Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person develops HIV. But this isnt the case for everyone as, according to HIV.gov, symptoms may not appear for a decade or longer.
Although the virus replicates quickly in the weeks after contracting it, symptoms in early HIV only tend to show up if the rate of cell destruction is high.
This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious or that an asymptomatic person cant transmit the virus to others.
What Are The Four Stages Of Hiv
The World Health Organization classifies human immunodeficiency virus into four stages
- Stage 1 : The CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage 2 : The CD4+ cell count is 350 to 499.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is 200 to 349.
- Stage 4 : The CD4+ cell count is less than 200.
The normal CD4+ cell count should be between 500 and 1600 cells per microliter. The higher the CD4+ cell count, the lower the chances of opportunistic diseases.
Early Symptoms Of Hiv
Acute HIV infection is the period immediately following exposure to the virus in which the immune system mounts an aggressive defense to control the virus. During this phase, anywhere from 50% to 90% of people will experience flu-like symptoms referred to as acute retroviral syndrome .
Symptoms of ARS tend to develop with two to four weeks of exposure and may include:
Acute symptoms tend to clear within 14 days but may last for several months in some people. Other people may have no symptoms at all.
You May Like: Screening For Sexually Transmitted Infections Icd 10
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself With Hiv

The best way to take care of yourself while living with HIV is to follow your treatment plan.
- Make sure to take your medications as prescribed and on time.
- Show up to all appointments so your healthcare team can monitor how youre feeling and know if theres a need to adjust your treatment.
- Follow your healthcare providers recommendations on how to avoid additional illnesses.
You May Like: How Many People Are Infected With Hiv
How Can You Tell If You Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. You canât rely on symptoms to tell whether you have HIV.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information so you can take steps to keep yourself and your partner healthy:
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV. People with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long and healthy lives and will not transmit HIV to their HIV-negative partners through sex. An undetectable viral load is a level of HIV in the blood so low that it canât be detected in a standard lab test.
- If you test negative, you have more HIV prevention tools available today than ever before, like pre-exposure prophylaxis , medicine people at risk for HIV take to prevent getting HIV from sex or injection drug use, and post-exposure prophylaxis , HIV medicine taken within 72 hours after a possible exposure to prevent the virus from taking hold.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If you have HIV and take HIV medicine as prescribed throughout your pregnancy and childbirth and give HIV medicine to your baby for 4 to 6 weeks after giving birth, your risk of transmitting HIV to your baby can be less than 1%. HIV medicine will protect your own health as well.
Use the HIV Services Locator to find an HIV testing site near you.
Causes Of Hiv Infection
It’s a fragile virus and does not survive outside the body for long.
HIV cannot be transmitted through sweat, urine or saliva.
Other ways of getting HIV include:
- sharing needles, syringes or other injecting equipment
- transmission from mother to baby during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding
The chance of getting HIV through oral sex is very low and will be dependent on many things, such as whether you receive or give oral sex and the oral hygiene of the person giving the oral sex.
Also Check: Lower Back Pain Tooth Infection
Is There A Cure
In 2008, scientists reported that Timothy Ray Brown, an American living in Berlin, was effectively “cured” of HIV following an experimental stem cell transplant. Despite the promise of a cure, the procedure proved highly risky, and subsequent attempts to repeat the results were either mixed or failed.
To date, only three other people have been declared “cured” of HIV. Even so, the insights gained from Brown and the others provided a general template for HIV cure research.
Today, scientists are largely focused on a “kick-kill” strategy. This involves designing medications able to “kick” HIV out of its hidden reservoirs, followed by drugs, vaccines, or immunotherapies that can effectively “kill” the newly released viruses. Research is ongoing.
Other scientists are focused on developing a “functional cure” for HIV. This is a vaccine that doesn’t eradicate HIV but instead prevents it from progressing without the need for antiretroviral drugs.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Most people have no symptoms or just a mild flu-like illness when they are first infected, and it may be difficult to tell the HIV apart from other viral infections. This illness, called seroconversion illness, often occurs around 10 to 14 days after infection.
Seroconversion illness can have a range of symptoms, including:
- swollen lymph glands in the neck, underarm or groin areas
After the initial illness, people with HIV infection usually have no other symptoms. However, the virus remains in the body.
Recommended Reading: Ear Nose And Throat Infection
How To Prevent Hiv From Progressing
The most effective way is to take antiretroviral medication as soon as possible and to do so consistently as prescribed.
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero.
The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the persons outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
Racial Sexual And Age
In the United States, the rate of HIV infection is highest in Blacks . The prevalence is also high among Hispanic persons . These increased rates result from socioeconomic factors rather than genetic predisposition.
