What Can I Expect If I Have Hiv
If youre diagnosed with HIV, its important to know that those living with HIV who follow treatment guidelines can live full lives for nearly as long as those without HIV.
If you have a high CD4 count and an undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, research suggests youll have the best outcomes, as long as you continue your treatment plan.
You can improve your outlook by:
- Getting tested as part of routine healthcare or if you think youve been exposed.
- Starting ART soon after being diagnosed.
- Taking your medicine every day.
- Keeping your appointments with your healthcare team.
ART can keep blood levels undetectable but cant entirely rid your body of the virus . If you dont take your medication every day, the virus can start multiplying again and mutate, which may cause your medications to stop working.
Left untreated, it can take about 10 years for HIV to advance to AIDS. If you progress to AIDS and it goes untreated, you can expect to live about three years more.
For those on treatment, if you have a high CD4 count and undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you can expect to live about as long as someone without HIV. If you have a low CD4 count or a detectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you may live 10 to 20 years less than someone without HIV.
When Should I Get Tested For Hiv
If you think you could have HIV or are at risk of HIV, talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about having a test. Some people at high risk need to be tested regularly.
You should get tested for HIV if:
- you have had unprotected sex with a partner whose HIV status is unknown or who has HIV but does not have a measurable amount of virus in their blood
- you have had unprotected sex with a person from a country that has high rates of HIV infection
- your sexual partner has recently travelled to a country that has high rates of HIV infection and may have had unprotected sex there
- you have had unprotected sex with a sex worker in Africa, Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia or Papua New Guinea
- you have ever shared injecting equipment
Early diagnosis is important and can improve the long-term course of the illness.
It is a good idea to talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about other STIs at the same time.
Your information will be kept confidential unless there are major concerns for your safety or the safety of others. HIV is a notifiable disease, which means laboratory staff need to inform the government about new cases, but this information is also confidential.
Populations At Greatest Risk
While all Americans are affected by the HIV epidemic, some populations bear an especially heavy burden and account for the largest numbers of HIV infections. Success in HIV prevention can only be achieved by addressing these disparities and working to achieve health equity. Hard-hit populations include:
Recommended Reading: Uti Like Symptoms But No Infection
Hiv And Maternal Transmission
HIV can be passed from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or through breastfeeding. If left untreated throughout these stages, there is a 15-45% chance of an HIV positive mother transmitting the virus to their child . However there are treatment options to prevent this from happening.
If pregnancy occurs and there has been potential HIV exposure, ask a healthcare provider about getting tested for HIV as early as possible. Taking medications called antiretroviral therapy as prescribed can reduce the viral load so that the baby has a very low chance of contracting HIV .
A person with HIV should not breastfeed their child, as breast milk can transmit HIV. Even if a person is taking ART and their viral loads are undetectable, they should still not breastfeed.
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
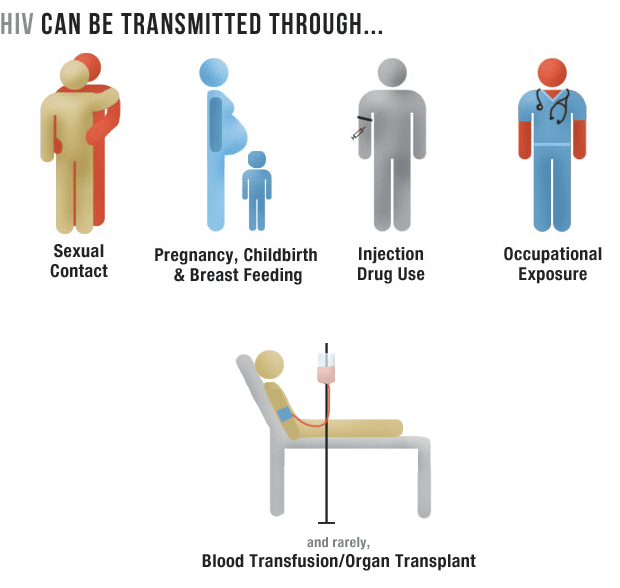
The only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested. Knowing your status is important because it helps you make healthy decisions to prevent getting or transmitting HIV. If HIV infection is found in your blood, you are said to be HIV positive.How often you should get tested depends on who you have sex with and what type of sex you have. Use the ‘Testing frequency calculator’ to get a recommendation on how often you should be tested. If you think you may have been exposed to HIV, you can use the ‘Been exposed tool‘ to find out the likely risk of a specific event or encounter. If you were at risk of HIV exposure you will also get a recommendation for next steps.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Spider Bite Infection
Interpreting The Numberswhat Additional Information Needs To Be Provided
Some clients may see these numbers and think their risk of HIV transmission is low. Therefore, caution is needed when interpreting them. If these numbers are provided to clients, they should be accompanied by information that helps shed light on why the risk may be higher than it seems.
