OI among PLWHIV who had poor adherence was 1.7 times higher than those classified as having good adherence. KaplanMeier analysis for specific OI in different categories of adherence level showed no crossing of lines between the poor and good adherence level.
Moreover, the hazard of developing OI among HIV- positive patients who had low CD4 count at baseline was 1.92 times times higher than those categorized as CD4 count of 351 cells. The goodness of fit for the model is illustrated using a Cox-Snell residual test.
|
Figure 5 The goodness of fit test for the Cox-proportional hazard regression model. |
Dont Miss: Can Metronidazole Treat Sinus Infection
Also Check: Can You Take Yeast Infection Medication While On Antibiotics
How Can You Prevent These Opportunistic Infections
The best way to prevent these OIs is to take antiretroviral drugs just before HIV progresses to AIDS. Staying in HIV medical care and regular testing are essential to staying healthy despite the presence of HIV loads throughout the body. Aside from taking HIV medications, the following are also necessary:
- Receiving vaccinations for other illnesses.
- Lessening risk for infections from contaminated food and water.
- Avoid sharing needles and syringes.
- Using condoms when engaging in sexual activity.
Clinical Laboratory And Medication
Describing on functional status, half of study participants were classified as working functional status. The mean baseline CD4 cell count was 342.04 cell/mm3 . Clinically, one-third of the study participants were classified as WHO clinical stage II. Besides, 87.3% of study participants had 10 g/dl and above hemoglobin level. At baseline, one-third of the participants were undernourished . Patients were taking a standardized three-drug ART regimen. These three drug regimens used in different combinations were tenofovir , lamivudine , nevirapine , zidovudine , and efavirenz . We found that the commonly taken regimen combinations by patients living with HIV were: TDF+3TC + EFV , TDF+3TC + NVP , AZT+3TC + NVP , and Others . Majority of the participants had a history of good adherence. Moreover, 79.7% of participants used CPT, but, below half , received IPT.
|
Table 2 Clinical, Laboratory, ART, and Other Medication-Related Information of HIV Patients on HIV Care at Dessie Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northeast, Ethiopia |
Also Check: Best Remedy For Infected Tooth
Temporal Trends And Aging In Neurologic Manifestations Of Hiv Infection
The spectrum of CNS complications of HIV-1 diseases is constantly evolving, and both quantitative and qualitative changes have been noted in recent years.76,281 Patients are living longer with ART, but they may become resistant to antiretrovirals. The clinical presentation of known diseases such as PML may be altered by ART-induced immune reconstitution,176 and new entities, such as severe HIV-associated leukoencephalopathy, have been described in ART-experienced individuals.281,282 Expanded tropism of JCV to cerebellar neurons has been demonstrated, which may have implications in the pathogenesis of cerebellar atrophy occurring in HIV-infected individuals.283 In addition, PIs are associated with a marked increase in serum cholesterol and triglycerides. Therefore long-term HIV-1infected individuals are at increased risk of developing cerebrovascular events.283,284 Stroke usually occurs in younger patients infected with HIV-1 compared with HIV-negative individuals, and, in some cases, it may be caused by a vasculopathy.285
Can Ois Be Treated
There are many medicines to treat HIV-related OIs, including antiviral, antibiotic, and antifungal drugs. The type of medicine used depends on the OI.
Once an OI is successfully treated, a person may continue to use the same medicine or an additional medicine to prevent the OI from coming back. The Clinical Info Drug Database includes information on many of the medicines used to prevent and treat OIs.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Cure A Bladder Infection
What Is An Opportunistic Infection
Opportunistic infections are infections that occur more often or are more severe in people with weakened immune systems than in people with healthy immune systems. People with weakened immune systems include people living with HIV.
OIs are caused by a variety of germs . OI-causing germs spread in a variety of ways, for example, in the air, in body fluids, or in contaminated food or water. Some OIs that people with HIV may get include candidiasis, Salmonella infection, toxoplasmosis, and tuberculosis . The Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in Adults and Adolescents with HIV provide detailed information on HIV-related OIs.
Most Common Ois In People Living With Hiv
Since combination antiretroviral treatment for HIV became available, the number of people living with HIV who have had opportunistic infections has dropped drastically. If you start HIV treatment early and continue to take your HIV drugs as they are prescribed, you will keep your immune system strong and likely never get one of these OIs. This means you will also likely never be diagnosed with AIDS.
Some of the most common opportunistic infections in people living with HIV include:
| Opportunistic Infection |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Does Zpack Treat Sinus Infection
Opportunistic Infections Vs Aids
While AIDS-defining illnesses can also be classified as opportunistic infections, the opposite is not necessarily true. Opportunistic infections are those caused by otherwise common, harmless viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites which can cause disease when immune defenses have been compromised.
Many opportunistic infections are not life-threatening and can develop even when a persons CD4 count is high. AIDS-defining illnesses, by contrast, tend to appear during later-stage disease when the CD4 count has dropped significantly.
Some opportunistic infections, such as herpes simplex, are only considered to be AIDS-defining when they spread beyond the tissue or organ where they are typically seen.
Dont Miss: Fungal Infection In Hiv Patient
Incidence Of Ois In Art
The most common OIs in ART-naive participants were oral candidiasis , unspecified tuberculosis , herpes zoster , PTB , bacterial pneumonia , and GUD . There were some differences in incidence across the regions based on a comparison of the 11 OIs and coinfections for which there was at least 1 study per region . There were no data available in ART-naive participants in Latin America for esophageal candidiasis, GUD, Cryptosporidium, PTB, or bacterial infections, or in Asia for bacteremia or enteritis. Overall, there was a slightly lower reported risk of all OIs except GUD and bacterial pneumonia in sub-Saharan Africa unspecified tuberculosis was most commonly diagnosed in Asia , and PCP , toxoplasmosis , and Kaposi sarcoma in Latin America.
Summary incident risk of each opportunistic infection by region and overall for antiretroviral therapy naive patients , and during the first year of ART . Abbreviations: GUD, genital ulcer disease HSV, herpes simplex virus PCP, Pneumocystis pneumonia TB, tuberculosis.
Also Check: Eczema In Ear Causing Infection
Also Check: Sinus Infection And Dry Eyes
Do People Infected With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Have An Increased Risk Of Cancer
Yes. People infected with HIV have a substantially higher risk of some types of cancer compared with uninfected people of the same age . The general term for these cancers is HIV-associated cancers. Three of these cancers are known as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome -defining cancers or AIDS-defining malignancies: Kaposi sarcoma, aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and cervical cancer. A diagnosis of any of these cancers in someone infected with HIV confirms a diagnosis of AIDS.
Compared with the general population, people infected with HIV are currently about 500 times more likely to be diagnosed with Kaposi sarcoma, 12 times more likely to be diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and, among women, 3 times more likely to be diagnosed with cervical cancer .
In addition, people infected with HIV are at higher risk of several other types of cancer . These other malignancies include cancers of the , liver, oral cavity/pharynx, and lung, and Hodgkin lymphoma .
In addition to being linked to an increased risk of cancer, HIV infection is associated with an increased risk of dying from cancer. HIV-infected people with a range of cancer types are more likely to die of their cancer than HIV-uninfected people with these cancers .