In the developed world, HIV infection is much more common in males. In 2015, males accounted for 81% of all diagnoses of HIV infection among adults and adolescents in the United States. Among heterosexuals, females are more likely to acquire HIV infection from an infected male than a male is from an infected female, but a large proportion of infections in males are due to homosexual contact, with or without injection drug use. Males are also more likely to acquire HIV infection from injection drug use alone.
Males were also more likely to acquire HIV infection through contaminated blood products for treatment of hemophilia before universal testing of the blood supply was instituted. The risk of HIV exposure from factor VIII concentrates has been virtually eliminated by viricidal treatment of plasma-derived factor VIII concentrates, as well as the introduction of recombinant factor VIII concentrates and the gradual elimination of albumin from the production process used for these products.
In the developing world, HIV infection is equally common in males and females. The primary route of HIV transmission in the developing world is heterosexual contact.
Read Also: Strong Antibiotics For Kidney Infection
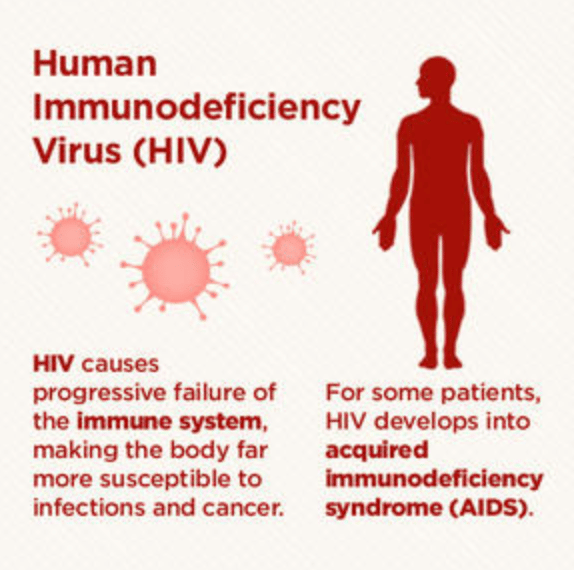
What Are Hiv & Aids
HIV is a virus called Human Immunodeficiency Virus which causes HIV infection. Once the virus enters the body, it attacks the CD4 cells in the immune system, and leaves its genetical materials in the cell. It uses the DNA of CD4 cell for self-reproduction and mixes back with blood in larger amounts by destroying the cell. It gradually causes the cells of the immune system to decrease, and destroys the defense system against other bacterial or viral diseases.
AIDS, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, is the advanced stage of HIV infection. It decreases the number of the main cells in the immune system, CD4 cells, by infecting them. If the disease is not treated after the virus is transmitted, the immune systems defense starts to fail within 10-12 years. When defense is insufficient, the body becomes vulnerable to all infections, and sometimes more than one infection occur. AIDS is the stage when the immune system fails to function due to HIV and other infections called opportunistic infections occur, sometimes alone and sometimes together. AIDS is not a disease in its own right.
Often-used definitions such as AIDS disease, AIDS patient or person with AIDS are wrong. People who are diagnosed during the time when cells of immune system decrease and diseases called opportunistic infections occur are the ones diagnosed with HIV infection at AIDS stage. Anyone living with HIV is not at AIDS stage, and people taking treatment never get to AIDS stage throughout their lives.
Stage : Aids Infection
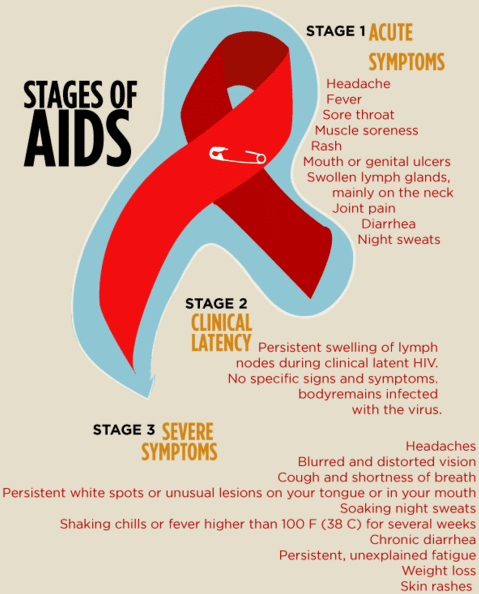
If a person with HIV does not receive effective treatment, the virus weakens the bodys ability to fight infection, finally leading to AIDS. According to the CDC, a persons life expectancy is reduced to 3 years in case of a lack of proper treatment. However, with effective and timely medication, HIV may never even progress into its following stages.