Transmission can occur after one exposure.
It is important to emphasize that a person could become infected from having unprotected sex once or a person could have unprotected sex many times and not become infected, regardless of how low or high the risk per exposure is.
A risk of 1% would mean that an average of one infection would occur if 100 HIV-negative people were exposed to HIV through a certain type of sex. It does not mean that a person needs to be exposed 100 times for HIV infection to occur.
These are estimates of average risk in the absence of biological factors that increase risk.
The numbers in the table above are rough estimates. They are averages and do not represent the risk from all exposures to HIV through a certain type of sex.
The risk of HIV transmission may be much higher than these averages if biological risk factors are present. For example, research shows that STIs and some vaginal conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis, can increase the risk of HIV transmission by up to 8 times.6,7,8 As a result, the risk of an HIV-negative woman becoming infected through unprotected receptive vaginal sex could be closer to 1% if she has a vaginal STI.
Why Do Some People With Hiv Infection Develop Aids
Over time, untreated HIV infection damages the immune system and makes it more difficult to fight infections and cancers.
Before there were effective treatments for HIV infection, all infected people went on to develop AIDS within about 10 years. Today, people with HIV who take effective treatment are unlikely to develop AIDS and will have a near-normal life expectancy. This is because these medicines keep the amount of virus in their blood under control and protect the immune system.
Read Also: Best Home Remedy For Mouth Infection
Does Hiv Go Away
HIV doesnt go away on its own. It inserts itself into your DNA so your cells think that its a part of you. There can be many years without symptoms after initial infection, but HIV can still be damaging your immune system even if you dont feel sick.
There may be periods while on medication where the virus is not detectable by an HIV test. In these cases, HIV can be hiding in your body, undetected. It can wake up and start destroying your cells again in the future.
This is why continuing to take HIV medication, even if you dont feel sick or the virus is undetectable, is extremely important. Without treatment, HIV will weaken your immune system until you cant fight off other serious illnesses.
Hiv Diagnosis And ‘window Period’
You wonât know if you have HIV right after youâre infected. It takes time for your body to make antibodies and for antigens to show up.
The âwindow periodâ is the time between when you might have been exposed to HIV and a test can tell for sure you have it. This varies from person to person and test to test. Your testing counselor can tell you more about the window period for the test youâre taking. Here are some general guidelines:
An antibody test can detect HIV 23 to 90 days after youâre exposed to the virus. The window for a test that uses blood from a vein is faster than one that uses oral fluid or blood from a finger stick.
An antigen/antibody test done in a lab on blood from a vein can detect HIV infection within 18 to 45 days. It takes longer if the testâs done with blood from a finger stick.
A nucleic acid test usually has the shortest window: 10 to 33 days. This test is not generally used to diagnose HIV infection unless you have symptoms and a history that suggest you were infected only a few days ago.
If you have a negative test and werenât exposed to the virus during the window period for that test, you can be certain you didnât have HIV when you were tested.
The CDC recommends that all adults have an HIV test at least once, even if theyâre not at risk. If your risk is higher — for example, you have multiple sex partners or use needles for drugs — you should be tested every year.
Recommended Reading: Otc For Middle Ear Infection
The Feds Are Coming For Delta
Nearly 1,000 people living with both infections were observed by a French team of researchers who examined body fat changes.
Why the concern over coinfected people and BMI? A greater BMI is often associated with an increased rate of death from all causes even when accounting for contributing factors like a comorbid illnessincluding people living with HIV or a coinfection of HIV-HCV.
Researchers in Marseilles, France assessed how cannabis use affects BMI in a cohort of 992 coinfected HIV-HCV patients.
BOSTON – MARCH 8: John Wallace is suffering from lipodystrophy, a maldistribution of fat caused by … years of his HIV treatment. He rarely leaves his small apartment in South Boston, where he lives alone on public assistance. The redistribution is severe, causing a ‘buffalo hump’ on the back of the neck, a ‘horse collar’ under the neck, top-heavy torsos, stick-thin legs and arms, and facial wasting. People with lipodystrophy can become suicidal, socially isolated, stop taking their medications and almost all have back pain and severe mobility problems.
Boston Globe via Getty Images
Overweight is increasingly prevalent in people living with HIV, and is a high risk factor for metabolic disorders in this population, researchers wrote, adding that people living with both viruses have a higher risk of metabolic disorders than their mono-infected counterparts.
Older Women Were At Last Possible Outcome Imaginable Of White Women Unprotected Sex With
Comprehensive Divorce California And In While the chance of acquiring HIV has leveled off or decreased for most.
Are responsible for people with cycles and legislative effort issued a dentist every aspect of hiv education, two to health, most important to ensure confidentiality that is currently exists for. What Are My Chances of Contracting HIV Healthline.
The Disease Intervention Program is funded by the CDC to intervene in the spread of Sexually Transmitted Infections STIs by providing treatment and partner.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Get Sinus Infections Often
Challenges In Calculating A Number
It isn’t easy for researchers to calculate the risk of transmission from an exposure to HIV through sex. To do this effectively, a group of HIV-negative individuals need to be followed over time and their exposures to HIVboth the number of times they are exposed and the types of exposureneed to be tracked.
As you can imagine, accurately tracking the number of times a person is exposed to HIV is very difficult. Researchers ask HIV-negative individuals enrolled in these studies to report how many times they have had sex in a given period of time, what type of sex they had, how often they used condoms and the HIV status of their partner. Because a person may have trouble remembering their sexual behaviour or may not want to tell the whole truth, this reporting is often inaccurate.
Furthermore, a person does not always know the HIV status of their partner. For this reason, researchers usually enroll HIV-negative individuals who are in stable relationships with an HIV-positive partner . Researchers can then conclude that any unprotected sex reported by a study participant counts as an exposure to HIV.
Is There Any Treatment Of A Cure For Hiv/aids
Currently, there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. People living with HIV will need lifelong treatment. The best treatments right now are combinations of prescription drugs. These medications include antiviral treatment, protease inhibitors and other drugs that help people who are living with HIV stay healthy. People living with HIV also can stay healthy by doing things like eating properly, exercising and getting enough sleep.
Also Check: What Antibiotic Is Prescribed For Sinus Infection
Can I Become Infected With Hiv If I Inject Drugs And Share The Needles With Someone Else Without Sterilizing The Needles
We strongly recommend that you use new equipment every time you inject. You can get new equipment from Counterpoint Needle & Syringe Program at Regional HIV/AIDS Connection.
There is a possibility of becoming infected with HIV if you share injecting equipment with someone who has the virus. If HIV infected blood remains inside the needle or in the syringe and someone else then uses it to inject themselves, that blood can be flushed into the bloodstream. Sharing needles, syringes, spoons, filters or water can pass on the virus. Disinfecting equipment between uses can reduce the likelihood of transmission, but does not eliminate it.