Additionally, The chances of HIV progressing to AIDS vary from person to person depending on various factors such as age, underlying health condition, genetic resistance to the particular HIV strain and the strain of HIV.
Various opportunistic infections and cancers help doctors identify this stage of HIV infection. Alongside, there are other symptoms as well.
Symptoms of AIDS infection
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Persistent fever
Even though most of these symptoms are gender-neutral and there are a few particular ones as well.
Also Check: When To See A Doctor For Yeast Infection
What Is Hiv And Aids
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which is the virus that causes HIV infection. The abbreviation HIV can refer to the virus or to HIV infection.
AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
HIV attacks and destroys the infection-fighting CD4 cells of the immune system. The loss of CD4 cells makes it difficult for the body to fight off infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can gradually destroy the immune system and HIV infection advances to AIDS.
How Is Hiv Treated
There is no vaccine or cure for HIV infection. However, there are effective treatments that can prevent the transmission of HIV and the progression to AIDS, and help ensure a near-normal life expectancy.
These treatments are known as antiretroviral therapy . They stop the virus from reproducing itself, which leads to a lower viral load. The treatment involves a combination of drugs used together.
HIV-positive people who take ART daily exactly as prescribed and achieve an undetectable viral load cant sexually transmit the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
Thanks to the improvements in treatment, HIV infection is now a manageable chronic disease for many people in countries like Australia.
Don’t Miss: Can A Tooth Infection Give You An Ear Infection
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for a reduced cost or for free.
Learn more about HIV self-testing and which test might be right for you.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it more difficult for some people to access traditional places where HIV testing is provided. Self-testing allows people to get tested for HIV while still following social distancing practices. Ask your local health department or HIV service organization if they offer self-testing kits.
What Are The Treatments For Hiv/aids
There is no cure for HIV infection, but it can be treated with medicines. This is called antiretroviral therapy . ART can make HIV infection a manageable chronic condition. It also reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Most people with HIV live long and healthy lives if they get and stay on ART. It’s also important to take care of yourself. Making sure that you have the support you need, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular medical care can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
Read Also: Yeast Infection Over The Counter Cvs
How Can Hiv Infection In Children Be Prevented
The most effective method for preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV is by initiating HIV-positive pregnant women on antiretroviral therapy as early as possible. ART decreases viral levels in the mothers bloodstream, thus reducing the risk that she will transmit the infection to her infant. ART should also be administered to a child before and after birth treatment will help a babys body resist infection.
Globally, an estimated 82% of pregnant or breastfeeding women living with HIV were receiving antiretroviral medicines to prevent transmission of HIV to their children in 2018.
How Is Hiv Spread
The spread of HIV from person to person is called HIV transmission. HIV is spread only through certain body fluids from a person who has HIV. These body fluids include:
HIV transmission is only possible through contact with HIV-infected body fluids. In the United States, HIV is spread mainly by:
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles or syringes, with someone who has HIV
The spread of HIV from a woman with HIV to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding is called perinatal transmission of HIV. For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on Preventing Perinatal Transmission of HIV.
You cannot get HIV by shaking hands or hugging a person who has HIV. You also cannot get HIV from contact with objects, such as dishes, toilet seats, or doorknobs, used by a person with HIV. HIV is not spread through the air or water or by mosquitoes, ticks, or other blood-sucking insects. Use the HIVinfo You Can Safely ShareWith Someone With HIV infographic to spread this message.
Also Check: Uti And Yeast Infection Together
The Who Clinical Staging System For Hiv/aids
Virtual Mentor.
For over twenty years, human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome have been significant public health concerns, and the epidemic continues to challenge humanity. The majority of the worlds new HIV infections occur in low- and middle-income countries, with two-thirds of the worlds HIV-infected population living in Africa . Many complex factors contribute to the disproportionate impact of HIV in resource-poor settings: poverty, disease stigma, cultural and social barriers to testing and treatment, insufficient health care infrastructure to support the large patient pool, lack of health literacy, limited provider training, inadequate medical equipment, scarce manpower to distribute health care throughout the region, and few qualified laboratory facilities .
- Provides guidance including when to start, switch, or stop prophylactic medications, antiretrovirals, and other interventions
- Assists clinicians in the assessment of a patients current clinical status
- Encourages clinical providers to offer diagnostic HIV testing to patients who exhibit clinical signs suggestive of HIV infection
- Classifies disease in a progressive sequence from least to most severe
- Is designed to be used with reference to current and previous clinical events, making it useful for surveillance purposes .
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can live and long and healthy life and will not transmit HIV to your HIV-negative partners through sex.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Itâs important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Recommended Reading: Yeast Infection Itchy At Night
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.