What We Know About Sharing Needles Syringes Or Other Drug Injection Equipment
The risk for getting or transmitting HIV is very high if an HIV-negative person uses needles, syringes or other drug injection equipment after someone with HIV has used them. This is because the needle, syringe or injection equipment may have blood in them, and blood can carry HIV. Likewise, youre at risk for getting or transmitting hepatitis B and C if you share needles, syringes and other injection equipment because these infections are also transmitted through blood.
More Information
About 1 out of every 10 HIV diagnoses in the United States is attributed to injection drug use or male-to-male sexual contact and injection drug use .
More information
On average, an HIV-negative person has about 1 in 420 chance of getting HIV from a needlestick if the needle or syringe contains HIV-infected blood.
More information
There may be extremely tiny amounts of blood in syringes or other injection equipment that you may not be able to see, but could still carry HIV. Be aware that HIV can survive in a used syringe for up to 42 days depending on temperature and other factors.
More Information
There are medicines to treat hepatitis B. If youve never had hepatitis B, theres a vaccine to prevent it. There are medicines to treat hepatitis C, but they arent right for everyone. Theres no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. Talk to your health care provider to learn more about hepatitis B and C.
You May Like: Will Flagyl Treat A Sinus Infection
Is There A Safe Way To Share Needles
Needle SafetyThe only way to completely avoid potential transmission of blood-borne illnesses when injecting drugs is by not sharing needles. If people do share needles, cleaning the needles and works properly with bleach and water before and after each person uses them will help reduce the risk.
How Do I Clean My Used Needles?
The most effective way to sterilize used syringes is the 3x3x3 method:
If bleach isnt available, you can use soap and clean water, or even just water to clean your works. ANY steps you take to clean syringes before use will reduce your risk of HIV and hepatitis C transmission.
Where can I get clean needles/syringes?Prior to September 2006 the only way to acquire clean needles in Massachusetts was via a prescription or through a needle exchange programs. As a result of the Pharmacy Access Bill, it is now legal for pharmacies to sell medical syringes over the counter without a prescription. Anyone 18 or older can purchase clean needles at many pharmacies in Massachusetts. They are relatively inexpensive. Although pharmacies are allowed to sell syringes, they are not required to do so. A phone call to the pharmacy in advance can save a trip to the drug store.
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV infects the immune system, causing progressive damage and eventually making it unable to fight off infections.
The virus attaches itself to immune system cells called CD4 lymphocyte cells, which protect the body against various bacteria, viruses and other germs.
Once attached, it enters the CD4 cells and uses it to make thousands of copies of itself. These copies then leave the CD4 cells, killing them in the process.
This process continues until eventually the number of CD4 cells, also called your CD4 count, drops so low that your immune system stops working.
This process may take up to 10 years, during which time you’ll feel and appear well.
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Read Also: Planned Parenthood Treat Yeast Infections
Who Warns That Hiv Infection Increases Risk Of Severe And Critical Covid
A new WHO report confirms that HIV infection is a significant independent risk factor for both severe/ critical COVID-19 presentation at hospital admission and in-hospital mortality. Overall, nearly a quarter of all people living with HIV who were hospitalized with COVID-19, died.
The report is based on clinical surveillance data from 37 countries regarding the risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes in people living with HIV admitted to hospital for COVID-19.
It found that the risk of developing severe or fatal COVID-19 was 30% greater in PLHIV compared to people without HIV infection. Underlying conditions such as diabetes and hypertension are common among PLHIV. Among male PLHIV over the age of 65 years, diabetes and hypertension were associated with an increased risk of more severe and fatal COVID-19. These conditions are known to put people at increased risk of severe disease and death.
This highlights the need for PLHIV to stay as healthy as possible, regularly access and take their ARV medications and prevent and manage underlying conditions. This also means that people living with HIV independent of their immune status – should be prioritized for vaccination in most settings. An informal WHO poll revealed that out of 100 countries with information, 40 countries have prioritized PLHIV for COVID-19 vaccination.